Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells (MDSC) Accumulate in Intestinal Transplant (IT) Recipients (rc) and Suppress Recipient T-Cell (T) Response Against Donor Antigen.
1Transplant Center, Dept. General Surgery, Digestive Disease &
Surgery Institute, Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, OH
2Dept. Immunology, Lerner Research Institute, Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, OH
Meeting: 2017 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 460
Keywords: Intestinal transplantation, T cells
Session Information
Session Name: Concurrent Session: Small Bowel: All Topics
Session Type: Concurrent Session
Date: Tuesday, May 2, 2017
Session Time: 2:30pm-4:00pm
 Presentation Time: 2:30pm-2:42pm
Presentation Time: 2:30pm-2:42pm
Location: E271b
[Introduction] Recent advances of immunosuppressive regimens have decreased rejection rate and improved rc survival of IT. MDSC are potent immature myeloid cells capable of suppressing T responses. The impact of MDSC on transplants remains unknown. [Materials & Methods] Thirty-eight IT rc were enrolled (January 2015 – November 2016). Thirty-four IT rc received induction therapy and all received steroids (st) and FK506 for maintenance. PBMC and mononuclear cells in intraepithelial and lamina propria layers were isolated. We phenotypically identified MDSC (flow cytometry): CD33+CD11b+lineage–HLA-DR-/low with 3 subsets, CD14–CD15– (L-MDSC), CD14+CD15– (M-MDSC), and CD14–CD15+ (G-MDSC). [Results] The No. of total and each subset of MDSC significantly increased in PBMC after IT as compared with pretransplant levels. The No. of MDSC positively correlated with serum IL-6 levels and the st administration index based on the relative potency, but not with serum TNF-α levels and FK506 trough levels. IL-6 and methylpredonisolone dramatically enhanced differentiation of MDSC from human BMC in vitro, suggesting st administration and IL-6 could induce accumulation of MDSC after IT. M-MDSC and L-MDSC expressed CCR1-3, and CXCR2, and G-MDSC expressed CXCR2, suggesting MDSC have the migratory potential to traffic to the intestinal graft expressing the chemokine ligands. Percentages of total and each subset of MDSC among CD45+ cells significantly increased in graft lamina propria mucosa after IT. All subsets of MDSC suppressed proliferation of CD4 and CD8 T. MDSC suppressed the inhibition of organoid colony formation of donor intestinal epithelial stem cells by sorted corresponding donor-reactive T (Fig.1). [Conclusion] MDSC accumulate in IT rc and might play an important role in controlling alloimmune responses. 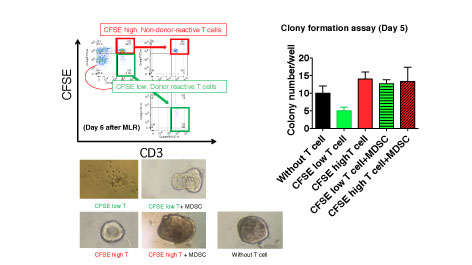
CITATION INFORMATION: Okano S, Kish D, Keslar K, Baldwin W, Fairchild R, Miller C, Abu-Elmagd K, Khanna A, Fujiki M, Fung J, Costa G, Hashimoto K. Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells (MDSC) Accumulate in Intestinal Transplant (IT) Recipients (rc) and Suppress Recipient T-Cell (T) Response Against Donor Antigen. Am J Transplant. 2017;17 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Okano S, Kish D, Keslar K, Baldwin W, Fairchild R, Miller C, Abu-Elmagd K, Khanna A, Fujiki M, Fung J, Costa G, Hashimoto K. Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells (MDSC) Accumulate in Intestinal Transplant (IT) Recipients (rc) and Suppress Recipient T-Cell (T) Response Against Donor Antigen. [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2017; 17 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/myeloid-derived-suppressor-cells-mdsc-accumulate-in-intestinal-transplant-it-recipients-rc-and-suppress-recipient-t-cell-t-response-against-donor-antigen/. Accessed March 13, 2026.« Back to 2017 American Transplant Congress
