Pneumocystis jiroveci Pneumonia (PJP) in Kidney and Pancreas Transplant Recipients in the Present Era of Routine Post-Transplant Prophylaxis: Risk Factors and Outcomes
University of Wisconsin, Madison.
Meeting: 2018 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 442
Keywords: Cytomeglovirus, Fungal infection, Infection, Prophylaxis
Session Information
Session Name: Concurrent Session: Kidney Infectious - Pot-Pourri
Session Type: Concurrent Session
Date: Tuesday, June 5, 2018
Session Time: 2:30pm-4:00pm
 Presentation Time: 3:18pm-3:30pm
Presentation Time: 3:18pm-3:30pm
Location: Room 608/609
PJP after transplant (TX) is associated with substantial morbidity and mortality. In the present era of universal and routine implementation of PJP prophylaxis (PPX) during the initial 6 to 12 months after TX, usually with trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (TMP-SMX), identifying risk factors for its occurrence can help identify patients who remain at increased risk, and therefore are most likely to benefit from ongoing PPX.
At our program, all kidney and/or pancreas TX recipients routinely receive prophylactic TMP-SMX for 12 months after TX. We reviewed 28 recipients who developed PJP any time after TX between 1994 and 2016. For comparison, 3 recipients without PJP matched on time from TX were identified for each case.
Median time to PJP diagnosis was 4.6 years (IQR: 1.4-9.6 years). Three patients developed PJP in the first year after PPX was stopped prematurely due to adverse effects. Recipients who developed PJP were older at time of TX (51.7 vs 46.2 years; p=0.05) and were more likely to be non-Caucasian (25.0 vs 9.5%; p=0.07), have received deceased TX (67.9 vs 52.4%; p=0.15), have higher number of HLA mismatches (82.1 vs 61.9% had ≥3/6, 3 being the median for the entire group; p=0.08), have prior history of BK viremia of at least 1000 copies/mL (21.4 vs 6.0%; p=0.01), CMV viremia (35.7 vs 6.0%; p<0.001), invasive fungal infections (7.1 vs 1.2%; p=0.01) and diarrheal illnesses due to Clostridium difficile or norovirus (10.7 vs 2.4%; p=0.1). T-cell depleting induction use, repeat TX, DGF and rejection rates were similar between the two groups. After multivariable adjustment, prior history of CMV viremia (odds ratio [OR] 6.5; p=0.001) and of invasive fungal infections (OR 2.6, p=0.006) remained significantly associated with subsequent diagnosis of PJP. PJP was associated with high mortality (32.1%) and worse graft survival (p=<0.001). 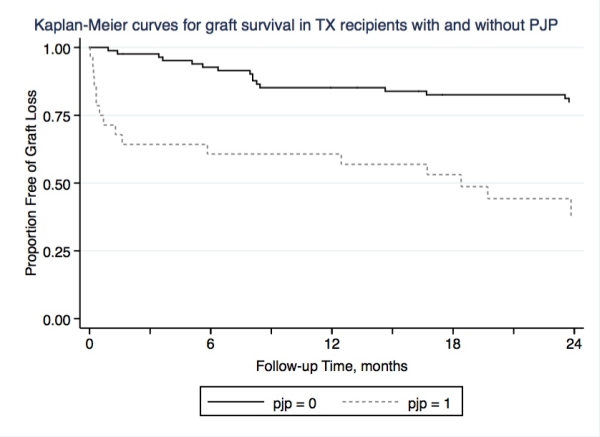
We recommend continuation or re-initiation of PJP PPX after the first year for kidney and pancreas TX recipients if their course is complicated by CMV viremia or invasive fungal infections.
CITATION INFORMATION: Garg N., Jorgenson M., Birschbach M., Descourouez J., Parajuli S., Astor B., Djamali A., Mandelbrot D. Pneumocystis jiroveci Pneumonia (PJP) in Kidney and Pancreas Transplant Recipients in the Present Era of Routine Post-Transplant Prophylaxis: Risk Factors and Outcomes Am J Transplant. 2017;17 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Garg N, Jorgenson M, Birschbach M, Descourouez J, Parajuli S, Astor B, Djamali A, Mandelbrot D. Pneumocystis jiroveci Pneumonia (PJP) in Kidney and Pancreas Transplant Recipients in the Present Era of Routine Post-Transplant Prophylaxis: Risk Factors and Outcomes [abstract]. https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/pneumocystis-jiroveci-pneumonia-pjp-in-kidney-and-pancreas-transplant-recipients-in-the-present-era-of-routine-post-transplant-prophylaxis-risk-factors-and-outcomes/. Accessed July 2, 2025.« Back to 2018 American Transplant Congress
