Rapid Detection of Kidney Transplant Injury by Quantifying Donor-Derived Cell-Free Deoxyribonucleic Acid via Massively Multiplex Polymerase Chain Reaction
1University of California San Francisco, San Francisco, CA, 2Natera Inc., San Carlos, CA
Meeting: 2019 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: A148
Keywords: Biopsy, Glomerular filtration rate (GFR), Kidney transplantation, Rejection
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session A: Biomarkers, Immune Monitoring and Outcomes
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Saturday, June 1, 2019
Session Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
 Presentation Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
Presentation Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
Location: Hall C & D
*Purpose: Plasma donor-derived cell-free DNA (dd-cfDNA) is a proven marker for allograft rejection in patients with kidney transplant (KT). Our goal was to assess performance of a novel single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP)-based massively multiplexed PCR (mmPCR) method to quantify dd-cfDNA and detect KT rejection in a cohort of biopsy-matched KT samples.
*Methods: 300 plasma samples from 193 KT patients were collected; 217 biopsy-matched samples were categorized as active rejection (AR; n=38, 34.2% (13/38) subclinical), borderline (BL; n=72), stable (STA; n=82), and other injury (OI; n=25). Samples were processed by mmPCR targeting 13,392 SNPs; dd-cfDNA was quantified, correlated with rejection status and compared with estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR). AR was defined as antibody- and/or T cell-mediated rejection (ABMR/TCMR) as per Banff 2017 criteria; samples were considered positive for AR based on a predetermined cut-off (dd-cfDNA: >1%; eGFR: <60.0).
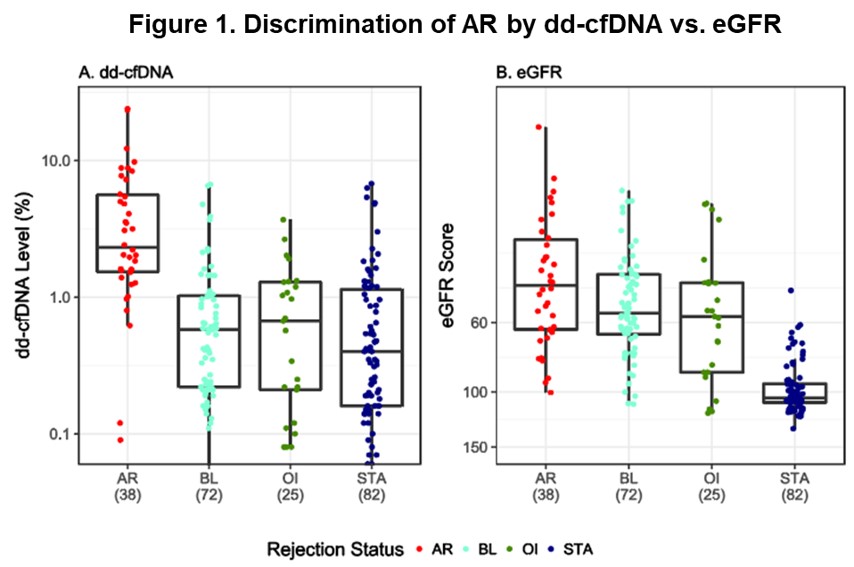
*Results: The median level of dd-cfDNA was significantly higher in AR (2.32%) compared with non-rejection (NR) groups (P<0.0001): BL (0.58%), STA (0.40%), OI (0.67%). Similarly, median eGFR scores in AR patients (45.67) were significantly lower (P<0.0001) than the NR group: BL (55.9), STA (104.5), OI (57.4) (Figure 1). The dd-cfDNA assay showed improved performance over eGFR, with high sensitivity (88.7% vs. 67.7%), specificity (72.6% vs. 65.3%) and AUC (0.87 vs. 0.74). Median dd-cfDNA did not differ significantly between ABMR (2.22%), ABMR/TCMR (2.56%), or TCMR (2.69%) groups (P=0.855). In addition, the performance of the assay did not show a significant difference in protocol (n=114) vs. for-cause (n=103) biopsies, indicating a possible use of the assay to avoid unnecessary protocol biopsies in a clinical setting and to detect subclinical AR. In cases of subclinical AR, median dd-cfDNA was 3.62% and median eGFR score was 57.0 at the time of biopsy; while in clinically apparent AR cases, median dd-cfDNA was 2.0% and median eGFR score was 40.8%.
*Conclusions: This novel SNP-based mmPCR assay enabled rapid detection of AR by dd-cfDNA and showed superior performance over the existing standard-of-care. Overall, the data suggest that combined dd-cfDNA and eGFR markers can accurately assess AR in KT patients.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Sigdel TK, Acosta F, Navarro S, Zimmermann B, Demko ZP, Moshkevich S, Billings PR, Sarwal MM. Rapid Detection of Kidney Transplant Injury by Quantifying Donor-Derived Cell-Free Deoxyribonucleic Acid via Massively Multiplex Polymerase Chain Reaction [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2019; 19 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/rapid-detection-of-kidney-transplant-injury-by-quantifying-donor-derived-cell-free-deoxyribonucleic-acid-via-massively-multiplex-polymerase-chain-reaction/. Accessed March 9, 2026.« Back to 2019 American Transplant Congress