Natural vs Induced ABO Antibodies in a Murine Model: Role of Sex and T Cells
1University of Alberta, Edmonton, AB, Canada, 2University of Melbourne, Melbourne, Australia
Meeting: 2022 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 280
Keywords: Mice, Natural antibodies, T cells
Topic: Basic Science » Basic Science » 04 - B-cell / Antibody /Autoimmunity
Session Information
Session Name: B-cell / Antibody /Autoimmunity
Session Type: Rapid Fire Oral Abstract
Date: Monday, June 6, 2022
Session Time: 3:30pm-5:00pm
 Presentation Time: 3:40pm-3:50pm
Presentation Time: 3:40pm-3:50pm
Location: Hynes Room 310
*Purpose: Interaction of ‘natural’ ABO antibodies (nAbs) with their cognate AB(H)-antigens (Ags) poses a high risk of rapid rejection of ABO-incompatible (ABOi) organ transplants. We previously demonstrated that a clear understanding of factors influencing ABO nAbs is crucial for successful ABOi heart transplantation. Here we investigated anti-A nAbs vs. intentionally-induced Abs (iAbs) with regard to role of sex and T cell requirement.
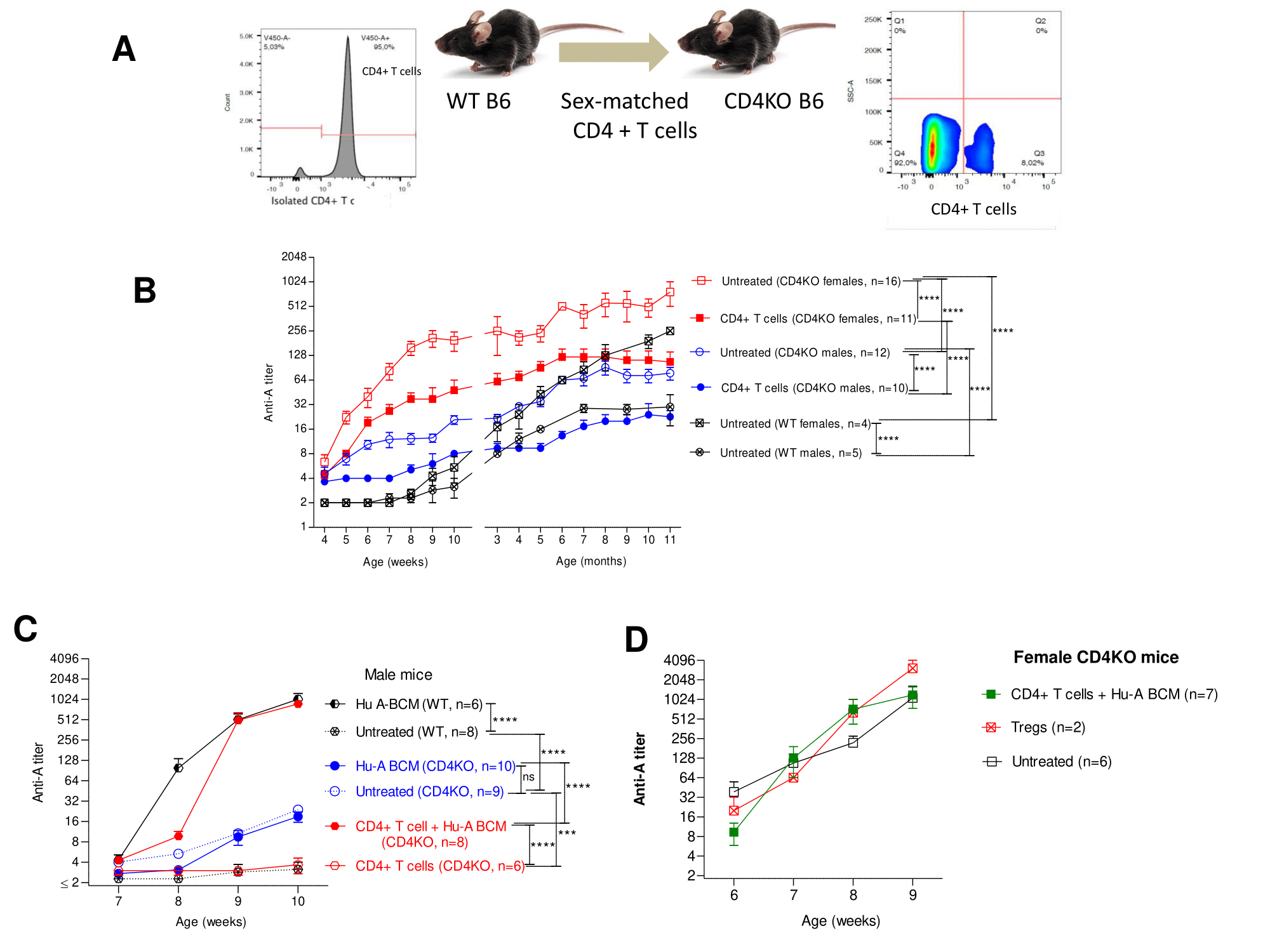
*Methods: Adult wild-type (WT) and CD4 T cell knock-out (CD4KO) mice (C57BL/6 (B6) background) received weekly i.p. injection x3 of human ABO-A blood cell membranes (Hu-A BCM; 100ul of 10% v/v) or left untreated. Serum anti-A Ab was measured by hemagglutination assay using ABO-A erythrocytes from our A-transgenic mouse line. To test for T cell help and/or suppression, sex-matched CD4+ T cells (8-12×106/mouse) or CD4+CD25+ T cells (1.7-2.8×106/mouse) from spleens of WT mice were transferred to CD4KO mice. After adoptive transfer, CD4+ T cell reconstitution in peripheral blood was confirmed and mice were left untreated or challenged with Hu-A BCM and assessed for anti-A Ab.
*Results: In contrast to WT mice, untreated CD4KO females produced dramatically more anti-A than males, rising substantially with puberty, and this was significantly suppressed in both sexes by adoptive transfer of sex-matched CD4+ T cells. Unlike WT mice, attempted sensitization of CD4KO mice with Hu-A BCM failed to induce additional anti-A beyond the already high levels in either sex; CD4+ T cell adoptive transfer rendered CD4KO mice responsive to A-sensitization. CD4+CD25+ T cell transfer into CD4KO mice neither suppressed anti-A nAbs nor rendered them responsive to A-sensitization (figure).
*Conclusions: When ABO ‘natural’ antibodies are discriminated from intentionally induced Abs, several important findings emerge: 1) Anti-A nAbs are produced without CD4+ T cell help in a sex- and age-dependent manner, suggestive of a role for sex hormones in regulating anti-A nAbs. 2) CD4+ T cells, but not CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells, down-regulate anti-A nAb production. 3) In contrast to anti-A nAbs, production of anti-A iAbs was CD4+ T cell-dependent without a sex bias.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Adam I, Motyka B, Tao K, Cowan PJ, West LJ. Natural vs Induced ABO Antibodies in a Murine Model: Role of Sex and T Cells [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2022; 22 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/natural-vs-induced-abo-antibodies-in-a-murine-model-role-of-sex-and-t-cells/. Accessed February 28, 2026.« Back to 2022 American Transplant Congress