Impact of Direct Acting Antiviral Agents (DAAs) for Hepatitis C Virus (HCV)-Induced Liver Diseases on Registration and Outcome on Waiting List (WL) for Liver Transplant (LT)
C. Antoine,1 C. Jasseron,1 F. Conti,2 S. Dharancy,3 C. Duvoux,4 A. Coilly.5
1Medical and Scientific Department, Agence de la Biomedecine, Agence de la Biomedecine, La Plaine Saint Denis, Saint Denis, France
2Department of Hepatology, University Hospital La Pitie, Paris, France
3Department of Hepatology, University Hospital Huriez, Lille, Nord Pas de Calais, France
4Department of Hepatology, University Hospital Henri Mondor, Créteil, Val de Marne, France
5Department of Hepatology, University Hospital Paul Brousse, Villejuif, Val de Marne, France.
Meeting: 2018 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 247
Keywords: Graft survival, Hepatitis C, Liver transplantation, Mortality
Session Information
Session Name: Concurrent Session: Liver: Viral Hepatitis
Session Type: Concurrent Session
Date: Monday, June 4, 2018
Session Time: 2:30pm-4:00pm
 Presentation Time: 2:42pm-2:54pm
Presentation Time: 2:42pm-2:54pm
Location: Room 602/603/604
2d-generation DAAs have dramatically improved the management of patients with HCV, including patients with advanced diseases. In France, since 2013, DAA have been largely used, however their impact on the LT waiting list had not been evaluated so far. In the present study we attempted to evaluate the impact of new DAAs on listing and outcome on the WL of HCV LT candidates.
The study included all adult candidates listed between 2000 and 2016 (N=5580) with special focus on HCV patients. We compared kinetics over time of transplant indications, outcome on WL and 1-year post-transplant survival.
Results: The number of candidates listed for HCV liver diseases increased by 104% from 2000 (n=194) to 2013 (n=395). We observed a switch in LT indications, HCC becoming predominant and representing 54% of HCV-candidates in 2016 and decompensated HCV-cirrhosis representing 38% of LT indications. Listing for retransplantation decreased by 35% since 2013. We also observed i) a significant decrease in WL mortality from 7.4 % in 2013 to 3.3% in 2016, ii) a decrease by 30% of delisting for worsening condition from 2014 to 2016, iii) a 82% increase of delisting for improving condition, iiii) a sharp increase of inactive patients on WL from 23% in 2013 to 60% in 2016.The 1y-graft survival rate has significantly improved between before and after extent use of DAAs.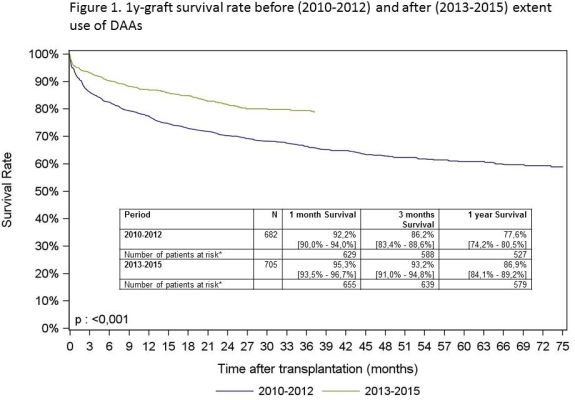
Our study strongly suggests that HCV candidates have been benefiting from access to DAAs. The decrease of transplant needs for HCV liver disease may contribute to the decrease of overall waiting list mortality and removal for worsening conditions observed in France for 2 years.
CITATION INFORMATION: Antoine C., Jasseron C., Conti F., Dharancy S., Duvoux C., Coilly A. Impact of Direct Acting Antiviral Agents (DAAs) for Hepatitis C Virus (HCV)-Induced Liver Diseases on Registration and Outcome on Waiting List (WL) for Liver Transplant (LT) Am J Transplant. 2017;17 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Antoine C, Jasseron C, Conti F, Dharancy S, Duvoux C, Coilly A. Impact of Direct Acting Antiviral Agents (DAAs) for Hepatitis C Virus (HCV)-Induced Liver Diseases on Registration and Outcome on Waiting List (WL) for Liver Transplant (LT) [abstract]. https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/impact-of-direct-acting-antiviral-agents-daas-for-hepatitis-c-virus-hcv-induced-liver-diseases-on-registration-and-outcome-on-waiting-list-wl-for-liver-transplant-lt/. Accessed February 25, 2026.« Back to 2018 American Transplant Congress
