Heart Transplant Outcomes in Patients Who Receive Hepatitis B Virus-Positive Donor Hearts: A UNOS Registry Analysis
1Keck Medicine of USC, Los Angeles, CA, 2Keck Medicine of USC, South Pasadena, CA, 3Harbor-UCLA Medical Center, Los Angeles, CA
Meeting: 2020 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 180
Keywords: Heart, Heart/lung transplantation
Session Information
Session Name: Heart Transplantation: It's All About the Outcomes
Session Type: Oral Abstract Session
Date: Saturday, May 30, 2020
Session Time: 3:15pm-4:45pm
 Presentation Time: 3:27pm-3:39pm
Presentation Time: 3:27pm-3:39pm
Location: Virtual
*Purpose: Hepatitis B infection in post-transplant patients posed a challenge in the setting of immunosuppression. However, the advent of anti-viral therapy for HBV has made it possible to expand the donor pool for heart transplant (HT) recipients. Little is known in long term outcomes of recipients who receive HBV+ donor hearts. We sought to characterize and assess HT outcomes in recipients who received from HBV+ donors.
*Methods: The UNOS registry was queried and identified 1,141 patients who received heart transplants from hepatitis B core Ab+ donors and 53,192 patients who received heart transplants from hepatitis B core Ab- donors. Multivariate Cox proportional hazard regression analysis was adjusted for age, sex, diabetes, ethnicity, ischemic time, dialysis, life support, waitlist time, and HLA mismatch. Kaplan-Meier survival was censored at 12y.
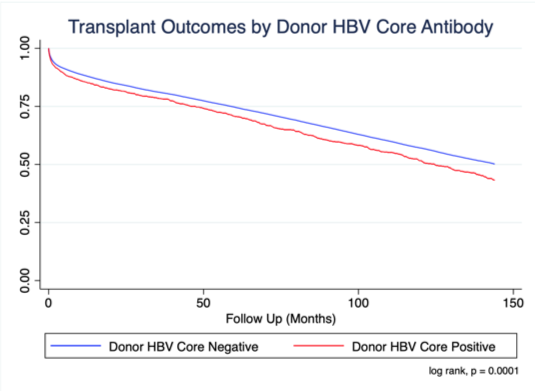
*Results: There were 1141 patients in the donor core HBV+ cohort, and 53,192 patients in the donor core HBV- cohort. The HBV+ cohort was younger (p<0.001) with increased IABP use (p=0.004) and longer ischemic times (p<0.001). No difference was observed in waiting time, diabetes, dialysis, VAD and ventilator use. The HBV+ donor cohort had unadjusted hazard ratio (HR) for all-cause mortality of 1.20 (CI 1.10-1.31, p<0.001). Multivariate analysis yielded a HR of 1.18 (CI 1.07-1.30, p=0.001). Survival in the HBV- donor cohort at 1, 5 and 10 years post-HT was 88, 74, and 57%, respectively; in the HBV+ donor cohort, survival at 1, 5 and 10 years post-HT was 85, 71, and 52%, respectively (log rank, p=0.0001).
*Conclusions: This is the largest reported series of post-HT HBV+ donor transplant outcomes. Survival was reduced in the HBV+ donor cohort compared to the HBV- donor cohort. Further study is warranted to better understand the factors that contribute to this disparity in outcomes.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Genyk P, Yang K, Chand R, Depasquale E. Heart Transplant Outcomes in Patients Who Receive Hepatitis B Virus-Positive Donor Hearts: A UNOS Registry Analysis [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2020; 20 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/heart-transplant-outcomes-in-patients-who-receive-hepatitis-b-virus-positive-donor-hearts-a-unos-registry-analysis/. Accessed March 12, 2026.« Back to 2020 American Transplant Congress