Mortality and Graft Loss Attributable to Readmission Following Kidney Transplantation.
Surgery, Johns Hopkins University, School of Medicine, Baltimore, MD.
Meeting: 2016 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 429
Keywords: Graft survival, Kidney transplantation, Mortality, Outcome
Session Information
Session Name: Concurrent Session: Kidney: Length of Stay/Readmission
Session Type: Concurrent Session
Date: Tuesday, June 14, 2016
Session Time: 2:30pm-4:00pm
 Presentation Time: 3:42pm-3:54pm
Presentation Time: 3:42pm-3:54pm
Location: Room 302
BACKGROUND: Early hospital readmission (EHR) following kidney transplantation (KT) is independently associated with graft loss and mortality. Prior work assumes that this association is constant over time. It is possible that the risk associated with EHR is different during the EHR hospitalization compared to the risk during post-EHR follow-up.
METHODS: We used USRDS data to study 56,076 adult Medicare primary first-time KT recipients from December 1999-October 2011. EHR was any hospitalization within 30 days of KT discharge. Cox proportional hazard models were used to estimate the association between death-censored graft loss, mortality, and EHR. Separate models were created for live and deceased donor recipients. All models were adjusted for age, sex, race, BMI, pre-emptive transplant, cause of ESRD, peak PRA, HCV, time on dialysis, HLA mismatch, recipient/donor weight ratio, donor race. Deceased donor models were also adjusted for pulsatile perfusion, CIT, terminal creatinine, donor hypertension and diabetes, ECD, DCD, and regional/national sharing.
RESULTS: During the readmission hospitalization, graft survival was worse (deceased: 17.220.925.4 p<0.001, live: 18.929.546.1 p<0.001) and mortality was higher (deceased: 15.019.324.8 p<0.001, live: 8.218.240.6, p<0.001) for recipients experiencing EHR. Immediately following EHR discharge, graft survival (deceased: 2.082.272.48 p<0.001, live: 1.992.352.78 p<0.001) and mortality (deceased: 2.142.382.65 p<0.001, live : 1.862.292.82 p<0.001) remained elevated. Post-EHR the hazard of graft loss decreased further by 13-16% per year (p<0.001) and the hazard of mortality decreased by 9-14% per year (p<0.001).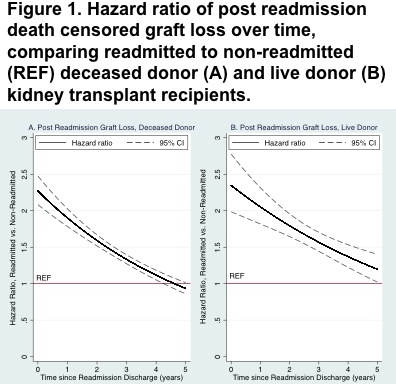
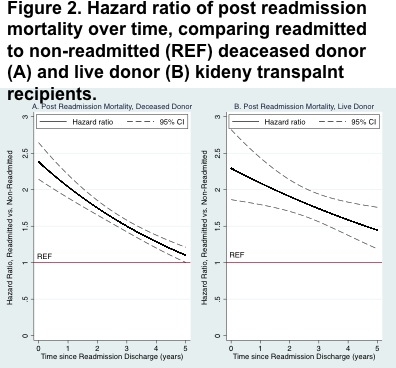
CONCLUSION: EHR is a strong predictor of graft loss and mortality during the EHR hospitalization and has a lasting albeit attenuated effect post-EHR.
CITATION INFORMATION: King E, Bowring M, Kucirka L, McAdams-DeMarco M, Massie A, Segev D. Mortality and Graft Loss Attributable to Readmission Following Kidney Transplantation. Am J Transplant. 2016;16 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
King E, Bowring M, Kucirka L, McAdams-DeMarco M, Massie A, Segev D. Mortality and Graft Loss Attributable to Readmission Following Kidney Transplantation. [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2016; 16 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/mortality-and-graft-loss-attributable-to-readmission-following-kidney-transplantation/. Accessed July 13, 2025.« Back to 2016 American Transplant Congress
