Pro- and Anti-Tolerogenic Microbiota Induce Distinct Gut Microbiome Metabolic Pathways and Loco-Regional Immune Responses
S. J. Gavzy1, R. Lakhan2, J. Iyyathurai2, V. Saxena2, Z. L. Lee2, B. Ma2, E. Mongodin2, J. S. Bromberg2
1University of Maryland School of Medicine, Baltimore, MD, 2University of Maryland, Baltimore, MD
Meeting: 2022 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 1318
Keywords: Effector mechanisms, Mice, T cells
Topic: Basic Science » Basic Clinical Science » 18 - Immunometabolism
Session Information
Session Time: 7:00pm-8:00pm
 Presentation Time: 7:00pm-8:00pm
Presentation Time: 7:00pm-8:00pm
Location: Hynes Halls C & D
Session Information
Session Time: 5:30pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 5:30pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 5:30pm-7:00pm
Location: Hynes Hall C
*Purpose: Colitis-associated Desulfovibrio desulfuricans (Desulfo) induces pro-inflammatory cytokine responses in dendritic cell and macrophage cell lines as well as primary cells. In contrast, Bifidobacterium pseudolongum (Bifido), recovered from pregnant mice, induces anti-inflammatory and pro-tolerant immunity. Bifido fecal microbiota transfer (FMT) results in decreased cardiac allograft inflammation and fibrosis in murine heterotopic heart transplants compared to Desulfo FMT. We investigated whether different microbiota could induce distinct metabolic profiles, modify LN architecture, and affect T cell trafficking and differentiation.
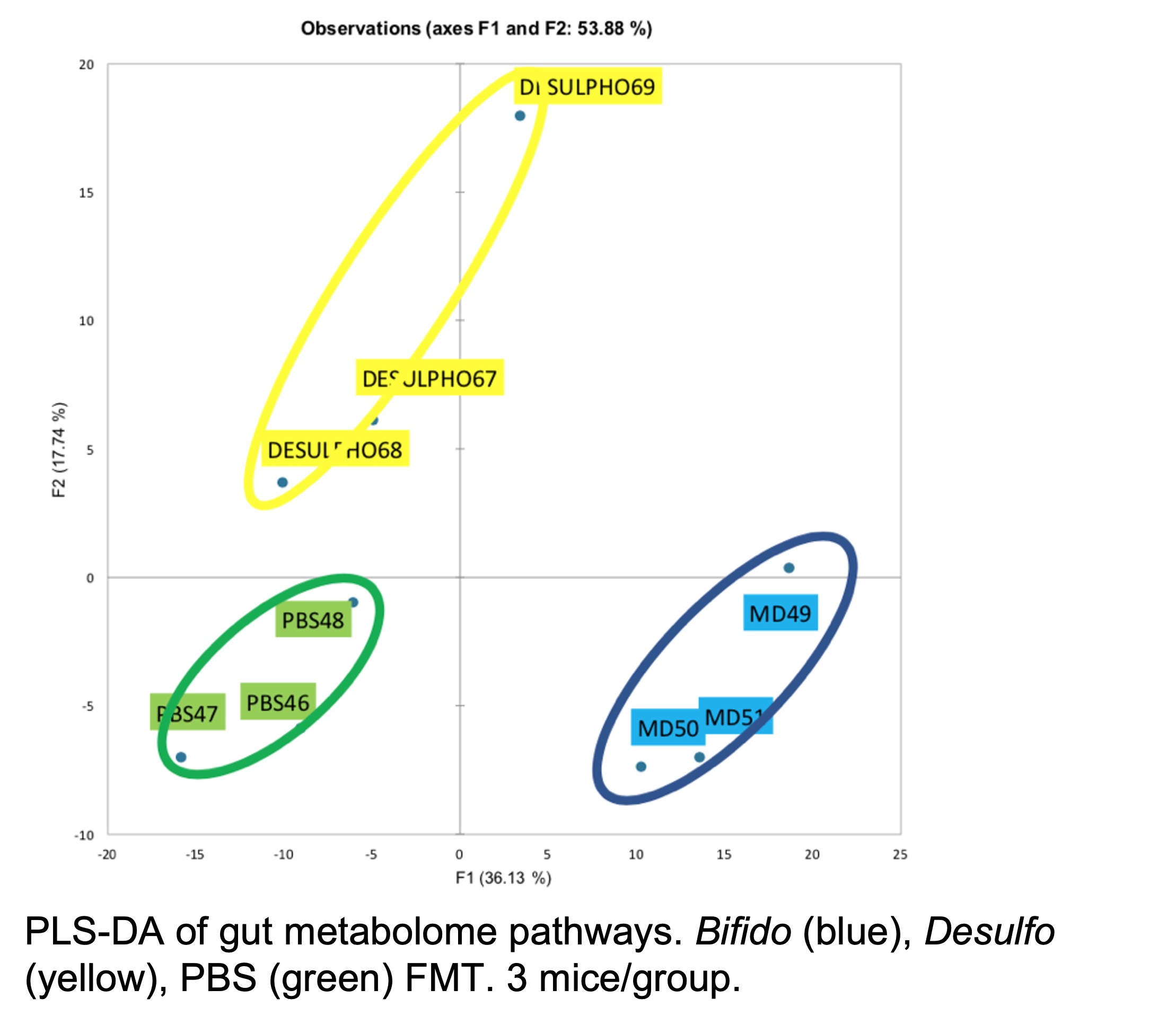
*Methods: C57BL/6 mice were treated with antibiotics followed by FMT with either Bifido, Desulfo, or PBS control, and then received BALB/c heart transplants, daily tacrolimus and adoptive transfer of alloantigen specific TEa T cell receptor transgenic T cells. Peripheral and mesenteric lymph nodes (pLN and mLN) were assessed by immunohistochemistry and flow cytometry. Intestinal permeability (IP) was assessed by FITC-dextran gavage. Metabolome profiling of stool post-transplant was performed using capillary electrophoresis-mass spectrometry, and metabolites were characterized using PubChem compound ID and visualized using partial least square-discriminant analyses (PLS-DA).
*Results: Desulfo FMT resulted in decreased laminin α4:α5 ratios in the mLN and Tregs in pLN (p<0.02) in comparison to Bifido FMT or control. Transferred TEa cells differentiated into fewer effector CD4 T cells (CD44+CD69–) in Bifido FMT treated mice compared to the Desulfo FMT and control groups. Desulfo FMT also increased IP (p<0.01). PLS-DA comparison of the gut metabolomes demonstrated highly distinct clustering of all three groups (Figure).
*Conclusions: Desulfo induced a stronger pro-inflammatory phenotype via decreased LN laminin α4:α5 ratios, decreased LN Treg, and increased IP while Bifido modulated effector T cell differentiation. Bifido and Desulfo induced distinct patterns of metabolic activities, which may yield actionable molecular targets for immunomodulation.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Gavzy SJ, Lakhan R, Iyyathurai J, Saxena V, Lee ZL, Ma B, Mongodin E, Bromberg JS. Pro- and Anti-Tolerogenic Microbiota Induce Distinct Gut Microbiome Metabolic Pathways and Loco-Regional Immune Responses [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2022; 22 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/pro-and-anti-tolerogenic-microbiota-induce-distinct-gut-microbiome-metabolic-pathways-and-loco-regional-immune-responses/. Accessed July 9, 2025.« Back to 2022 American Transplant Congress