Prospective Intensive Monitoring for Anamnestic DSA Responses Allows Near Elimination of Early Clinical AMR
1U Cincinnati, Cincinnati, OH, 2Christ Hospital, Cincinnati, OH
Meeting: 2021 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 323
Keywords: HLA antibodies, Rejection, Sensitization
Topic: Clinical Science » Kidney » Kidney Acute Antibody Mediated Rejection
Session Information
Session Name: Kidney Antibody Mediated Rejection
Session Type: Rapid Fire Oral Abstract
Date: Tuesday, June 8, 2021
Session Time: 4:30pm-5:30pm
 Presentation Time: 5:00pm-5:05pm
Presentation Time: 5:00pm-5:05pm
Location: Virtual
*Purpose: Anamnestic donor specific antibody (aDSA) responses can result in severe, graft threatening antibody-mediated rejection (AMR). We hypothesized that intensive DSA monitoring (IDM) for aDSA will allow early detection/treatment thereby limiting graft injury and improving outcomes.
*Methods: From May 2016 to Oct 2019 IDM for aDSA was prospectively implemented in high risk patients (pts). High risk for aDSA was defined by:1)previous transplant (txp), 2)female with preexposure to paternal antigen, 3)pretransplant DSA, 4)post-txp oliguric ATN/slow function in pts with previous HLA exposure, 5)current cytotoxic PRA >25%,peak cytotoxic PRA or calculated PRA >50%, 6)positive T or B cell flow crossmatch. IDM was performed on PTD 0,1,2,3,5,7,14,30,90,180,360. Biopsies (Bx) were obtained for aDSA>5000 or renal dysfunction. aDSA was defined as DSA within 14 posttransplant days (PTD). aDSA were treated for MFI>5000 or progressive increases or AMR on Bx.
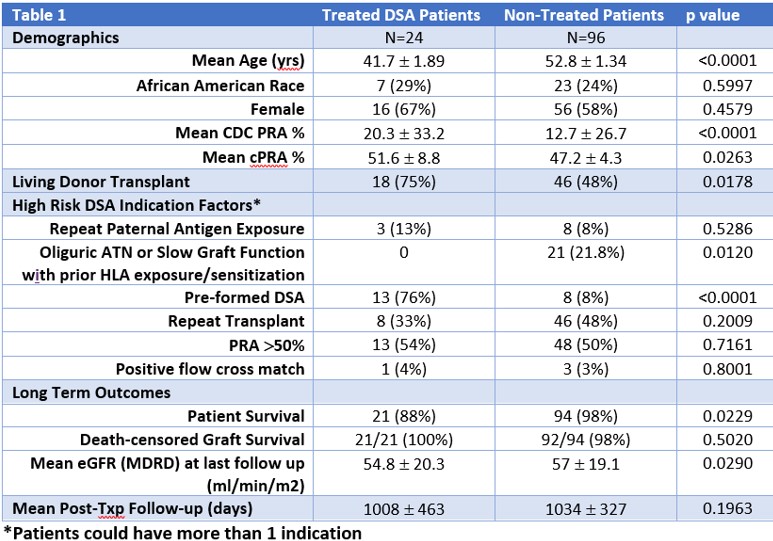
*Results: 120 pts underwent IDM: 57(47.5%) developed aDSA of whom 33/57(57.8 %) resolved without treatment. 24/57 (42%) pts were treated for aDSA. After the first 5 allograft Bx each demonstrated early/mild AMR, Bx were deemed unnecessary. After treatment, 11 (69%) pts without Bx cleared aDSA and 3 (38%) patients with AMR on Bx cleared aDSA (overall treated DSA clearance (14/24pts),57.8%). Amongst treated pts,16/24(66.7%) were treated without Bx and 8/24 (33.3%) patients had Bx meeting AMR criteria. Of treated pts, 15/24 (62.5%) had peak aDSA>5000 MFI. The strongest factor predictive of requirement for treatment was pre-existing DSA (p<0.0001). 4 pts had acute graft dysfunction due to aDSA with highest peak creatinine being 2.48 mg/dl. Overall death-censored graft survival was >98% with mean follow-up>1000 days. Deaths in treated pts were not due to overimmunosuppression. [table1]
*Conclusions: 1) 47.5% of high risk pts developed aDSA, in whom 57.8% resolved with observation alone, 2) 42% of aDSA were treated with clearance in over half of pts, 3) IDM allows for early aDSA detection with avoidance of renal dysfunction in 97% of pts, 4) early aDSA detection enables avoidance of early post transplant allograft Bx,4) pretransplant DSA is the strongest predictor for aDSA requiring treatment, and 5) IDM allows early DSA detection/management with overall DCGS >98% at mean follow-up of>1000 days in a high risk population.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
McGowan M, Bickenbach A, Shields AR, Alloway RR, Brailey P, Portwood E, Alquist C, Christianson A, Jawdeh BAbu, Cuffy M, Kremer J, Bumb S, Govil A, Anand M, Kaur T, Woodle ES. Prospective Intensive Monitoring for Anamnestic DSA Responses Allows Near Elimination of Early Clinical AMR [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2021; 21 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/prospective-intensive-monitoring-for-anamnestic-dsa-responses-allows-near-elimination-of-early-clinical-amr/. Accessed February 25, 2026.« Back to 2021 American Transplant Congress