Identification of Molecular Markers for Liver Cirrhosis by Single-nucleus Rna Sequencing
1Surgery, James D Eason Transplat Institute, Memphis, TN, 2Surgery, Center for Biomedical Informatics, Memphis, TN, 3Surgery, Institute for Genome Sciences, School of Medicine, Baltimore, MD, 4Surgery, Program in Transplantation University of Maryland, Baltimore, MD, 5Surgery, Division of Surgical Science University of Maryland, Baltimore, MD
Meeting: 2021 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 1089
Keywords: Genomic markers, Liver, Liver cirrhosis, Obesity
Topic: Clinical Science » Liver » Liver: Cirrhosis - Portal Hypertension and Other Complications
Session Information
Session Name: Liver: Cirrhosis - Portal Hypertension and Other Complications?
Session Type: Poster Abstract
Session Date & Time: None. Available on demand.
Location: Virtual
*Purpose: Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is characterized by metabolic syndrome and the accumulation of fat in the liver cells (hepatocytes) leading to inflammation and potentially cirrhosis. Hereby, we assessed the use of single-cell/nucleus genomics to identify the molecular and cellular mechanisms of fibrosis/cirrhosis caused by NASH at single cell resolution.
*Methods: Single cell or nucleus sequencing identifies the genomic and transcriptomics information from individual cells using next-generation sequencing (NGS) platform. We isolated single nuclei from fresh-frozen (FF) samples including normal, fatty, fibrotic and cirrhotic liver tissues (NASH cirrhosis). We used 10x Genomics Chromium Platform and generated data in their Cell-Ranger Pipeline. Unsupervised “Seurat” package was used to generate cluster and cell identification.
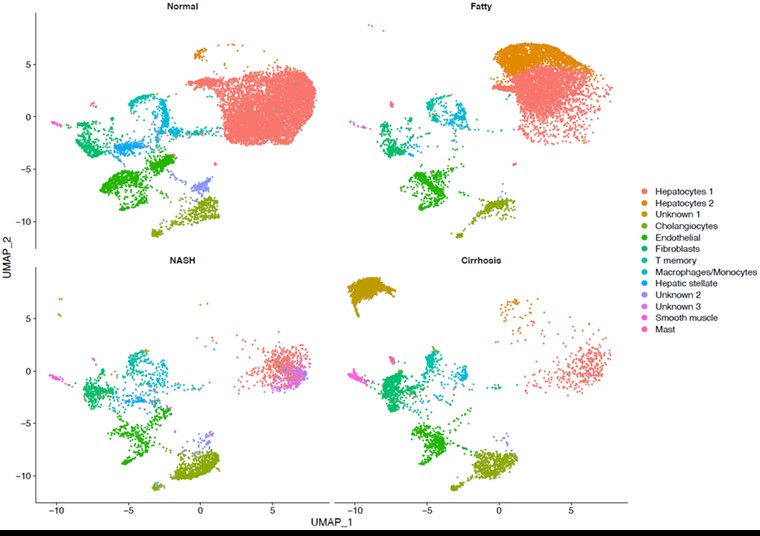
*Results: We identified two different hepatocyte clusters in fatty liver samples. Furthermore we observed a significant decrease of healthy number of hepatocytes in NASH and cirrhotic samples due to the replacement of epithelial cells with fibrotic cell. Replacement of those cells has been correlated with the elevated level of CACNA1C, CFTR, COL4A1, and COL4A2. Interestingly, there was a distinct class of unknown cells in cirrhotic livers that deserve further investigation (Fig 1).
*Conclusions: In this study, we identified different cell/nucleus clustering on the liver sample type, ranging from normal to cirrhotic, highlighting the cellular shift occurring during different stages of liver disease leading to NAFLD-Cirrhosis
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Kuscu C, Kuscu C, Akram M, Shetty A, Maluf DG, Eason J, Mas V. Identification of Molecular Markers for Liver Cirrhosis by Single-nucleus Rna Sequencing [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2021; 21 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/identification-of-molecular-markers-for-liver-cirrhosis-by-single-nucleus-rna-sequencing/. Accessed February 28, 2026.« Back to 2021 American Transplant Congress