Rituximab Induction in Cardiac Transplantation Is Associated with Accelerated Coronary Artery Vasculopathy: CTOT11.
On Behalf of the CTOT11 Consortium, Brigham & Women's Hospital, Boston, MA.
Meeting: 2016 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 571
Keywords: Arteriosclerosis, CD20, Heart/lung transplantation, Immunosuppression
Session Information
Session Time: 8:30am-10:00am
 Presentation Time: 9:45am-10:00am
Presentation Time: 9:45am-10:00am
Location: Veterans Auditorium
Purpose
The NIH-funded study CTOT11: Prevention of Cardiac Allograft Vasculopathy Using Rituximab (RIT) Therapy in Cardiac Transplantation, was a randomized clinical trial in non-sensitized primary heart transplant (HTX) recipients designed to determine whether B cell depletion would attenuate the development of coronary artery vasculopathy (CAV).
Methods
CTOT-11 was a placebo controlled, multicenter, double-blinded study which randomized 163 HTX with PRA <10% to RIT 1000 mg IV or matching placebo (PLAC) on days 0 and 12 post-transplant. Primary outcome was change in percent atheroma volume (PAV) from baseline to one year measured by intravascular ultrasound (IVUS). Secondary outcomes included treated episodes of acute rejection, de novo anti HLA antibodies, effector/memory and Treg subsets, and phenotypic differentiation of B cells.
Results
163 HTX were enrolled with no significant differences between RIT and PLAC groups in the following characteristics: mean age 55 yrs, 85% male, 78% white, 45% mechanical circulatory support, 47% UNOS status 1A, 41% ischemic etiology, 23% diabetes, 20% CMV D+R-, average ischemic time 3.1 hours. 92.6% received maintenance CNI, MMF, steroids; 2.5% azathioprine; 4.9% mTOR inhibitor. Mortality at 12 months was 3.4% RIT vs 6.8% PLAC, p=0.47; there were no re-transplants or PTLD. The rate of treated rejection was 24.7% RIT vs 32.4% PLAC, p=0.28. Paired IVUS measures were available at baseline and 1 year in 86 subjects (49 RIT, 37 PLAC). The mean (±SD) increase in PAV at 12 mos was 6.8 ± 8.2% RIT vs 1.9 ± 4.4% PLAC (p=0.0019) 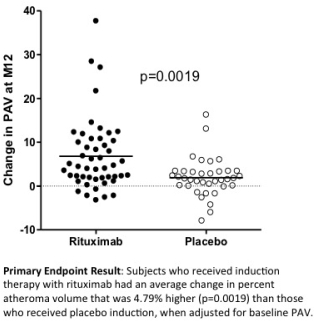 .
.
Conclusions
We hypothesized that RIT would result in a reduction in PAV change compared to PLAC. Unexpectedly, we observed a significant increase in PAV change with RIT compared to PLAC (delta PAV =4.8%). Survival and treated rejection at 1 year were not different. While these findings require further study, RIT should be used with caution as induction therapy in primary unsensitized HTX patients.
CITATION INFORMATION: Chandraker A, Kobashigawa J, Stehlik J, Givertz M, Pierson R, Pinney S, Joren M, Nissen S, Guleria I, Morrison Y, Armstrong B, Bridges N, Sayegh M, Starling R. Rituximab Induction in Cardiac Transplantation Is Associated with Accelerated Coronary Artery Vasculopathy: CTOT11. Am J Transplant. 2016;16 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Chandraker A, Kobashigawa J, Stehlik J, Givertz M, Pierson R, Pinney S, Joren M, Nissen S, Guleria I, Morrison Y, Armstrong B, Bridges N, Sayegh M, Starling R. Rituximab Induction in Cardiac Transplantation Is Associated with Accelerated Coronary Artery Vasculopathy: CTOT11. [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2016; 16 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/rituximab-induction-in-cardiac-transplantation-is-associated-with-accelerated-coronary-artery-vasculopathy-ctot11/. Accessed March 12, 2026.« Back to 2016 American Transplant Congress
