Generation of Calculated Panel-Reactive Antibody Values Using a Reference Panel of Bone Marrow Donors
1Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, CA
2Tulane University School of Medicine, New Orleans, LA
3Baylor Scott & White, Temple, TX
4National Marrow Donor Program, Minneapolis, MN.
Meeting: 2018 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: B119
Keywords: Allocation, Histocompatibility antigens, HLA antibodies, Panel reactive antibodies
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session B: Kidney Deceased Donor Allocation
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Sunday, June 3, 2018
Session Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Location: Hall 4EF
Introduction: Calculated panel-reactive antibody (CPRA) is the official metric of sensitization used by the United Network for Organ Sharing (UNOS) for kidney allocation. The reference panel for CPRA is derived from low-resolution HLA typing of 14,282 kidney donors. This panel may be undersized, especially for minority ethnic groups. We sought to compare CPRA values generated from the UNOS reference panel to values generated from a reference panel derived from high-resolution HLA typing of 6.6 million bone marrow registry donors.
Methods: A data set of high-resolution HLA-A~B~C~DQB1~DRB1 haplotype frequencies were obtained from the National Marrow Donor Program (NMDP). Frequencies for high-resolution HLA alleles were summed to UNOS antigen equivalents. CPRA was calculated using both NMDP haplotype frequencies (CPRANMDP) and standard UNOS frequencies (CPRAUNOS) for a cohort of 17,053 sensitized kidney transplant candidates added to the waiting list between 2009-10-01 and 2014-12-03. The panels were compared using a Cox proportional hazard model with CPRA as a time-varying predictor for time to transplant.
Results: Antigen frequencies were similar between the NMDP and UNOS panels, but linkage disequilibrium between HLA-C or -DQB1 and other HLA loci was lower in the UNOS panel. As a result, there were 6,200 candidates (36%) whose CPRANMDP was ≥ 1% different than their CPRAUNOS. For candidates with CPRA of ≥ 80%, CPRANMDP (p<0.001) but not CPRAUNOS (p=0.06) predicted a decreased likelihood of kidney transplant. Applying the current priority points in the UNOS kidney allocation system to this cohort, 3,203 candidates would move point groups based on CPRANMDP as compared to CPRAUNOS. 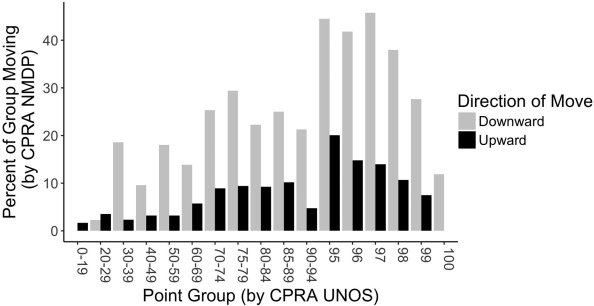
Conclusions: Using NMDP haplotype frequencies as the reference panel for generating CPRA values is feasible and may improve equity in organ allocation by providing a more accurate estimate of haplotype frequencies in the population.
CITATION INFORMATION: Kransdorf E., Gragert L., Pando M., Kaur N., Patel J., Kim I., Zhang X., Maiers M., Kobashigawa J. Generation of Calculated Panel-Reactive Antibody Values Using a Reference Panel of Bone Marrow Donors Am J Transplant. 2017;17 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Kransdorf E, Gragert L, Pando M, Kaur N, Patel J, Kim I, Zhang X, Maiers M, Kobashigawa J. Generation of Calculated Panel-Reactive Antibody Values Using a Reference Panel of Bone Marrow Donors [abstract]. https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/generation-of-calculated-panel-reactive-antibody-values-using-a-reference-panel-of-bone-marrow-donors/. Accessed March 14, 2026.« Back to 2018 American Transplant Congress
