Global Expression Profiles of miRNA and Expression Patterns and Localization of the miR-21 in One-Hour Biopsy Specimens of Human Kidney Tansplantation from Donors after Cardiac Death
1Urology, Fujita-Health University, Toyoake/Aichi, Japan
2Transplant Surgery, Fujita-Health University, Toyoake/Aichi, Japan.
Meeting: 2018 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: A26
Keywords: Biopsy, Donors, Kidney transplantation, non-heart-beating
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session A: Biomarkers, Immune Monitoring and Outcomes
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Saturday, June 2, 2018
Session Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
 Presentation Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
Presentation Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
Location: Hall 4EF
Because of the global shortage of renal grafts, kidney transplantation (KTx) from donors after cardiac death (DCDs) is an alternative way of obtaining KTx from brain-dead donors. Although the prognosis of DCD KTx is gradually improving, the graft often suffers from a delayed graft function (DGF); as such, managing DGF is essential for post-KTx patient care. In an attempt to characterize the etiology of DGF, genome-wide gene expression profiling of miRNA was performed using renal biopsy samples obtained at 1 h after KTx from DCDs (n=18), and the data were compared with those of KTx from living donors (LDs) (n=18). A SurePrintG3 Human miRNA Microarray kit (Release 16.0; Agilent Technologies) was used, and a total of 2,549 miRNA genes were analyzed. After performing Z-scoring of the miRNA expression,a total of 20 genes showed significantly different expression profiles between the 2 groups (p<0.00001 by Welch's t-test test). Seventeen genes were up-regulated, while three were down-regulated in the DCD kidneys. The validation of the microarray experiments was performed by real-time polymerase chain reaction. The miR-21, miR-514 and miR-509-3p genes were up-regulated, and miR-378 was down-regulated significantly in the DCD group relative to the LD group (p<0.005). We also performed in situ hybridization while focusing on the expression patterns and localization of the miR-21 gene. The miR-21 expression was much higher in the renal tubule cytoplasm, in addition to the nucleus of tubules and glomeruli in the DCD kidneys than in the LD kidneys and kidneys from brain dead donors. 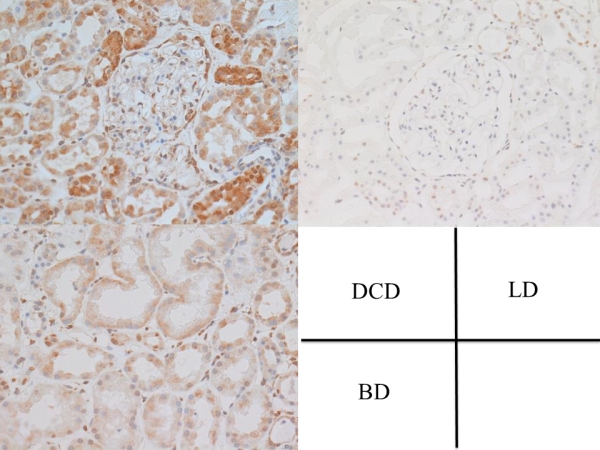 miR-21 is a recently identified, typical miRNA that functions as a regulator and is known to be involved in apoptosis as well as the inflammatory and fibrotic signaling pathways in acute kidney injury. These data suggest good miRNA candidates for biomarkers that may be useful for controlling DGF.
miR-21 is a recently identified, typical miRNA that functions as a regulator and is known to be involved in apoptosis as well as the inflammatory and fibrotic signaling pathways in acute kidney injury. These data suggest good miRNA candidates for biomarkers that may be useful for controlling DGF.
CITATION INFORMATION: Kusaka M., Fukami N., Sasaki H., Kawai A., Kenmochi T., Ito T., Shiroki R., Hoshinaga K. Global Expression Profiles of miRNA and Expression Patterns and Localization of the miR-21 in One-Hour Biopsy Specimens of Human Kidney Tansplantation from Donors after Cardiac Death Am J Transplant. 2017;17 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Kusaka M, Fukami N, Sasaki H, Kawai A, Kenmochi T, Ito T, Shiroki R, Hoshinaga K. Global Expression Profiles of miRNA and Expression Patterns and Localization of the miR-21 in One-Hour Biopsy Specimens of Human Kidney Tansplantation from Donors after Cardiac Death [abstract]. https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/global-expression-profiles-of-mirna-and-expression-patterns-and-localization-of-the-mir-21-in-one-hour-biopsy-specimens-of-human-kidney-tansplantation-from-donors-after-cardiac-death/. Accessed March 10, 2026.« Back to 2018 American Transplant Congress
