Role of Induction Therapy in Low Immune Risk Kidney Transplant Recipients.
Nephrology and Hypertension, Allegheny General Hospital, Pittsburgh, PA.
Meeting: 2016 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: B117
Keywords: Graft survival, Induction therapy, Kidney transplantation
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session B: Drug Minimization
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Sunday, June 12, 2016
Session Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Location: Halls C&D
Induction therapy improves outcomes in kidney transplant recipients (KTRs) by reducing early acute rejection. In the current era of potent maintenance immunosuppression, the role of induction in low immune risk KTRs has not been critically evaluated.
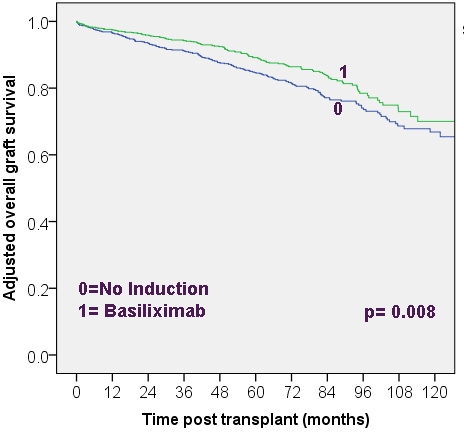
Using OPTN/UNOS database, we identified low immune risk adult KTRs from 2001-2011 who were discharged on tacrolimus/mycophenolic acid with steroid (chronic steroid maintenance [CSM] group)or without steroid (early steroid withdrawal [ESW] group). For the study, KTRs were considered low immune risk if they met all of the following criteria: first transplant, current PRA <20% and HLA mismatches <3. Using Cox model with adjustment for donor, recipient and transplant related factors, graft and patient outcomes were compared for no induction group separately to groups that received induction therapy with non-depleting (basiliximab/daclizumab) or depleting- Alemtuzumab or Thymoglobulin antibody in both CSM and ESW groups. Results: table 1 and fig 1 for ESW gp.
| Adjusted overall graft failure risk | Adjusted death censored graft failure risk | Adjusted patient death risk | ||
| HR (95% CI) | HR (95% CI) | HR (95% CI) | ||
| ESW group | No induction (n=831) vs. Basiliximab/Daclizumab (n=976) | 1.37 (1.09-1.71)* | 1.51 (1.08-2.11)** | 1.33 (0.99-1.80)*** |
| No induction (n=831) vs Alemtuzumab (n=1283) | 1.04 (0.93-1.16) | 0.79(0.58-1.07) | 1.04 (0.78-1.39) | |
| No induction (n=831) vs. Thymoglobulin (n=1928) | 1.11 (0.91-1.34) | 1.12 (0.86-1.48) | 1.09 (0.84-1.41) | |
| CSM group | No induction (n=3844) vs. Basiliximab/Daclizumab (n=4337) | 0.97 (0.89-1.07) | 0.91 (0.80-1.03) | 1.02 (0.91-1.14) |
| No induction (n=3844) vs. Alemtuzumab (n=231) | 1.13 (0.97-1.32) | 0.68 (0.45-1.03) | 0.90 (0.59-1.37) | |
| No induction (n=3844) vs. Thymoglobulin (n=3265) | 0.98 (0.89-1.08) | 0.95 (0.83-1.10) | 1.00 (0.88-1.13) | |
| *= p of 0.008; **= p of 0.016; ***= p of 0.059 | ||||
In summary, lack of observable graft and patient survival benefits with any induction agent in CSM group and depleting induction agents in ESW group among the low immune risk KTRs maintained on tacrolimus/mycophenolic acid could likely be related to competing risks of complications related to enhanced immunosuppression.
CITATION INFORMATION: Chopra B, Sureshkumar K. Role of Induction Therapy in Low Immune Risk Kidney Transplant Recipients. Am J Transplant. 2016;16 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Chopra B, Sureshkumar K. Role of Induction Therapy in Low Immune Risk Kidney Transplant Recipients. [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2016; 16 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/role-of-induction-therapy-in-low-immune-risk-kidney-transplant-recipients/. Accessed March 7, 2026.« Back to 2016 American Transplant Congress
