Is MELD Score a Significant Predictor of Post-Transplant Mortality? An Old Issue with Simple Answer.
1Surgery, University of Washington, Seattle, WA
2Nephrology, University of Washington, Seattle, WA
3Hepatology, University of Washington, Seattle, WA.
Meeting: 2016 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: B172
Keywords: Liver transplantation, Outcome, Prognosis, Renal failure
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session B: Kidney Issue in Liver Transplantation
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Sunday, June 12, 2016
Session Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Location: Halls C&D
The predictive value of the Model for End-Stage Liver Disease (MELD) score for post-transplant survival has been under constant debate. Some investigators tried to introduce better predictors involving additional recipient variables, however these predictors either were not validated or were too complicated. The main goal of this study was to investigate possible factor(s) decrease MELD score value in predicting post-transplant survival.
The SRTR data of all patients (≥18 years old) who underwent liver transplantation between 3/1/2002 to 12/31/2013 was investigated. Patients with re-transplants, living donor liver transplants, multi-organ transplants, and those who received exception points were excluded. Kaplan- Meier with long-rank analysis was used to compare patient survival in three MELD categories (15-22, 23-32, 33-40) with Serum Creatinine (SCr) > or ≤ 2 at the time of transplant.
The data on 31,682 transplant recipients with a mean age of 52.3 ± 10.5 years were included. Our results showed that long-term post-liver transplant survival of patients with abnormal renal function (SCr>2) is worse than patients with normal SCr in each MELD category 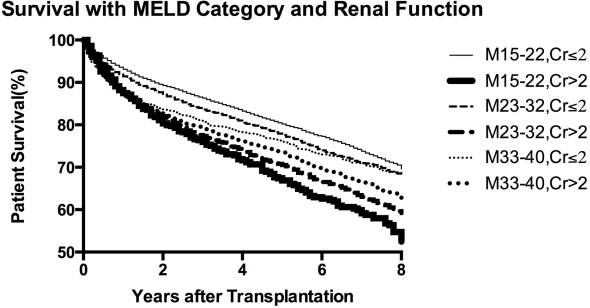 . Remarkably, the 5-year survival of patients with MELD 33-40 and normal SCr was better than patients with low MELD (15-22) and SCr >2 (73.9% vs 65.9%, p < 0.0001). For the two other components of MELD, INR and bilirubin, groups with higher levels had better survival, thus, highlighting the more significant role of SCr in predicting patients' long-term transplant survival.
. Remarkably, the 5-year survival of patients with MELD 33-40 and normal SCr was better than patients with low MELD (15-22) and SCr >2 (73.9% vs 65.9%, p < 0.0001). For the two other components of MELD, INR and bilirubin, groups with higher levels had better survival, thus, highlighting the more significant role of SCr in predicting patients' long-term transplant survival.
Among MELD score parameters, SCr has the most significant impact on long-term liver transplant survival. Modification of the MELD score with higher weight given to SCr may be considered to be able to use it as a post-liver transplant survival predictor.
CITATION INFORMATION: Rahnemai-Azar A, Perkins J, Montenovo M, Rayhill S, Bakthavatsalam R, Leca N, Blosser C, Di Castro I, Bhattacharya R, Reyes J, Sibulesky L. Is MELD Score a Significant Predictor of Post-Transplant Mortality? An Old Issue with Simple Answer. Am J Transplant. 2016;16 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Rahnemai-Azar A, Perkins J, Montenovo M, Rayhill S, Bakthavatsalam R, Leca N, Blosser C, Castro IDi, Bhattacharya R, Reyes J, Sibulesky L. Is MELD Score a Significant Predictor of Post-Transplant Mortality? An Old Issue with Simple Answer. [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2016; 16 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/is-meld-score-a-significant-predictor-of-post-transplant-mortality-an-old-issue-with-simple-answer/. Accessed March 9, 2026.« Back to 2016 American Transplant Congress
