Novel Discovery of Super-antigen That Mobilize Regulatory Cd8 T Cells Inhibits Donor-specific Antibody and Protects Heart Allografts from Antibody-mediated Rejection
1Brigham and Women's Hospital/Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, 2Dana Farber Cancer Institute/Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, 3Brigham and Women's Hospital, Boston, MA, 4Massachusetts General Hospital/Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA
Meeting: 2021 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 298
Keywords: Alloantibodies, Immunodominant peptide, Lymphocyte activation, Tolerance
Topic: Basic Science » Lymphocyte Biology: Signaling, Co-Stimulation, Regulation
Session Information
Session Time: 10:50am-11:50am
 Presentation Time: 11:00am-11:10am
Presentation Time: 11:00am-11:10am
Location: Virtual
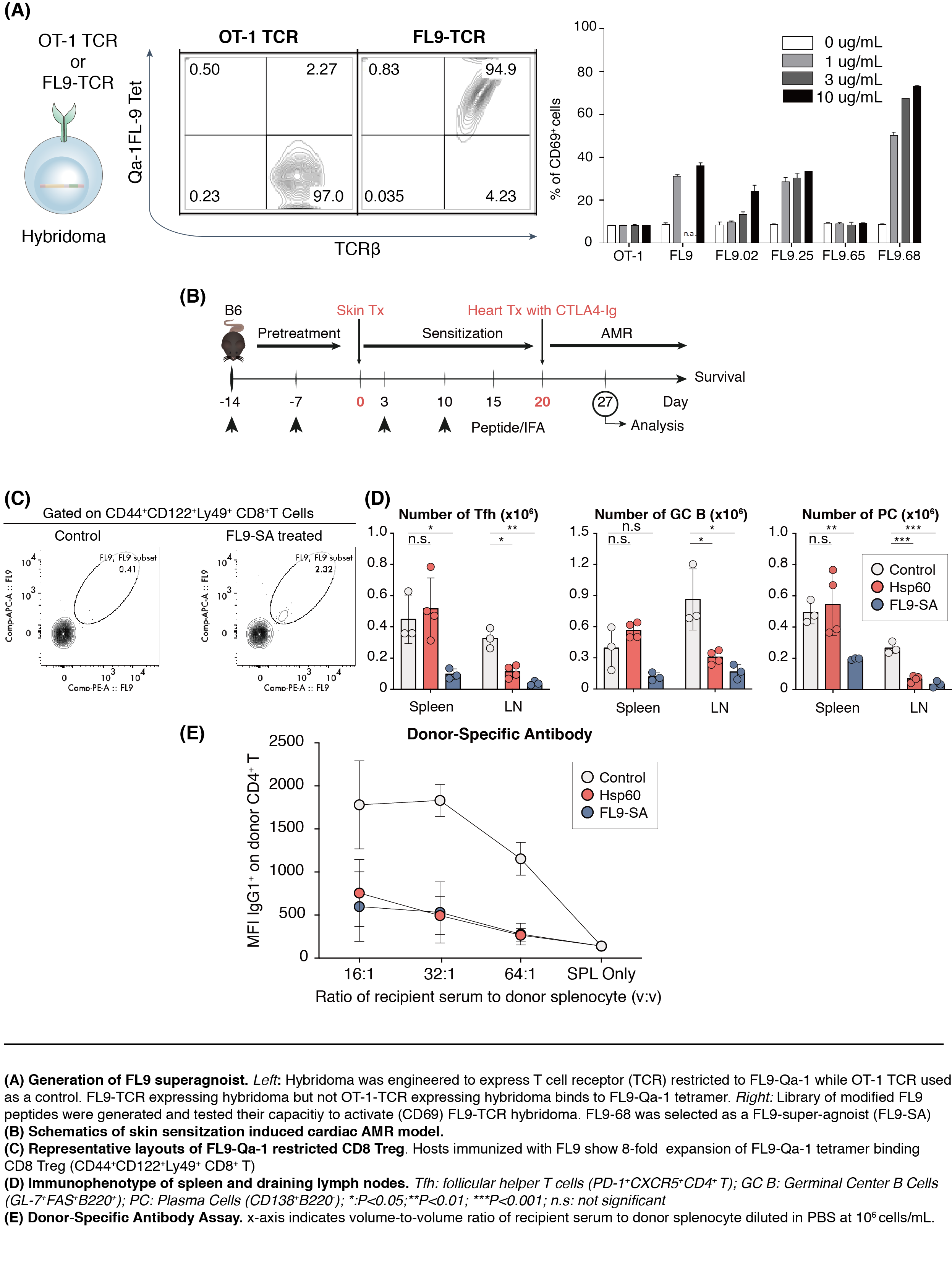
*Purpose: Antibody-mediated rejection (AMR) is a critical barrier to long-term allograft survival. We showed that Qa-1 (HLA-E in humans) restricted CD8+ T cells (CD8 Treg) play an essential role in controlling humoral immunity by killing alloreactive CD4+ T cells, especially follicular helper T cells (Tfh) that upregulate Qa-1 under immunologic stress conditions. We previously showed that interruption of CD8+ T cell receptor (TCR) binding to Qa-1 unleashes Tfh proliferation and leads to severe AMR in murine cardiac transplantation. In this study, we identified stress peptides (SPs) presented by Qa-1, modified one of these peptides to engineer a super-agonist (SA), and tested the efficacy of SPs in mobilizing CD8 Treg. Finally, we examined if SPs subdue allo-sensitization and protect heart grafts from AMR.
*Methods: Based on previous mass-spectrometry studies, we selected two SPs – FL9 and Hsp60p216 – that associate with Qa-1 under immunologic stress conditions. We then sorted FL9-Qa-1 tetramer binding CD8 Tregs, sequenced their TCR, and expressed on hybridoma. We also generated a library of modified FL9 sequences and compared their antigenicity using the TCR engineered hybridoma. After selecting FL9-SA, we performed BALB/c to B6 skin transplantation with or without Hsp60p216 and FL9-SA, followed by heart transplantation to induce AMR.
*Results: We successfully generated FL9-SA using our TCR engineered hybridoma system. Immunization with SPs significantly expanded SP-Qa-1 tetramer binding CD8 Treg. Compared to the control group, hosts treated with SPs during sensitization showed a significant reduction in Tfh and mature B cells including plasma cells. FL9-SA was substantially more efficacious than Hsp60p216. More importantly, donor-specific antibody (DSA) was significantly decreased in SP-treated groups, resulting in protection of heart allografts.
*Conclusions: Eliciting CD8 Treg response with Qa-1-associating SPs subdue germinal center reaction and DSA formation. Especially, the super-agonist that we generated showed superior biological efficacy in mobilizing CD8 Treg. Exploiting the mechanism of CD8 Treg through the study of Qa-1-associating peptides may offer a novel strategy to suppress AMR, which lacks effective therapeutic options.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Choi JY, Nakagawa H, Solhjou Z, Yatim K, Zhang H, Patel P, Mohammed MTawfeek, Riella L, Kim H, Cantor H, Azzi J. Novel Discovery of Super-antigen That Mobilize Regulatory Cd8 T Cells Inhibits Donor-specific Antibody and Protects Heart Allografts from Antibody-mediated Rejection [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2021; 21 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/novel-discovery-of-super-antigen-that-mobilize-regulatory-cd8-t-cells-inhibits-donor-specific-antibody-and-protects-heart-allografts-from-antibody-mediated-rejection/. Accessed March 5, 2026.« Back to 2021 American Transplant Congress