Sensitization via Pregnancy Generates Alloantibody and Cross-Reactive Xeno-Antibody in a Non-Human Primate Model
Surgery, Duke University, Durham, NC
Meeting: 2020 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: A-278
Keywords: Alloantibodies, Pregnancy, Sensitization, Xenoreactive antibodies
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session A: Xenotransplantation
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Saturday, May 30, 2020
Session Time: 3:15pm-4:00pm
 Presentation Time: 3:30pm-4:00pm
Presentation Time: 3:30pm-4:00pm
Location: Virtual
*Purpose: Women are disproportionately represented among highly sensitized waitlist candidates and within HLA-incompatible transplantation programs. Due to difficulties obtaining compatible donors, sensitized patients are seen as potential first-in-human recipients of xenotransplantation. Use of Gal-Knockout (GKO) porcine donors have reduced rejection risk in xenotransplantation; however, efficacy in the context of HLA sensitization, including sensitization via pregnancy,needs further study. In a preclinical non-human primate model, we sought to examine the effect of pregnancy in multiparous recipients on humoral incompatibility to allografts and xenografts.
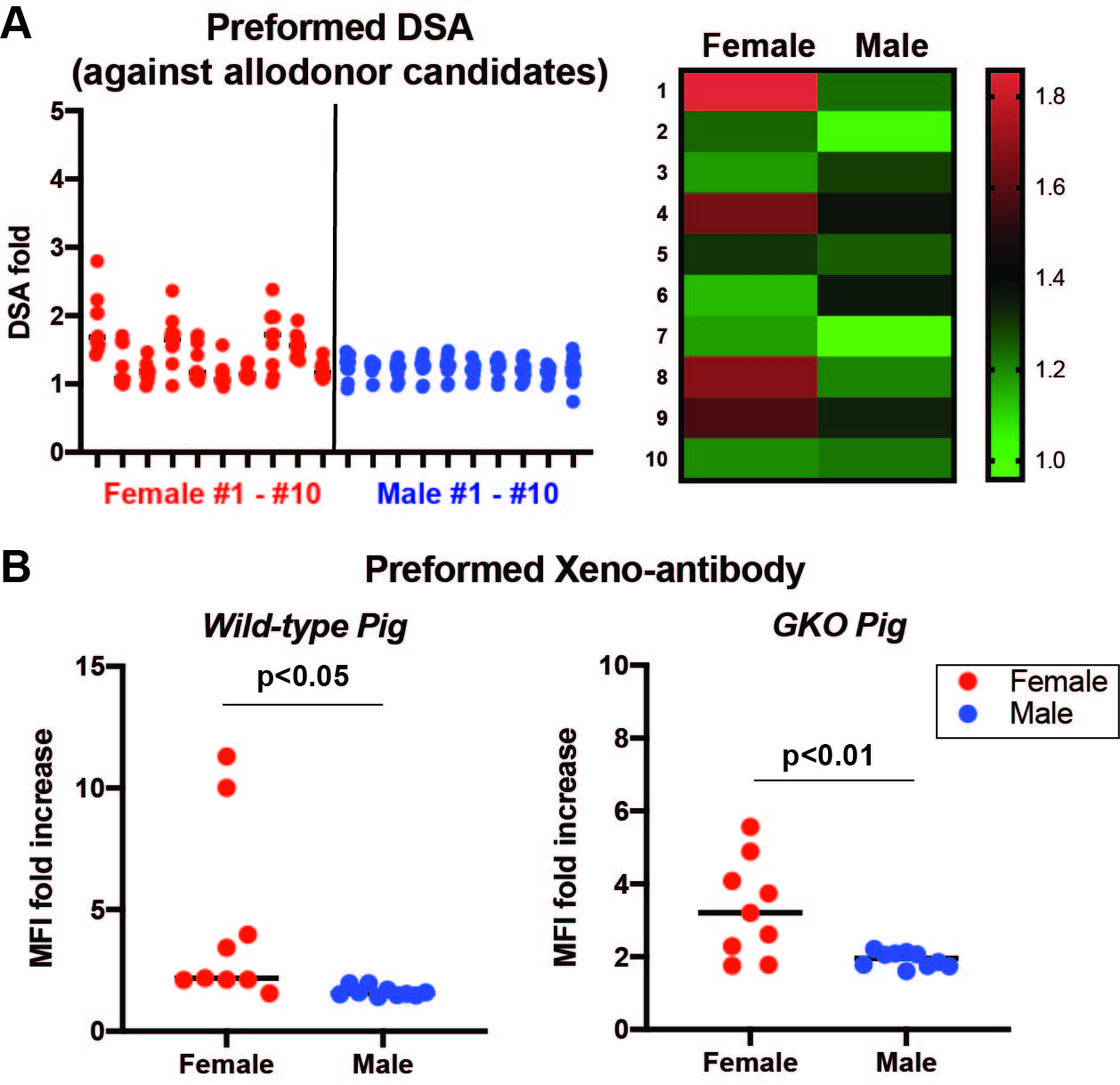
*Methods: We tested plasma from 10 multiparous female and 10 naïve male rhesus macaques for allo- and xeno-reactive antibodies using 10 NHP donors and 2 porcine donors (wild type [WT] and Gal-Knockout [GKO]) in flow cytometric T and B cell (not shown) crossmatch tests. We report T-cell cross match (class I) values as normalized ratios (fold increased to no plasma control).
*Results: Multiparous female monkeys demonstrate greater class I and II reactivity against a range of potential NHP donors, compared to male monkeys (Figure A). In addition, compared to male monkeys, multiparous femaless demonstrated greater cross reactivity against cells from WT pig donors (p<0.05). Interestingly, these multiparous females showed higher preformed antibody level against GKO donor cells compared to male monkeys (p<0.01). (Figure B).
*Conclusions: Multiparous female monkeys demonstrate increased humoral immunity against potential allo and xeno-donors. Humoral risk for multiparous females was not diminished by the lack of a-1,3-galactosyltransferase in GKO pig donors. Xenotransplantation offers difficult to transplant patients greater access to organs, however, multiparous females may not benefit from this new transplant modality.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Yoon J, Manook M, Fitch Z, Schmitz R, Choi A, Jackson AM, Knechtle S, Kwun J. Sensitization via Pregnancy Generates Alloantibody and Cross-Reactive Xeno-Antibody in a Non-Human Primate Model [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2020; 20 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/sensitization-via-pregnancy-generates-alloantibody-and-cross-reactive-xeno-antibody-in-a-non-human-primate-model/. Accessed March 1, 2026.« Back to 2020 American Transplant Congress