mRNA Transcript Profiles of 14 Genes in Plasma Exosome Predict Risk for Antibody-Mediated Rejection (ABMR) of Renal Allografts
1Transplant Immunology Laboratory, Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, CA
2Comprehensive Transplant Center, Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, CA
3Pathology, Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, CA.
Meeting: 2018 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 23
Keywords: Gene expression, Kidney transplantation, Non-invasive diagnosis, Rejection
Session Information
Session Name: Concurrent Session: Kidney Acute Antibody Mediated Rejection
Session Type: Concurrent Session
Date: Sunday, June 3, 2018
Session Time: 2:30pm-4:00pm
 Presentation Time: 3:18pm-3:30pm
Presentation Time: 3:18pm-3:30pm
Location: Room Hall 4B
Background: Previously we reported that mRNA transcript profiles of 4 genes (gp130, SH2D1B, TNFα and CCL4) in plasma exosome could predict the risk of ABMR, a major obstacle for successful renal transplant (Tx) in HLA-sensitized patients. Here we studied more candidate genes in more renal Tx patients to improve the predictive value for ABMR by profiling plasma exosomal mRNA.
Methods: Total RNA was extracted from exosome purified from 174 EDTA-plasma samples (12 ABMR, 13 cell-mediated rejection [CMR], 13 ABMR/CMR, 38 no rejection Control [18 desensitized {DES}/20 non-DES] cases) for reverse transcription, pre-amplification and then qPCR of 105 candidate genes. The mRNA transcript levels of each gene were presented as relative quantity (RQ) vs. a reference RNA after normalized with a housekeeping gene, GAPDH. The average RQ of multiple samples of each patient within 1 month prior to diagnosis of rejection or over the 1st year post-Tx in the Control groups were used for comparison among all groups for each gene.
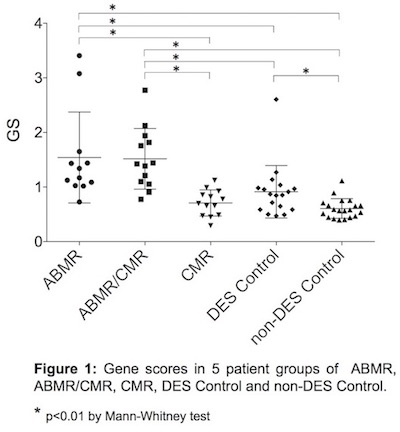
Results: Among 105 candidate genes, 14 genes (gp130, SH2D1B, TNFα, CXCL9, CXCL10, CXCL11, STAT1, PMP22, C1qB, PLPP3, KLRC1, IFI27, IL-10, IL-21R) showing significantly different mRNA transcript levels in ABMR and/or ABMR/CMR compared to CMR and/or Control groups, were selected to generate gene scores (GSs). The GSs were significantly higher in ABMR and ABMR/CMR groups vs. CMR and Control groups with improved discrimination of ABMR and ABMR/CMR (Area Under Curve [AUC]: 0.924), compared with previous 4-gene GS (AUC: 0.796) (Figure 1). The best cutoff point of current GS at 1.02 or above yielded sensitivity of 88.0% and specificity of 88.2% for predicting ABMR.
Conclusions: A comprehensive GS based on the mRNA transcript levels of 14 genes in plasma exosome can predict the risk of ABMR in renal Tx patients. Validation study in a larger cohort of patients is warranted to confirm the validity of this GS.
CITATION INFORMATION: Zhang H., Huang E., Nast C., Kahwaji J., Vo A., Jordan S., Toyoda M. mRNA Transcript Profiles of 14 Genes in Plasma Exosome Predict Risk for Antibody-Mediated Rejection (ABMR) of Renal Allografts Am J Transplant. 2017;17 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Zhang H, Huang E, Nast C, Kahwaji J, Vo A, Jordan S, Toyoda M. mRNA Transcript Profiles of 14 Genes in Plasma Exosome Predict Risk for Antibody-Mediated Rejection (ABMR) of Renal Allografts [abstract]. https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/mrna-transcript-profiles-of-14-genes-in-plasma-exosome-predict-risk-for-antibody-mediated-rejection-abmr-of-renal-allografts/. Accessed March 11, 2026.« Back to 2018 American Transplant Congress