Importance of B Cell Antigen Specificity in Breg Dependent Tolerance.
Transplantation Unit, Department of Surgery, Massachusetts General Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA
Meeting: 2017 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 487
Session Information
Session Name: Concurrent Session: B Cells: Regulation and Tolerance
Session Type: Concurrent Session
Date: Tuesday, May 2, 2017
Session Time: 4:30pm-6:00pm
 Presentation Time: 5:42pm-5:54pm
Presentation Time: 5:42pm-5:54pm
Location: E350
Introduction: We have previously shown that anti-CD45RB induced islet and cardiac allograft tolerance is B cell dependent and can be adoptively transferred to naïve hosts by regulatory B cells (Bregs) in a Treg dependent manner. However, the requirement for antigen specificity in the induction and effector actions of Bregs has not been carefully examined. We used a newly available BcR transgenic mouse line (OB-1), with ubiquitous B cell specificity for ovalbumin (OVA+) to investigate the role of antigen specificity in B cell dependent tolerance.
Methods: OVA+ B6 transgenic mouse skin was transplanted onto WT, uMT (B cell deficient) or OB-1 B6 recipients, with and without anti-CD45RB antibody treatment. MLR was performed using OT-II (OVA specific CD4T cell transgenic) T cells stimulated by OVA+ B6 splenocytes. Naïve or activated (CpG x 3 days followed by LPS/PMA/ionomycin x 5 hours) WT or OB-1 B6 B cells were added to asses their ability to inhibit antigen specific T cell proliferation.
Results: OVA+ skin grafts were rejected by uMT, WT, and OB-1 recipients in 16.3±1.3, 19.6±1.5, and 24.4±2.3 days (p<0.01), respectively. Similar to islet and cardiac transplant models, short term anti-CD45 antibody treatment significantly prolonged OVA skin graft survival in both WT and OB-1 recipients (>50d). Experiments adoptively transferring B cells from mice accepting OVA+ skin to naïve B6 hosts grafted with OVA+ grafts are currently in progress. In vitro, T cell proliferation was not suppressed by either naive WT or naive OB-1 B cells. However, CpG activated WT B cells suppressed T cell proliferation ~80% and CpG activated OB-1 B cells >90% suppression.
Conclusion: We have developed a model of antigen specific rejection and tolerance to OVA that allows specific tracking of donor specific B cells and examination of their interaction with donor antigen specific T cells in vivo. These studies will allow precise and detailed examination of the antigen specific actions of regulatory B cells in vivo.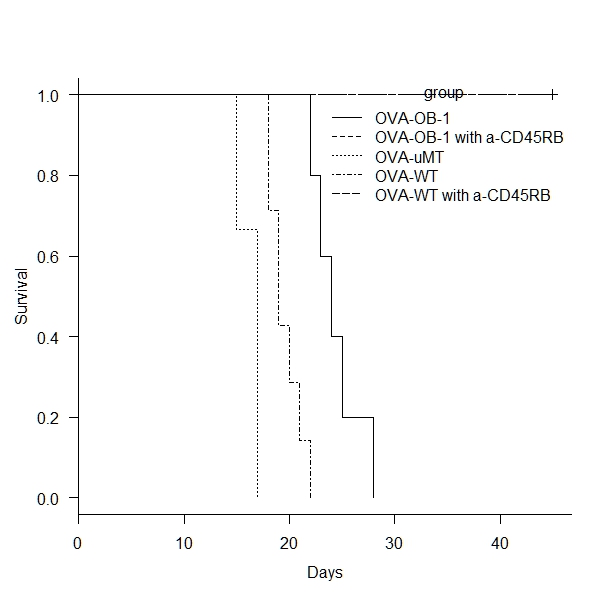
CITATION INFORMATION: Kimura S, Kojima L, Aburawi M, Fontan F, Kim J, Deng K, Tector H, Lee K, Yeh H, Markmann J. Importance of B Cell Antigen Specificity in Breg Dependent Tolerance. Am J Transplant. 2017;17 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Kimura S, Kojima L, Aburawi M, Fontan F, Kim J, Deng K, Tector H, Lee K, Yeh H, Markmann J. Importance of B Cell Antigen Specificity in Breg Dependent Tolerance. [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2017; 17 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/importance-of-b-cell-antigen-specificity-in-breg-dependent-tolerance/. Accessed February 26, 2026.« Back to 2017 American Transplant Congress
