Optimization of Pancreatic Islet-Like Clusters from hiPSCs for Cell Therapy in Type 1 Diabetes.
Surgery, Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston, MA
Meeting: 2017 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 514
Keywords: Endothelial cells, Pancreas, Stem cells
Session Information
Session Name: Concurrent Session: Islet Transplant
Session Type: Concurrent Session
Date: Tuesday, May 2, 2017
Session Time: 4:30pm-6:00pm
 Presentation Time: 5:30pm-5:42pm
Presentation Time: 5:30pm-5:42pm
Location: E352
Introduction
Treatment for Type 1 Diabetes (T1D) includes pancreas or islets of Langerhans transplantation. Pancreatic beta-like cells from differentiated human induced pluripotent stem cells (hiPSCs) offer a functionally consistent scalable treatment source for islet replacement. We developed a new method to form human pancreatic beta-like clusters in a chemically defined system, using human endothelial cells (hECs) as supporting cells, resulting in differentiation of hiPSCs into pancreatic beta-like cells and engraftment after transplantation. This study represents a novel method for use of cell clusters that function as a treatment for T1D.
Methods
Embryoid bodies (EBs) were derived using a ROCKi-free/Spin-free technique, developed in our lab, which allows scalable and uniform EBs with interlaced human endothelial cells. The differentiation protocol is based on the developmental process during pancreatic organogenesis using two novel soluble factors. The cells were tested in vitro and in vivo to study their function and efficacy in reversing diabetes in a diabetic mouse model.
Results
Islet-like clusters obtained with our differentiation protocol showed the main features of primary pancreatic islets (Fig.1A), staining positive for insulin using dithizone (Fig.1B), expressing the main genetic markers of pancreatic beta cells (Fig.1C) co-staining for C-peptide and insulin, as well as PDX-1 and GLUT-2 (Fig.1D-F). Our islet-like clusters did not show co-expression of insulin and glucagon, typical of foetal beta cells (Fig.1G). When tested for insulin secretion in vitro, our islet-like clusters showed glucose responsiveness in a dose-dependent manner (Fig.1H). Transplantation of our islet-like clusters into diabetic mice showed normalization of hyperglycemia one week after surgery (Fig.1I).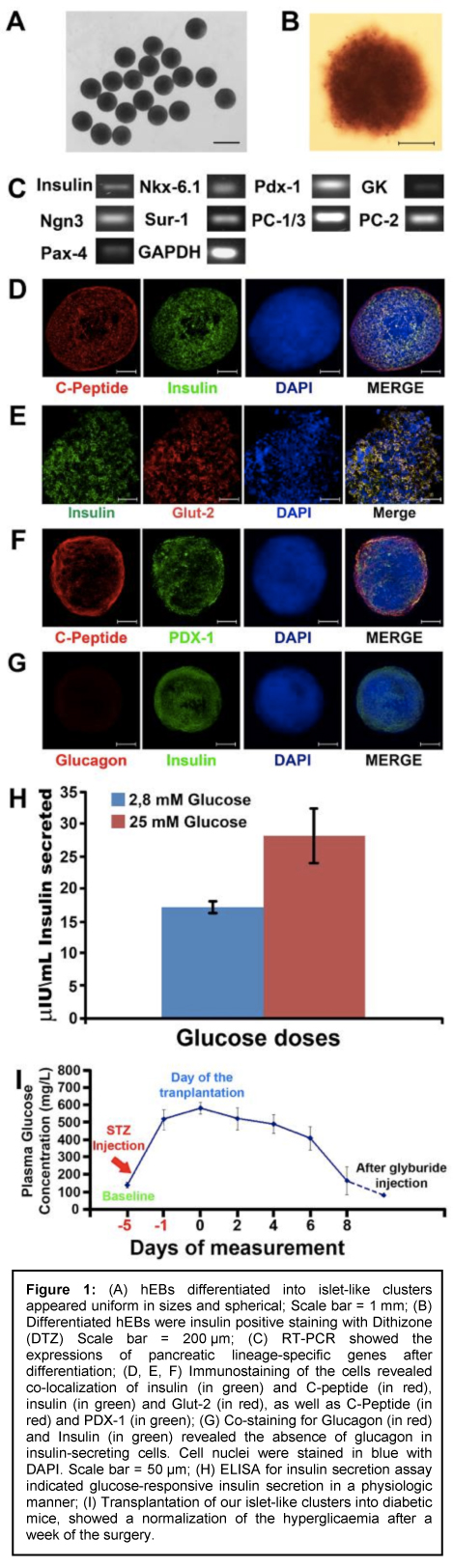 Conclusions
Conclusions
Suspension culture of hiPSC-EBs interlaced with hECs, in chemically defined medium, successfully differentiated into pancreatic beta-like clusters useful for in vitro studies, and possibly pharma and clinical uses. These results demonstrate that our clusters reverse hyperglycemia in a diabetic mouse model.
CITATION INFORMATION: Pettinato G, Kyriazis P, Thompson M, Koulmanda M, Fisher R. Optimization of Pancreatic Islet-Like Clusters from hiPSCs for Cell Therapy in Type 1 Diabetes. Am J Transplant. 2017;17 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Pettinato G, Kyriazis P, Thompson M, Koulmanda M, Fisher R. Optimization of Pancreatic Islet-Like Clusters from hiPSCs for Cell Therapy in Type 1 Diabetes. [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2017; 17 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/optimization-of-pancreatic-islet-like-clusters-from-hipscs-for-cell-therapy-in-type-1-diabetes/. Accessed March 9, 2026.« Back to 2017 American Transplant Congress
