Immunosuppressive Ability of NFkB Inhibitor: Withaferin A.
1Transplant Surgery, Virginia Commonwealth University, Richmond, VA
2Hume-Lee Transplant Center, VCU Health System, Richmond, VA
3Simmons Transplant Institute, Baylor Scott and White Health, Dallas, TX
Meeting: 2017 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: A147
Keywords: CD4, Immune deviation, Inflammation, Islets
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session A: Immunosuppression
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Saturday, April 29, 2017
Session Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
 Presentation Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
Presentation Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
Location: Hall D1
Background
The advent of steroid-free protocol by the Edmonton group encouraged islet transplant as a therapy for Type-1 Diabetes. However, long-term dysfunction in islet transplantation is a major challenge. Current immunosuppression protocols are toxic to the beta cells resulting in graft loss. Withaferin A (WA) is a plant-derived molecule which has been used as an anti-inflammatory agent due to its ability to block the Nuclear Factor Kappa B (NFkB) pathway. Since immune cell activation is regulated by NFkB, we hypothesized that WA can be used to suppress the immune system without harming the islets. The purpose of this study to demonstrate the safety of WA to islets and its immunosuppressive ability.
Methods
Human and mouse islets were cultured with or without WA at various concentrations, viability and glucose-stimulated insulin secretion was measured. Splenocytes extracted from mice were stained with 10uM CFSE for 10 mins. Stained cells were stimulated with CD3/CD28 beads in the presence or absence of 1ug/mL WA and cultured for 5 days. T cell proliferation and intracellular cytokine staining for IFNy in CD4 and CD8 cells was performed. Results were confirmed using purified mouse T cells and human T cells. All experiments were performed in triplicates and repeated using three donors.
Results
The viability and stimulation index of islets was not affected by WA up to a concentration of 1ug/ml. Flow cytometric analysis revealed that the proliferation of T cells was significantly inhibited by WA in mouse splenocytes, purified T cells and human T cells. 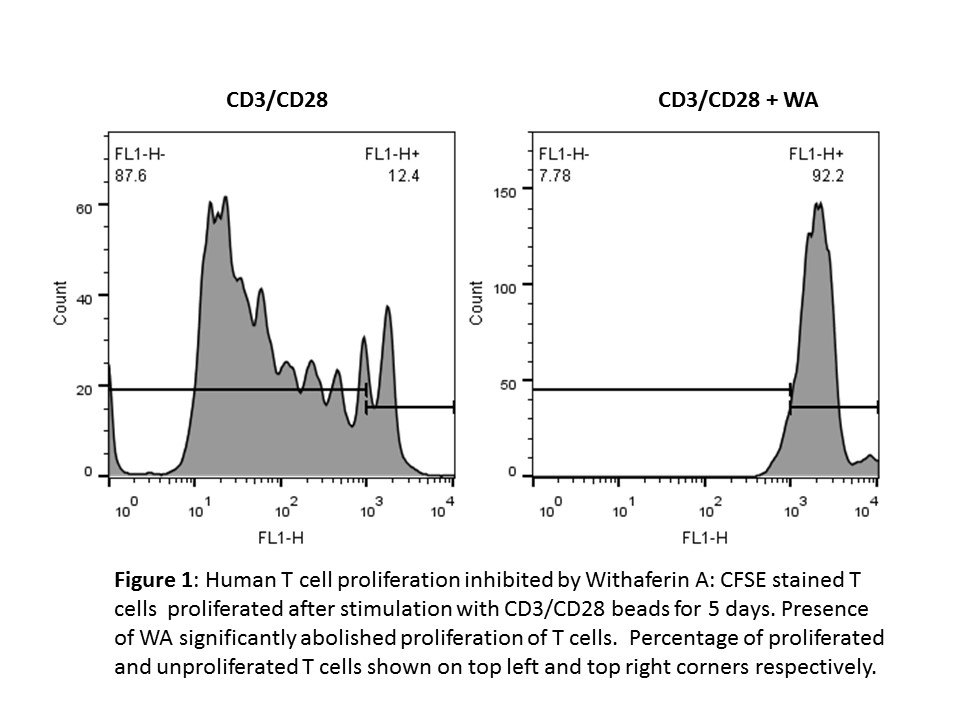 Further analysis of intracellular cytokines revealed for reduced percentage of CD4+IFNy+ (35% vs 25%; P<0.05) and CD8+IFNy+ (45% vs. 15%, P<0.05) cells.
Further analysis of intracellular cytokines revealed for reduced percentage of CD4+IFNy+ (35% vs 25%; P<0.05) and CD8+IFNy+ (45% vs. 15%, P<0.05) cells.
Conclusion
The low dose of WA showed no toxic effect on islets viability and function demonstrating its safety. T cell activation was significantly inhibited by WA and Th1 cell proportion was reduced. The use of WA has great potential as an immunosuppressive agent in islet transplantation.
CITATION INFORMATION: Kanak M, Shindo Y, Levy M, Naziruddin B. Immunosuppressive Ability of NFkB Inhibitor: Withaferin A. Am J Transplant. 2017;17 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Kanak M, Shindo Y, Levy M, Naziruddin B. Immunosuppressive Ability of NFkB Inhibitor: Withaferin A. [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2017; 17 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/immunosuppressive-ability-of-nfkb-inhibitor-withaferin-a/. Accessed February 22, 2026.« Back to 2017 American Transplant Congress
