Identification and Comprehensive Validation of Prognostic Genes After Ischemic and Reperfusion Injury Across Different Donor Types in Renal Transplantation
Department of Urology, Beijing Chao-Yang Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing, China
Meeting: 2021 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: LB 38
Keywords: Graft survival, Ischemia, Kidney transplantation, N/A
Topic: Basic Science » Ischemia Reperfusion & Organ Rehabilitation
Session Information
Session Name: Ischemia Reperfusion & Organ Rehabilitation
Session Type: Poster Abstract
Session Date & Time: None. Available on demand.
Location: Virtual
*Purpose: Ischemic and reperfusion injury (IRI) remains an inevitable and major challenge for renal transplant patients. The current study aims to obtain overall insights into potential mechanisms and seek prognostic molecular as biomarkers and potential therapeutic targets of IRI for transplantation patients.
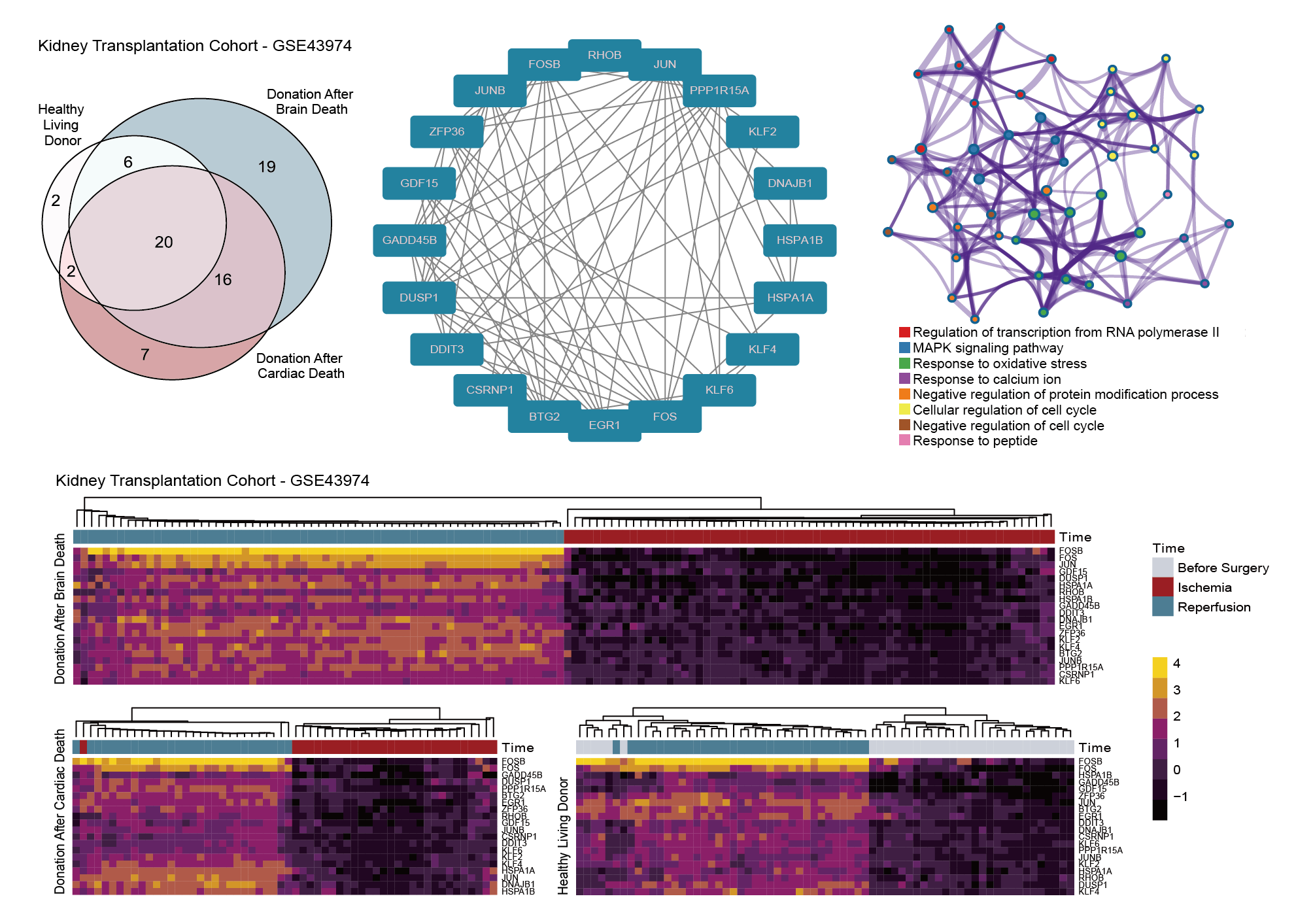
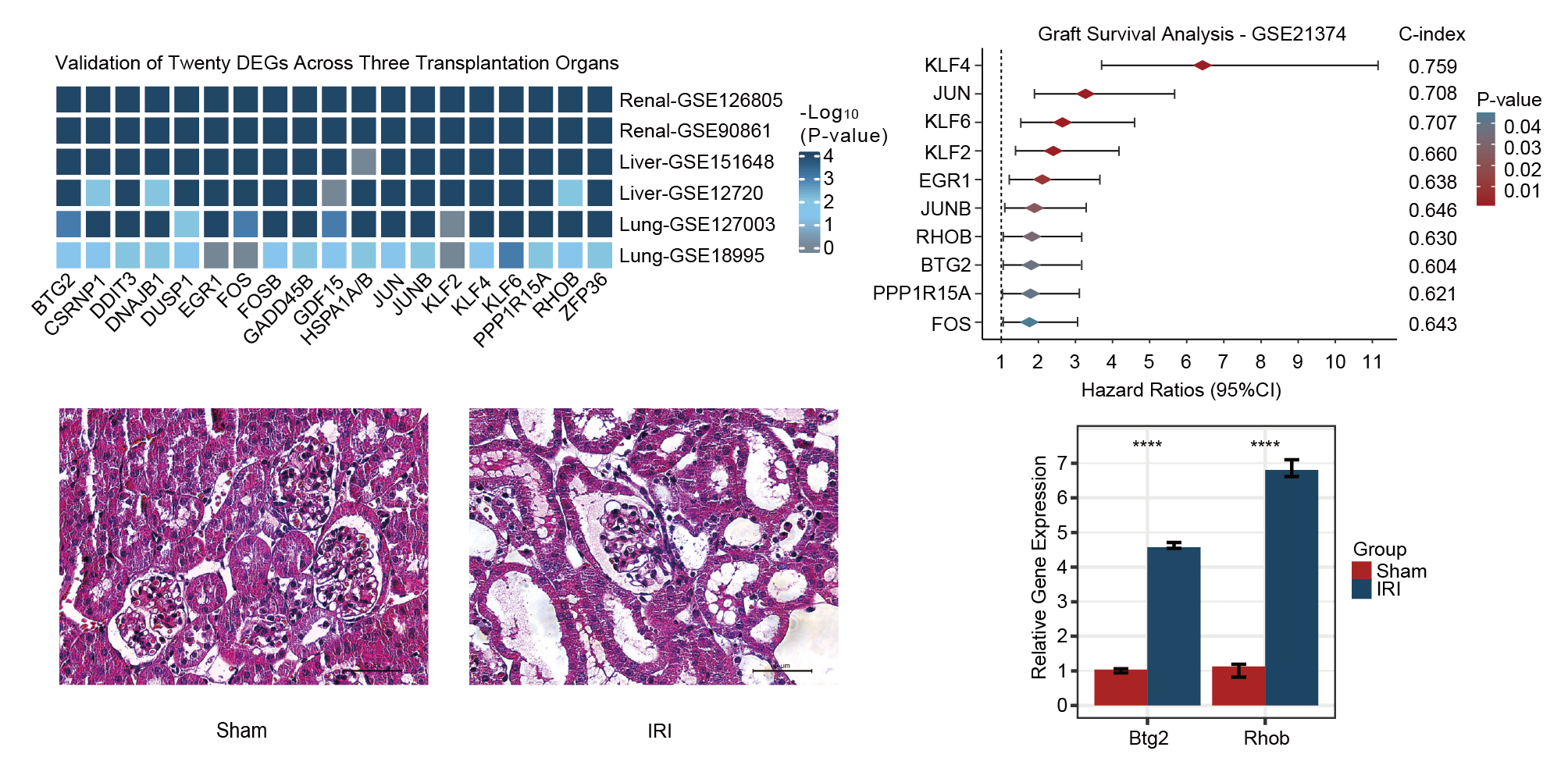
*Methods: After systematically screened the database, we collected gene expression profiles of over 1000 samples after IRI from eight independent cohorts in the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database. Differentially expressed genes (DEGs) of IRI across different donor types (living donor, cardiac death and brain death) were identified in the discovery cohort of renal transplantation and validated in six independent cohorts including renal, liver and lung transplantations. Additionally, protein-protein interaction (PPI) network and functional enrichment analyses were performed. Then, the above DEGs were further applied to graft survival analysis in a renal transplantation cohort to investigate their prognostic value. Finally, two novel genes of renal IRI were verified in mice renal IRI model using quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR).
*Results: Twenty DEGs upregulated after IRI across different donor types and multiple organs were successfully identified and validated. The PPI network showed that these DEGs were strongly connected and enriched in multiple biological processes about transcription and cell cycle. Among DEGs, upregulation of ten genes was found to be associated with poor long-term kidney allograft survival. Finally, two novel prognostic genes were successfully verified by qRT-PCR in the mice renal IRI model.
*Conclusions: We successfully identified and validated twenty IRI-associated genes throughout different donor types and transplant organs. Besides, ten of them were significantly associated with renal graft survival, which offered promising and novel therapeutic targets for transplantation patients to treat IRI.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Zhang D, Wang Y, Wang Y, Hu X. Identification and Comprehensive Validation of Prognostic Genes After Ischemic and Reperfusion Injury Across Different Donor Types in Renal Transplantation [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2021; 21 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/identification-and-comprehensive-validation-of-prognostic-genes-after-ischemic-and-reperfusion-injury-across-different-donor-types-in-renal-transplantation/. Accessed March 9, 2026.« Back to 2021 American Transplant Congress