Maribavir (MBV) versus Investigator-Assigned Therapy (IAT) for Refractory Cytomegalovirus (CMV) Infection (with or without Resistance) in Solid Organ Transplant (SOT) Recipients: Subgroup Safety Analysis of a Phase 3 Study
R. M. La Hoz1, D. Florescu2, D. Kumar3, F. Saliba4, J. Gu5, A. Sundberg5
1Univ. Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, TX, 2Univ. Nebraska Medical Center, Omaha, NE, 3Univ. Health Network, Toronto, ON, Canada, 4Univ. Paris Saclay, Paris, France, 5Takeda Development Center Americas, Inc., Lexington, MA
Meeting: 2022 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 50
Keywords: Adverse effects, Cytomeglovirus, Safety
Topic: Clinical Science » Infection Disease » 24 - All Infections (Excluding Kidney & Viral Hepatitis)
Session Information
Session Name: Cytomegalovirus and other Herpes Viruses
Session Type: Rapid Fire Oral Abstract
Date: Sunday, June 5, 2022
Session Time: 3:30pm-5:00pm
 Presentation Time: 3:30pm-3:40pm
Presentation Time: 3:30pm-3:40pm
Location: Hynes Ballroom B
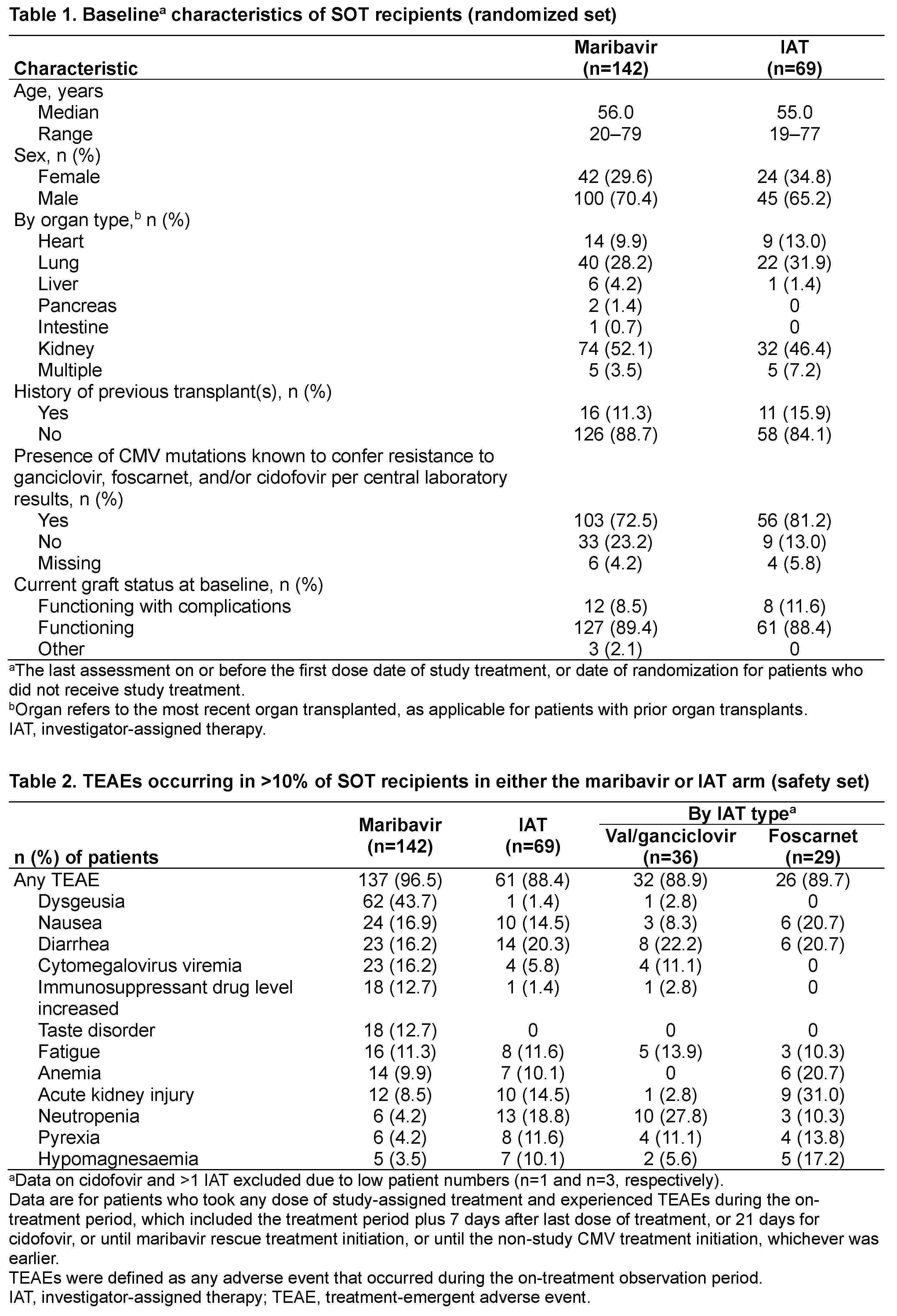
*Purpose: In a Phase 3 study of MBV vs IAT (val/ganciclovir, foscarnet, or cidofovir) for refractory CMV infection (with/without resistance; R/R) in hematopoietic cell transplant (HCT) or SOT recipients (NCT02931539), MBV was superior to IAT for CMV viremia clearance at Wk 8 (55.7% vs 23.9%), with a consistent benefit seen for SOT recipients (55.6% vs 26.1%, respectively). This subgroup analysis reports safety data from the SOT subgroup.
*Methods: Transplant recipients (≥12 years old) with confirmed CMV infection (plasma viral load ≥910 IU/mL) R/R to recent treatment (tx) were randomized 2:1 to MBV 400 mg BID or IAT for 8 wks, with 12 wks’ follow-up. Pre-specified safety analyses for SOT recipients included assessment of graft outcomes (randomized set [pts randomized to tx groups]), tx-emergent adverse events (TEAEs) and tx-related TEAEs (safety set [pts received study-assigned tx]).
*Results: Of the 352 patients (pts) randomized, 211 (59.9%) were SOT recipients (142 MBV, 69 IAT [36 val/ganciclovir, 29 foscarnet, 1 cidofovir, 3 >1 IAT]). The baseline characteristics of the SOT recipients were balanced between tx groups; most pts had resistance mutations at baseline (Table 1). During the overall study period, no SOT recipients had graft loss, although 9 (6.3%) MBV and 4 (5.8%) IAT-assigned pts experienced acute rejection. Rates of overall on-tx TEAEs (% pts) were 96.5% for MBV and 88.4% for IAT. Dysgeusia was the most frequently reported TEAE for MBV; rates of neutropenia and acute kidney injury (AKI) were lower for MBV than val/ganciclovir and foscarnet, resp. (Table 2). Overall, 61 (43.0%) pts treated with MBV experienced tx-related dysgeusia (IAT: 0). No patients experienced tx-related neutropenia in the MBV arm (val/ganciclovir: 8 [22.2%]) and the rate of tx-related AKI was lower for MBV (4 [2.8%]) than foscarnet (9 [31.0%]).
*Conclusions: In SOT recipients, rates of TEAEs were similar between tx groups; dysgeusia was the most reported TEAE for MBV. The frequencies of neutropenia and AKI (AEs common with IAT) were lower for MBV than val/ganciclovir and foscarnet, resp. These data in the subgroup of SOT recipients are consistent with the previously reported safety results observed in the overall population of the Phase 3 SOLSTICE study. Funding: Takeda Development Center Americas, Inc.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Hoz RMLa, Florescu D, Kumar D, Saliba F, Gu J, Sundberg A. Maribavir (MBV) versus Investigator-Assigned Therapy (IAT) for Refractory Cytomegalovirus (CMV) Infection (with or without Resistance) in Solid Organ Transplant (SOT) Recipients: Subgroup Safety Analysis of a Phase 3 Study [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2022; 22 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/maribavir-mbv-versus-investigator-assigned-therapy-iat-for-refractory-cytomegalovirus-cmv-infection-with-or-without-resistance-in-solid-organ-transplant-sot-recipients-subgroup-safety-analy/. Accessed March 9, 2026.« Back to 2022 American Transplant Congress