Immune Tolerance Monitoring in Renal Allograft Tolerance Induced by Transient Mixed Chimerism in Nonhuman Primates and Humans.
Center for Transplantation Science, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, MA.
Meeting: 2016 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: D88
Keywords: Kidney transplantation, Mixed chimerism, Monitoring, Tolerance
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session D: Clinical Science: Tolerance: Clinical Studies
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Tuesday, June 14, 2016
Session Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Location: Halls C&D
Background: Successful induction of allograft tolerance in MHC-mismatched kidney transplantation has been achieved after induction of transient chimerism in both nonhuman primates (NHP) and humans. However, development of a reliable assay to monitor tolerance is critically important to safely taper immunosuppression.
Method: Six NHP and four human recipients of combined kidney and bone marrow transplantation (CKBMT) who achieved long-term renal allograft survival without immunosuppression were studied. Differential T-cell responses were evaluated by CFSE-MLR co-stained for CD4, CD8 and Foxp3.
Results: NHP tolerant recipients evaluated at 2.1±0.9 years after transplantation showed donor-specific CD8+ T cell hyporesponsiveness but displayed vigorous anti-donor CD4+ T cell proliferation. Interestingly, among these proliferated CD4+ cells, significantly higher Foxp3+ cell proliferation was observed against donor, compared with third party stimulators (Fig. A). In contrast, consistently high anti-donor CD8+ and CD4+ T cell responses with limited Treg expansion were observed in rejectors (data not shown). In humans, although assays were performed at markedly later time points (4.7±1.8 years), tolerant patients displayed much greater loss of anti-donor CD8+ and CD4+ T cells responses. However, unlike NHPs, Treg expansion was not significant and CD4+ T cell responses were limited (Fig. B). Finally, we prospectively monitored T cell responses in one recent human CKBMT recipient who achieved renal allograft tolerance. Although anti-donor CD8+ T cell responses gradually disappeared, significant CD4+ responses and Treg expansion were observed at day 325 as observed in most NHP recipients. However, anti-donor Treg responses eventually disappeared by day 727, as observed in other human tolerant recipients (Fig. C).
Conclusion: Regulatory mechanisms were suggested in NHPs at 2 years. More robust loss of anti-donor T cell responses was observed in human tolerant recipients, although these recipients were tested at later time points than the NHP.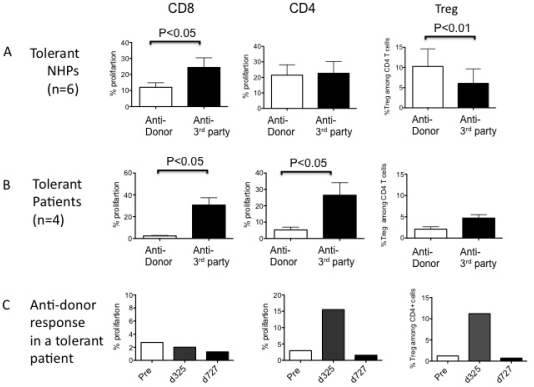
CITATION INFORMATION: Hotta K, Oura T, Crisalli K, Sachs D, Cosim B, Kawai T. Immune Tolerance Monitoring in Renal Allograft Tolerance Induced by Transient Mixed Chimerism in Nonhuman Primates and Humans. Am J Transplant. 2016;16 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Hotta K, Oura T, Crisalli K, Sachs D, Cosim B, Kawai T. Immune Tolerance Monitoring in Renal Allograft Tolerance Induced by Transient Mixed Chimerism in Nonhuman Primates and Humans. [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2016; 16 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/immune-tolerance-monitoring-in-renal-allograft-tolerance-induced-by-transient-mixed-chimerism-in-nonhuman-primates-and-humans/. Accessed March 3, 2026.« Back to 2016 American Transplant Congress
