Induction Immunosuppression in ABO-Incompatible Liver Transplant Recipients
1Keck Medicine of USC, Los Angeles, CA, 2Keck School of Medicine, Los Angeles, CA
Meeting: 2022 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 1085
Keywords: Immunosuppression, Interleukin-2 receptor, Liver, Rejection
Topic: Clinical Science » Liver » 54 - Liver: Immunosuppression and Rejection
Session Information
Session Name: Liver: Immunosuppression and Rejection
Session Type: Poster Abstract
Date: Sunday, June 5, 2022
Session Time: 7:00pm-8:00pm
 Presentation Time: 7:00pm-8:00pm
Presentation Time: 7:00pm-8:00pm
Location: Hynes Halls C & D
*Purpose: ABO-incompatible (ABO-i) liver transplantation (LT) has been associated with an increased risk of AMR, as well as poor patient and graft survival. With advances in desensitization strategies and immunosuppression (IS), outcomes in ABO-i LT have become equivalent to that of ABO-compatible LT, primarily in living donor LT. However, there is limited data available in ABO-i deceased donor LT, where desensitization strategies cannot be implemented. Therefore, this study evaluated induction IS on the incidence of allograft rejection in A2-to-O LT in the absence of desensitization.
*Methods: In this single-center retrospective study of adult ABO-i liver transplant recipients between January 2010 and January 2021, we reviewed the efficacy and safety of induction IS. Exclusion criteria included prior history of LT, patients under 18 years of age, and patients who underwent plasmapheresis or received intravenous immune globulin pre-transplant. The primary outcome evaluated incidence of allograft rejection. Secondary endpoints included incidence of biliary complications, graft survival, and patient survival.
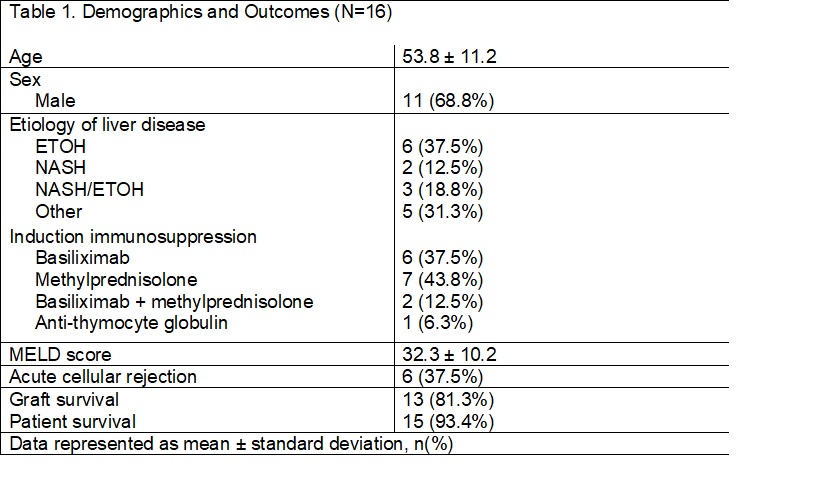
*Results: A total of sixteen patients have been reviewed thus far in this ongoing research study. The average age of the cohort was 53.8 ± 11.2 years. Most patients were male (68.8%) with an underlying etiology of liver disease from alcoholic cirrhosis (37.5%). Induction IS was not consistent across the cohort as 7 patients (43.8%) received methylprednisolone, 6 patients (37.5%) received basiliximab, two patients (12.5%) received both basiliximab and methylprednisolone, and one (6.3%) patient received rabbit anti-thymocyte globulin. Of the 16 patients, 37.5% experienced biopsy proven acute cellular rejection with a median time to onset of rejection of 15 days and mean Rejection Activity Index score of 4.2 ± 1.3. There were no cases of AMR. Biliary complications were diagnosed in 6 (37.5%) patients, which may have led to overrepresentation of ACR. Graft survival for the cohort was 81.3% with a median time to graft loss of 180 days, and patient survival was 93.4%. Neither of the patients who received both basiliximab and methylprednisolone induction experienced allograft rejection or graft loss.
*Conclusions: This single-center review suggests that ABO-i LT can be safely performed in the absence of desensitization, as outcomes are similar to reported literature for ABO-compatible LT. Basiliximab and methylprednisolone induction may be optimal for this population.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Shaikh S, Hasan I, Kaur N. Induction Immunosuppression in ABO-Incompatible Liver Transplant Recipients [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2022; 22 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/induction-immunosuppression-in-abo-incompatible-liver-transplant-recipients/. Accessed February 23, 2026.« Back to 2022 American Transplant Congress