Fibrinolysis Shutdown Subtype of Early Allograft Dysfunction Represents the Predominant Cohort of Patients with Graft Failure Following Liver Transplantation
1University of Colorado, Aurora, CO, 2Univeristy of Colorado, Aurora, CO, 3Childrens Hospital Colorado, Aurora, CO, 4University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus, Aurora, CO
Meeting: 2022 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 521
Keywords: Endothelial activation, Graft failure, Liver transplantation, Surgery
Topic: Clinical Science » Liver » 51 - Liver: Retransplantation and Other Complications
Session Information
Session Name: Retransplantation and Other Complications
Session Type: Rapid Fire Oral Abstract
Date: Tuesday, June 7, 2022
Session Time: 5:30pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 6:10pm-6:20pm
Presentation Time: 6:10pm-6:20pm
Location: Hynes Room 313
*Purpose: Early allograft dysfunction (EAD) is associated with an increased rate of graft failure in liver transplantation (LT), but a mechanism remains unclear. Recent experience with COVID-19 has identified that microvascular clots related to fibrinolysis shutdown [ SD (lack of ability to break down clot)] drives organ failure, which can be treated with tissue plasminogen activator (tPA). It remains unclear how SD interacts with EAD, and if it may be associated with a worse outcome in LT. We hypothesize that fibrinolysis shutdown with EAD would be an unfavorable combination with an increased risk of graft failure compared to patients with EAD without SD.
*Methods: Adult liver transplant recipients underwent thrombelastography (TEG) on post-operative day-1 to assess for fibrinolysis shutdown. Fibrinolysis activity was quantified by the amount of clot strength lost from peak clot strength in 30-minutes (LY30) in the presence of tPA (75ng/ml). SD was defined as an LY30 of 0%, indicative or no fibrinolytic activity in the presence of a fibrinolytic activator (median LY30 = 8% in healthy volunteers). EAD was defined on laboratory measurements defined and validated by Olthoff et al. Graft survival analysis was conducted with logistic regression analysis when controlling for recipient severity of liver disease (MELD) and graft quality (donor risk index). Survival time was assessed with Kaplan Meier curve.
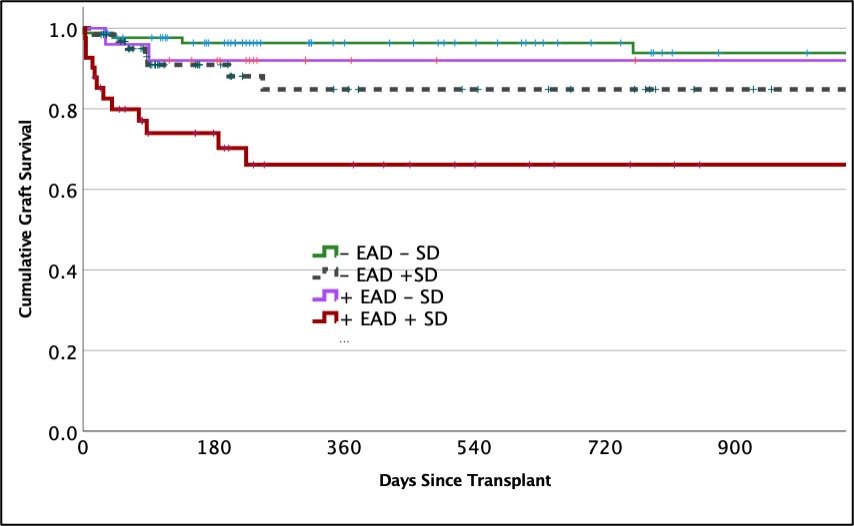
*Results: 230 liver transplant patient recipients with a median laboratory MELD of 23 were included in the analysis. Graft failure rate was 13% with a median follow up time of 345 days. EAD occurred in 31%, and SD was present in 45%. The combination of EAD and SD was associated with a 46% graft loss rate which was significantly higher than EAD without SD (8% p<0.001). When controlling for MELD, and donor risk index, EAD (OR 3.3 95%CI 1.3-8.4 p=0.014) and fibrinolysis shutdown (OR 2.9 95%CI 1.1-7.9 p=0.034) were independent predictors of graft failure. Graft survival times were significantly different when patients were stratified by EAD and SD (figure p<0.001).
*Conclusions: The combination of EAD and SD bodes poor prognosis following liver transplantation. The stark difference in survival warrants further investigation if activation of the fibrinolytic system can safely improve graft survival time in LT recipients with EAD without the risk of excessive bleeding.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Moore HB, Nydam TL, Adams M, Ferrell T, Rodriguez I, Yoeli D, Choudhury R, Pomposelli J, Pomfret EA. Fibrinolysis Shutdown Subtype of Early Allograft Dysfunction Represents the Predominant Cohort of Patients with Graft Failure Following Liver Transplantation [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2022; 22 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/fibrinolysis-shutdown-subtype-of-early-allograft-dysfunction-represents-the-predominant-cohort-of-patients-with-graft-failure-following-liver-transplantation/. Accessed March 9, 2026.« Back to 2022 American Transplant Congress