Factors Influencing Cost Among Kidney, Liver, and Heart Transplant Patients in a Private Payer Setting
1Optum, Minneapolis
2Saint Louis University, St. Louis.
Meeting: 2015 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: A232
Keywords: Economics, Heart/lung transplantation, Kidney transplantation, Liver transplantation
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session A: Non Organ Specific, Economics, Public Policy, Allocation, Ethics
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Saturday, May 2, 2015
Session Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
 Presentation Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
Presentation Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
Location: Exhibit Hall E
The factors influencing cost in solid organ transplantation have been evaluated by many individual centers, as well as nationally for Medicare patients. However, the majority of transplant recipients are commercially insured and there are few published studies for the commercially insured population. There is a need to understand risk factors that impact cost from a private payer perspective, to inform value-based management policies and strategies by payers.
Methods: All subjects underwent transplant evaluation and were privately insured via either a commercial or Medicare Advantage plan. We estimated marginal effects on total medical expenses from evaluation through 1-year post-transplant with robust regression models, risk adjusted by recipient demographics, region, and comorbidity.
Results: 16,187 patients were evaluated between January 2010 and April 2014 with follow up through September 2014. Cases included 9,809 kidney, 4,767 liver and 1,611 heart patients from 145 hospitals with 455 transplant programs. Average total cost from evaluation to 1-year post-transplant were kidney ($264k), liver ($419k) and heart ($726k). Factors contributing to increased cost in this population included graft failure, transplant from hospital for liver and heart, and several early post-transplant complications such as organ dysfunction, hemorrhage for kidney, pneumonia for kidney and liver, urinary tract infection and dialysis for liver and heart. The proportion of each factor attributing to the total cost is listed in the Table.
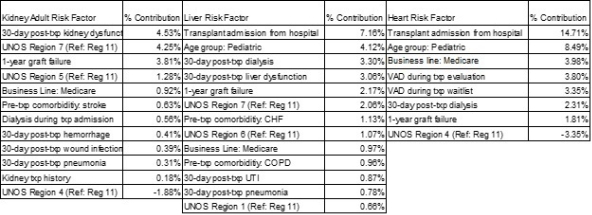
Conclusion: This study identified several key factors of interest that are significantly associated with cost in a commercially insured solid organ transplant population. Such factors may be prime targets for cost containment and quality assessment process improvement initiatives. It is also possible that these factors, combined with additional factors that impact important clinical outcomes, may form the basis for multi-factorial transplant program performance assessments.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Bannister W, Wu C, Schnitzler M, Irwin F, Bonagura A. Factors Influencing Cost Among Kidney, Liver, and Heart Transplant Patients in a Private Payer Setting [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2015; 15 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/factors-influencing-cost-among-kidney-liver-and-heart-transplant-patients-in-a-private-payer-setting/. Accessed March 14, 2026.« Back to 2015 American Transplant Congress
