Mhealth Coaching Improves Patient Activation and Nutritional Behaviors in Diverse Renal Transplant Recipients
1Psychiatry, Duke University, Durham, NC, 2Biostatistics, Duke University, Durham, NC, 3Internal Medicine, Duke University, Durham, NC, 4School of Nursing, Duke University, Durham, NC, 5Pediatrics, Duke University, Durham, NC
Meeting: 2022 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 1741
Keywords: Efficacy, Kidney, Outcome
Topic: Clinical Science » Kidney » 50 - Health Equity and Access
Session Information
Session Time: 7:00pm-8:00pm
 Presentation Time: 7:00pm-8:00pm
Presentation Time: 7:00pm-8:00pm
Location: Hynes Halls C & D
*Purpose: Kidney transplant recipients who are not actively engaged in their care and lack self-management skills have poor transplant outcomes. These suboptimal outcomes are disproportionately observed among Black transplant recipients compared with their White counterparts. mHealth technologies may be effective in racial and ethnic minority populations, who are the most active users of the mobile web. This study aimed to determine whether a mHealth intervention pilot improved patient activation, engagement, and nutritional behaviors in a diverse kidney transplant population.
*Methods: Sixteen kidney transplant recipients (7 Black; 9 non-black) ages 14-50 were randomized to either mHealth app (Pattern Health Platform) for self-management monitoring (n=9) or monitoring plus personalized nurse coaching based upon self-determined behavior goals ( n=7). Outcomes were ascertained at 3 months and included: patient activation measured by Patient Activation Measure (PAM), self-management assessed via Partners in Health (PIH), and nutritional behaviors assessed via the Nutrition Self-Efficacy Score; feasibility and acceptability were also examined. One way ANCOVA was used to compare PAM, PIH, and Nutrition Self-Efficacy Score between arms.
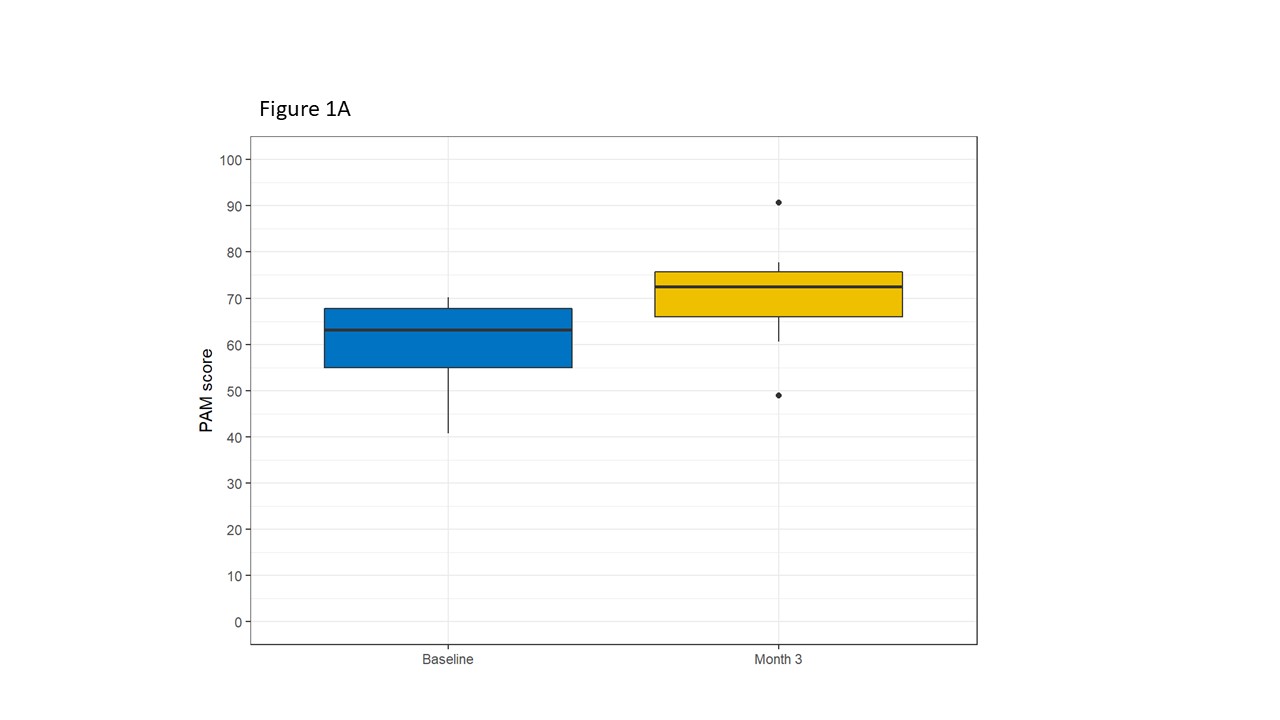
*Results: PAM significantly increased in the overall cohort from baseline to 3 months by an average of 11 points (95% CI: 3.2 to 18.8), Fig 1A. There was no difference in engagement measured by PIH. The mean change for Nutrition Self-Efficacy Score was 5.2 and higher in the app plus coaching arm compared to app alone. Black participants had higher mean Nutrition Self-Efficacy Score (80.5) compared to non-Black participants (75.6) after 3 months. 10 participants (63%) thought the system was easy to use, and for the 7 patients in the coaching arm the average coaching helpfulness score (range 1-10) was 7.7 (SD 2.2).
*Conclusions: Overall, the mHealth Intervention was easy to use, the coaching component was readily accepted, and improvements were demonstrated in patient-reported outcomes. Both Black and non-Black participants benefitted from the intervention, and Black kidney transplant patients differentially improved in nutrition self-efficacy. This highlights the potential use of this tailored mHealth intervention to reduce health care inequities in kidney transplantation.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Pollack M, Stauffer N, Lee H, Satoru I, Ellis M, Diamantidis C, Docherty S, Chambers ET. Mhealth Coaching Improves Patient Activation and Nutritional Behaviors in Diverse Renal Transplant Recipients [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2022; 22 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/mhealth-coaching-improves-patient-activation-and-nutritional-behaviors-in-diverse-renal-transplant-recipients/. Accessed July 12, 2025.« Back to 2022 American Transplant Congress