Protocol Donor Specific Antibody Monitoring After Kidney Transplantation: What Is the Utility?
MUSC, Charleston, SC.
Meeting: 2015 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: A99
Keywords: Alloantibodies, Flowcytometry crossmatching, Kidney transplantation
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session A: Kidney Antibody Mediated Rejection
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Saturday, May 2, 2015
Session Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
 Presentation Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
Presentation Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
Location: Exhibit Hall E
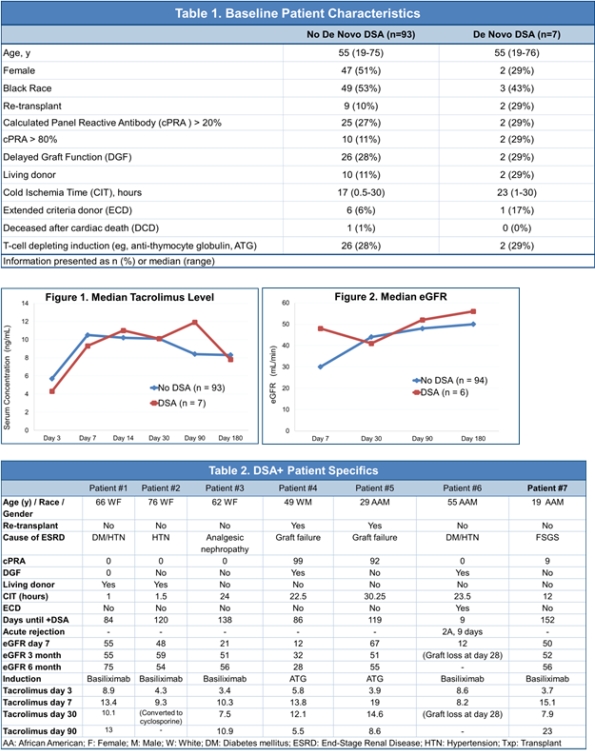
De novo DSA has been shown to be a negative predictor of graft outcomes. However, the utility of routine DSA monitoring in the overall kidney transplant population has yet to be proven as an effective practice. Recently DSA monitoring was implemented as part of routine care along with protocol biopsies at our institution. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the utility of routine DSA monitoring as part of a surveillance biopsy protocol after kidney transplantation.
Methods: This is a single-center retrospective cohort review assessing the outcomes and resource utilization associated with protocol-based DSA measurement. Patient and transplant specific characteristics and short term outcomes were collected for all adult patients who received solitary kidney transplants after implementation of the protocol. All patients had negative flow cytometry crossmatch and no pre-transplant DSA.
Results: One hundred patients were identified in the new protocol cohort over 8 months. The protocol included biopsies and DSA monitoring at 3 and 6 months post-transplant. DSA was checked with 65 biopsies in 59 patients; 7 patients had detectable de novo DSA. DSA detection resulted in no additional treatment, did not change the treatment course, and did not lead to differences in eGFR at 6 months. No biopsies had C4d deposition or histological signs of antibody mediated rejection that had detected DSA. There were no consistent patient-specific characteristics among the 7 patients who developed DSA; patients developed both class I and class II DSA. The cost to measure DSA is $1600 and an additional $500 for the screen performed; total cost to the cohort was $136,500.
Conclusion: Despite a high immunologic risk population and the frequent use of non-cell depleting induction therapy, protocol DSA measurement with surveillance biopsies revealed a low prevalence of early DSA detection. A larger patient cohort with long-term outcomes is necessary to fully assess the utility of protocol DSA measurement in kidney transplant recipients.
 .
.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Staino C, Pilch N, Moussa O, Boyle K, Casale J, Covert K, Fleming J, Taber D, Meadows H, Mardis C, Chavin K, Nadig S, McGillicuddy J, Bratton C, Srinivas T, Baliga P. Protocol Donor Specific Antibody Monitoring After Kidney Transplantation: What Is the Utility? [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2015; 15 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/protocol-donor-specific-antibody-monitoring-after-kidney-transplantation-what-is-the-utility/. Accessed March 9, 2026.« Back to 2015 American Transplant Congress
