Graft Failure in Recurrent IgA Nephropathy Following Living Kidney Transplantation: Predictive Factors Analysis of 102 Biopsies
Organ Transplant Unit, The First Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou, Guangdong, China.
Meeting: 2018 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: B179
Keywords: Biopsy, Graft failure, Kidney transplantation, Recurrence
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session B: Kidney Living Donor: Long Term Outcomes
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Sunday, June 3, 2018
Session Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Location: Hall 4EF
Aim To investigate the predictive factors related to graft failure in recurrentIgA nephropathy (IgAN) following living kidney transplantation. Methods We identified a series of 102 biopsies diagnosed as recurrent IgAN following living kidney transplantation from July 2003 to October 2017 at our centre. All biopsies were evaluated according to the Lee's classification and the 2009 Oxford classification.The clinical and pathological characteristics at the time of biopsy, and the outcomes were retrospectively analyses. Results The 4-year graft cumulative survival rate after be diagnosed as recurrent IgAN by biopsy is 72.2% (a mean ± SD follow up of 3.4 ± 1.9 years). 64 cases (62.7%) recurred within 5 years after transplantation (Group 1) and the other 38 cases (37.2%) recurred more than 5 years (Group 2) 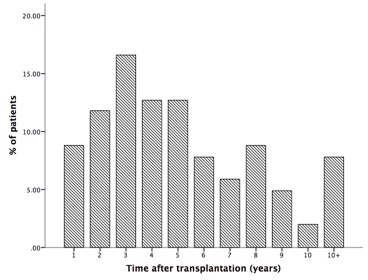 ; the Lee's classification (p = 0.01), the degree of endocapillary hypercellularity (E) in Oxford classification (p = 0.03) and the mesangial C1q deposition (p = 0.02) was detected higher in Group 2 versus in Group 1. At multivariate analysis, 24-h urinary protein level and the increased serum creatinine (sCr) ( > 50% of the sCr baseline) at the time of biopsy are the independent predictive factors related to graft failure in recurrent IgAN, the hazard ratio (HR) for 24-h urinary protein level > 2g is 5.1 (confidence interval 1.5-17.1), for the increased sCr is 6.4 (confidence interval 2.2-18.5). Conclusion IgAN recurred frequently within 5 years after transplantation, the histopathological injury occurred earlier than clinical features in late recurrent IgAN; heavy proteinuria (24-h urinary protein level > 2g),an increased sCr as the initial symptoms, a high lesions(grade IV or V) of Lee's classification and the mesangial C1q deposition indicate high risk of graft failure.
; the Lee's classification (p = 0.01), the degree of endocapillary hypercellularity (E) in Oxford classification (p = 0.03) and the mesangial C1q deposition (p = 0.02) was detected higher in Group 2 versus in Group 1. At multivariate analysis, 24-h urinary protein level and the increased serum creatinine (sCr) ( > 50% of the sCr baseline) at the time of biopsy are the independent predictive factors related to graft failure in recurrent IgAN, the hazard ratio (HR) for 24-h urinary protein level > 2g is 5.1 (confidence interval 1.5-17.1), for the increased sCr is 6.4 (confidence interval 2.2-18.5). Conclusion IgAN recurred frequently within 5 years after transplantation, the histopathological injury occurred earlier than clinical features in late recurrent IgAN; heavy proteinuria (24-h urinary protein level > 2g),an increased sCr as the initial symptoms, a high lesions(grade IV or V) of Lee's classification and the mesangial C1q deposition indicate high risk of graft failure.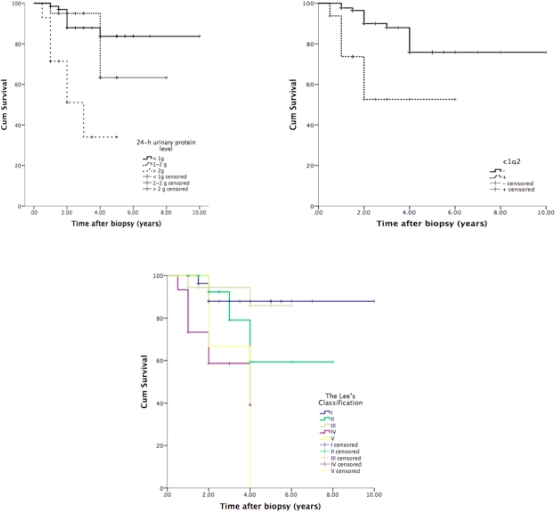
CITATION INFORMATION: Zhang J., Qiu J., Chen G., Wang C., Chen L. Graft Failure in Recurrent IgA Nephropathy Following Living Kidney Transplantation: Predictive Factors Analysis of 102 Biopsies Am J Transplant. 2017;17 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Zhang J, Qiu J, Chen G, Wang C, Chen L. Graft Failure in Recurrent IgA Nephropathy Following Living Kidney Transplantation: Predictive Factors Analysis of 102 Biopsies [abstract]. https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/graft-failure-in-recurrent-iga-nephropathy-following-living-kidney-transplantation-predictive-factors-analysis-of-102-biopsies/. Accessed March 12, 2026.« Back to 2018 American Transplant Congress
