Impact of Induction Therapy on Outcomes in HIV + Renal Transplant Recipients
1Medicine, Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center (BIDMC), Boston, MA
2The Transplant Institute, BIDMC, Boston, MA
3Surgery, BIDMC, Boston, MA
4Pharmacy, BIDMC, Boston, MA.
Meeting: 2015 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 284
Keywords: HIV virus, Induction therapy, Kidney transplantation
Session Information
Session Name: Concurrent Session: Kidney: Induction
Session Type: Concurrent Session
Date: Monday, May 4, 2015
Session Time: 4:00pm-5:30pm
 Presentation Time: 4:12pm-4:24pm
Presentation Time: 4:12pm-4:24pm
Location: Room 120-ABC
Purpose: Kidney transplantation in HIV+ recipients has been complicated by higher than expected acute rejection rates (AR). Induction immunosuppression may or may not impact this outcome. The purpose of our study is to assess the role of induction therapy on AR, patient and allograft survival, infection and CD4 + t cell recovery.
Methods: Retrospective review of HIV+ renal transplant recipients who received induction therapy (n=30) between 2004-2014, including patients reported in the HIV-TR multisite study (U01 AI052748). Patients received induction with rabbit antithymocyte globulin (rATG) or basiliximab, tacrolimus, mycophenolate mofetil and corticosteroids.
| Basiliximab induction (n=14) | rATG induction (n=16) | P value | |
| Recipient age | 47.1 ± 7.3 | 46.6 ± 8.5 | 0.86 |
| African American | 10 (71) | 3 (19) | 0.01 |
| Caucasian | 4 (29) | 6 (38) | 0.71 |
| Hispanic | 0 | 4 (25) | 0.10 |
| Other race | 0 | 3 (19) | 0.23 |
| Male gender | 11 (79) | 14 (88) | 0.64 |
| HCV+ | 1 (7) | 4 (25) | 0.34 |
| Living donor | 5 (36) | 3 (19) | 0.42 |
| Deceased donor | 9 (64) | 13 (81) | 0.42 |
| Delayed graft function | 6 (43) | 9 (56) | 0.72 |
| Median length of follow-up (years) | 7.6 ± 2.4 | 4.2 ± 1.9 | <0.001 |
| Rejection at 1 year | 3 (21) | 2 (14) | 0.64 |
| Rejection at 3 years (cumulative) | 5 (36) | 2 (14) | 0.20 |
| 1 year patient survival | 14 (100) | 16 (100) | 1.00 |
| 1 year graft survival | 11 (79) | 14 (88) | 0.64 |
| Serious infections (per patient) | 3.7 ± 2.9 | 1.1 ± 1.4 | 0.06 |
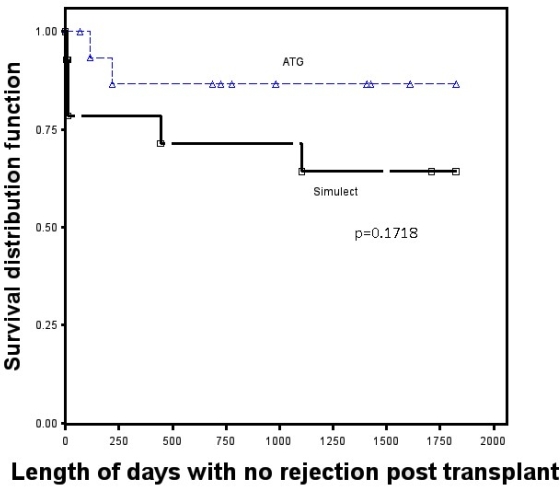
A trend towards lower AR at 3 years, and higher 1-year graft survival was observed in the rATG group. CD4 counts were only significantly lower in the rATG group at 8 weeks (170±88 vs. 340±157, p=0.004) and 1 year post transplant (250±79vs. 414±231, p=0.03). There were no opportunistic infections.
Our data suggests a trend towards reduced AR, graft failure and serious infections with use of rATG. CD4 + t cell suppression was less than expected and not associated with an increase in infections. The data from this retrospective cohort suggests that rATG induction may be advantageous in the HIV+ renal transplant population.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Kershaw C, Rogers C, Pavlakis M, Tang H, Alonso C, Khwaja K, Evenson A, Raven K, Wong M. Impact of Induction Therapy on Outcomes in HIV + Renal Transplant Recipients [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2015; 15 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/impact-of-induction-therapy-on-outcomes-in-hiv-renal-transplant-recipients/. Accessed July 13, 2025.« Back to 2015 American Transplant Congress
