Proteomic Analysis of Extracellular Vesicles Derived From a Potent Donor-specific Regulatory T Cell-enriched Population Demonstrates Multiple Markers of Immune Suppression
1Transplantation Research Center, Renal Division, Brigham and Women's Hospital, Boston, MA, 2Center for Interdisciplinary Cardiovascular Sciences, Division of Cardiovascular Medicine, Brigham and Women's Hospital, Boston, MA
Meeting: 2021 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: LB 37
Keywords: Kidney transplantation, T cells, Tolerance
Topic: Basic Science » Lymphocyte Biology: Signaling, Co-Stimulation, Regulation
Session Information
Session Name: Lymphocyte Biology: Signaling, Co-Stimulation, Regulation
Session Type: Poster Abstract
Session Date & Time: None. Available on demand.
Location: Virtual
*Purpose: Extracellular vesicles (EVs) are emerging as vital mediators of intercellular communication and immune regulation. Regulatory T cells (Tregs) play an integral role in immune suppression and are both avid EV secretors and acquirers. However, the challenges of expanding human Tregs ex vivo and isolating pure EVs have limited molecular investigations largely to their microRNA cargoes. Using EVs isolated from donor Antigen-Specific T cell-enriched immune-Regulatory cell Lines (ASTRLs) with known suppressive function, we performed an in-depth proteomic analysis of Treg EVs and identified pathways of EV-mediated immune suppression.
*Methods: ASTRLs were expanded ex vivo from peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) of 4 transplant recipients prior to EV isolation/characterization from culture media via differential ultracentrifugation and nanoparticle tracking analysis (NTA). Global proteomics was performed by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry; statistical analysis/visualization was completed in Qlucore Omics Explorer. Gene ontology (GO), pathway over-representation and protein-protein interaction (PPI) network analyses was performed using Consensus Path DB and STRING, respectively. ATPase functional capacity was assessed with a commercial kit.
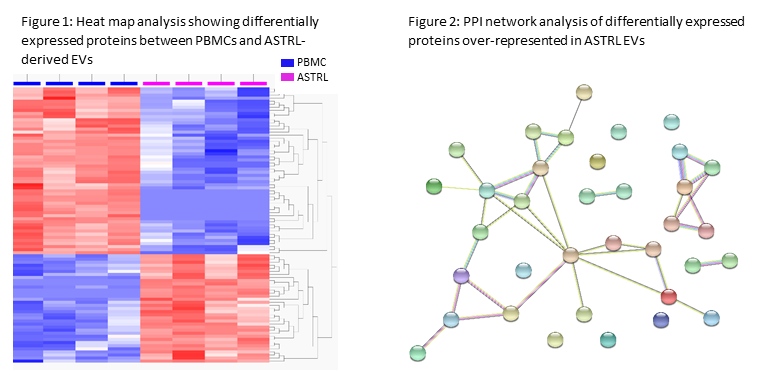
*Results: Of the 1,704 unique proteins identified, 848 were known to be EV-associated. NTA confirmed isolated particle size was consistent with that of EVs (mean diameter 133.9 +/- 3.1 nm). 89 differentially expressed proteins were detected between PBMC and ASTRL-derived EVs, 35 of which were over-represented in ASTRL-EVs (q<0.05, fold-change >2; Figure 1). Enrichment analysis of those 35 proteins revealed significant over-representation of pathways involved in immunity, including negative regulation of T cell activation, antigen receptor signaling, and ATP hydrolysis coupled transmembrane transport. PPI network analysis with unbiased clustering identified 7 local network clusters (Figure 2), including those associated with ATP hydrolysis. ATP hydrolysis assay confirmed functional EV ATPase capacity.
*Conclusions: These findings provide insight into Treg EV-mediated mechanisms of immune suppression, suggest EVs play a key role in the Treg response, and implicate ATP hydrolysis as a putative mechanism.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Schreiber B, Tripathi S, Blaser M, Pham T, Kuraoka S, Singh SA, Aikawa E, Chandraker A. Proteomic Analysis of Extracellular Vesicles Derived From a Potent Donor-specific Regulatory T Cell-enriched Population Demonstrates Multiple Markers of Immune Suppression [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2021; 21 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/proteomic-analysis-of-extracellular-vesicles-derived-from-a-potent-donor-specific-regulatory-t-cell-enriched-population-demonstrates-multiple-markers-of-immune-suppression/. Accessed March 3, 2026.« Back to 2021 American Transplant Congress