Long-Term Efficacy of Direct-Acting Antiviral Agents
J. Zhang, W. Sun, J. Lin, Y. Tian, L. Ma, L. Zhang, Y. Zhu
Beijing Friendship Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing, China
Meeting: 2019 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: D245
Keywords: Efficacy, Hepatitis C, Kidney transplantation, Viral therapy
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session D: Non-Organ Specific: Viral Hepatitis
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Tuesday, June 4, 2019
Session Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Location: Hall C & D
*Purpose: Long-term efficacy of direct-acting antiviral agents (DAAs) therapy in kidney transplant recipients was unknown. Thus, we aimed to evaluate it in a Chinese cohort of HCV-infected kidney transplant recipients.
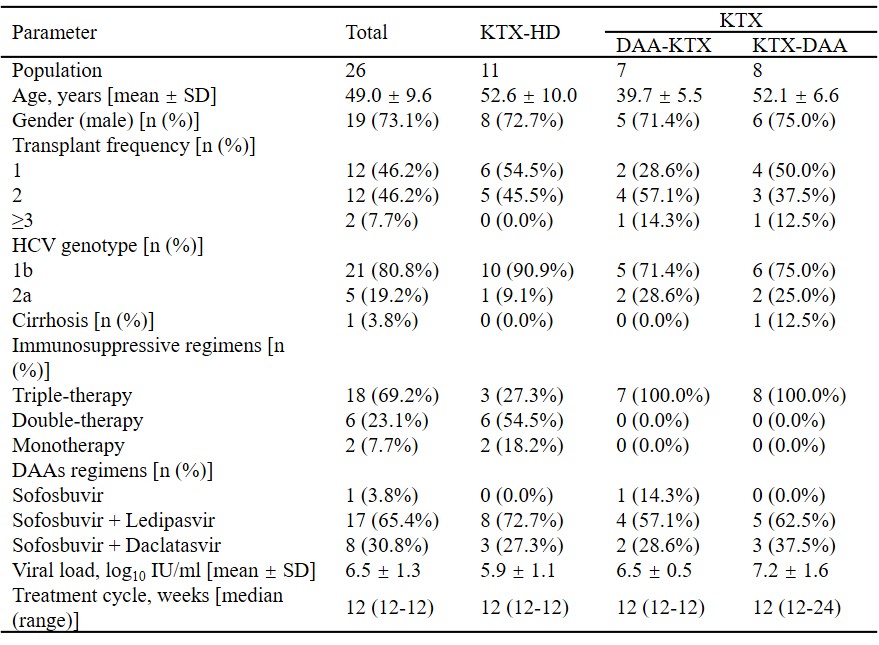
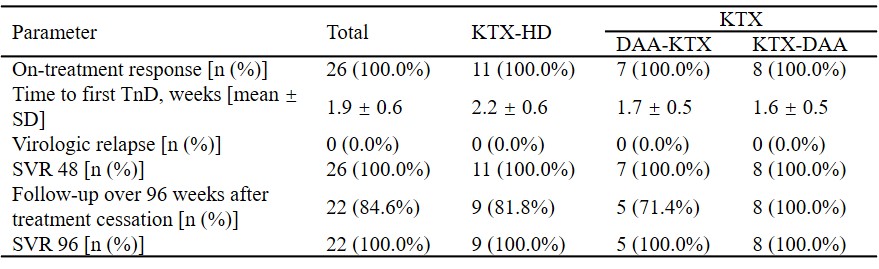
*Methods: Single-center and retrospective study of HCV-infected kidney transplant recipients initiating an DAAs regimen between January 2015 and December 2017 was conducted. Totally 26 kidney transplant (KTX) recipients were divided into three groups, including KTX-Hemodialysis (HD) Group, DAA-KTX Group and KTX-DAA Group. On-treatment response was defined as target not detected within 12 weeks. Sustained virologic response (SVR) was defined as HCV-RNA negativity after treatment cessation.
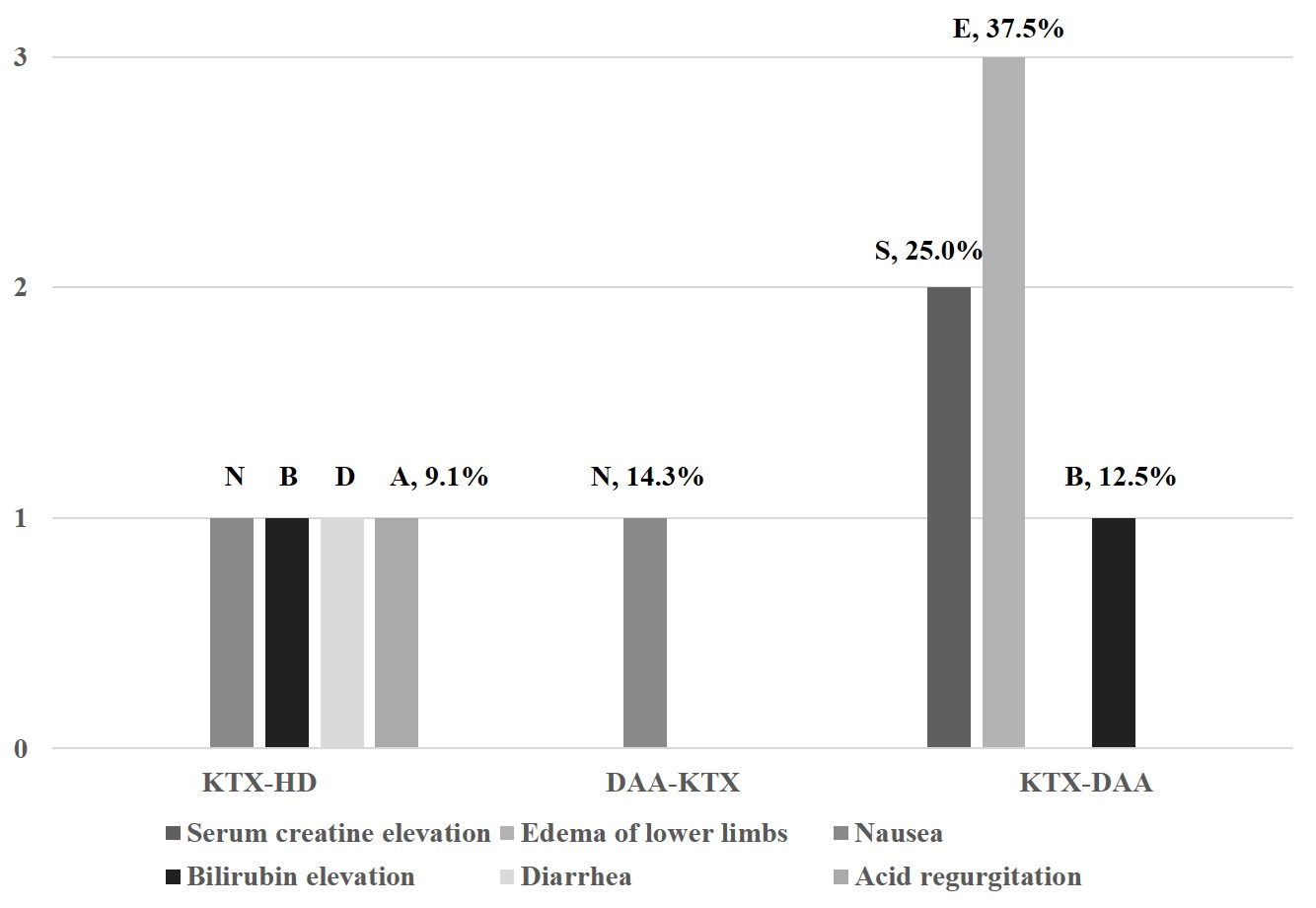
*Results: HCV genotype was predominantly 1b (80.8%), followed by 2a. All (100%) patients achieved on-treatment response. Time to target not detected was 1.9 ± 0.6 weeks, with no significant difference among the three groups. All (100%) patients achieved SVR 48 and 22/26 patients achieved SVR 96, with an SVR rate of 100%. Trough levels of Tacrolimus remained stable under DAAs therapy, without any dose adjustment. Common adverse events were nausea, diarrhea, acid regurgitation, bilirubin elevation in KTX-HD group, nausea in DAA-KTX group, and edema of lower limbs, serum creatine elevation, bilirubin elevation in KTX-DAA group. All patients recovered after treatment cessation without reductions in dose, or withdrawal of DAAs or immunosuppressive agents.
*Conclusions: Antiviral treatment with DAAs in HCV-infected kidney transplant recipients is persistently effective and well tolerated during long-term follow-up. A regular monitoring of renal function in patients who receive DAAs regimens with preexisting impaired renal function is strongly recommended. Furthermore, the trough calcineurin inhibitors levels were recommended to be frequently monitored.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Zhang J, Sun W, Lin J, Tian Y, Ma L, Zhang L, Zhu Y. Long-Term Efficacy of Direct-Acting Antiviral Agents [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2019; 19 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/long-term-efficacy-of-direct-acting-antiviral-agents/. Accessed March 9, 2026.« Back to 2019 American Transplant Congress