Nonadherence Post-Kidney Transplant is Associated with Increased Immune Activation Detected by Peripheral Blood Gene Expression Assay
M. S. Naseer, H. Shokouh-Amiri, T. Creamer, R. McMillan, S. Tandukar, D. Aultman, G. B. Zibari, N. Singh
Transplant, John C. McDonald Regional Transplant Center - Willis Knighton Health System, Shreveport, LA
Meeting: 2022 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 1368
Keywords: Gene expression, Kidney transplantation, Non-invasive diagnosis, Rejection
Topic: Clinical Science » Kidney » 33 - Kidney Psychosocial
Session Information
Session Time: 7:00pm-8:00pm
 Presentation Time: 7:00pm-8:00pm
Presentation Time: 7:00pm-8:00pm
Location: Hynes Halls C & D
*Purpose: Nonadherence to immunosuppressive medications is common post-transplantation. We hypothesized that nonadherence results in a heightened alloimmune response in kidney transplant recipients (KTRs), which may lead to adverse allograft outcomes post-transplant. AlloMap (CareDx®) is a non-invasive peripheral blood gene expression assay associated with genes involved in the immune response. Our center has been using donor-derived cell-free DNA (dd-cf-DNA) (AlloSure; CareDx®) and AlloMap for immune surveillance in KTRs enrolled in the OKRA registry since Nov 2019.
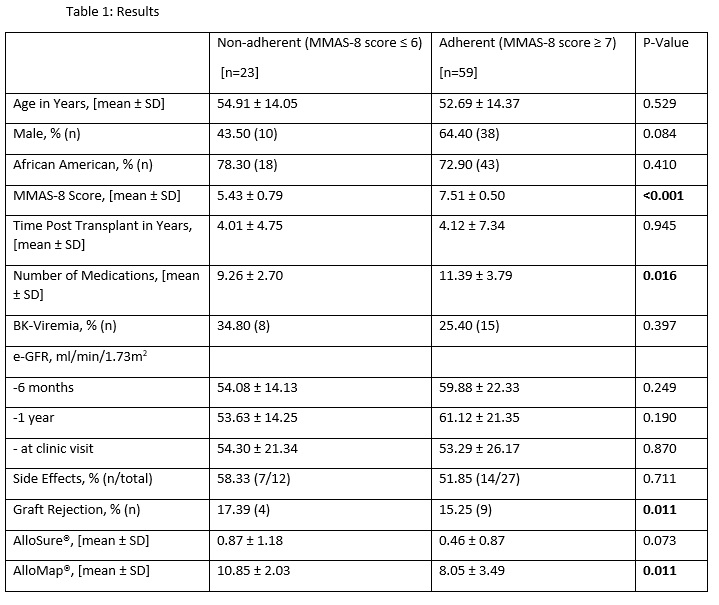
*Methods: This was a cross-sectional observational study of stable 82 KTRs seen in the outpatient transplant clinic for a routine follow-up visit. The Morisky Medication Adherence Scale (MMAS-8), a structured eight-question survey with a score from 0 to 8, was administered to the patients seen in the clinic from Sep 15 to Nov 15, 2020, to assess the self-reported medication adherence. Patients with a score less than or equal to 6 on MMAS-8 were categorized as non-adherent and the ones with a score greater than or equal to 7 were categorized as adherent. The baseline demographics, number of medications, side effects from medications, and information about prior history of BK-viremia and cumulative graft rejection episodes were collected. The AlloSure® and AlloMap® were drawn on the day or within a week prior or after the clinic visit and compared between the non-adherent and adherent groups.
*Results: At baseline, non-adherent patients as compared with adherent patients were on a lower number of medications (9.26 ± 2.70 vs. 11.39 ± 3.79, p = 0.01), had more graft rejections episodes (17.39% vs. 15.25%, p = 0.01), and depicted higher AlloMap® values post-transplant (10.85 ± 2.03 vs. 8.05 ± 3.49, p = 0.01) [Table 1].
*Conclusions: Nonadherence, as measured by MMAS-8, is associated with increased immune activation and a history of more prior graft rejection episodes. Further longitudinal data will be needed to assess if heightened immune activity in stable KTRs results in poor allograft outcomes. Additionally, AlloMap® may be a good tool to measure the occult non-adherence in stable KTRs.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Naseer MS, Shokouh-Amiri H, Creamer T, McMillan R, Tandukar S, Aultman D, Zibari GB, Singh N. Nonadherence Post-Kidney Transplant is Associated with Increased Immune Activation Detected by Peripheral Blood Gene Expression Assay [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2022; 22 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/nonadherence-post-kidney-transplant-is-associated-with-increased-immune-activation-detected-by-peripheral-blood-gene-expression-assay-2/. Accessed March 13, 2026.« Back to 2022 American Transplant Congress