Extracellular Vesicles Derived from Huc-MSCs Alleviate Rat Hepatic Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury by Suppressing Oxidative Stress and Neutrophil Inflammatory Response
1Department of Hepatic Surgery and Liver Transplantation Center of the Third Affiliated Hospital, Organ Transplantation Institute, Guangzhou, Guangdong, China
2Guangdong Key Laboratory of Liver Disease Research, Key Laboratory of Liver Disease Biotherapy and Translational Medicine of Guangdong Higher Education Institutes, the Third Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou, Guangdong, .
Meeting: 2018 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: D252
Keywords: Neutrophils, Oxidant stress, Stem cells
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session D: Stem Cell, Cellular Therapies and Regenerative Medicine
Session Type: Poster Sessoin
Date: Tuesday, June 5, 2018
Session Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Location: Hall 4EF
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) have been reported possessing therapeutic effects on immunoregulation, tissue repair and regeneration from bench to bedside. Extracellular vesicles (EVs) derived from MSCs could contribute to these progressions via paracrine function, which are considered as a replacement of stem cell-based therapies. However, the efficacy and underlying mechanisms of EVs-based treatment in hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury (IRI) remain unclear. Here, we demonstrated that human umbilical cord MSC-derived extracellular vesicles (huc-MSC-EVs) could protect against IRI-induced hepatic apoptosis through reducing the infiltration of neutrophils into inflammation microenvironment of hepatic tissue in vivo.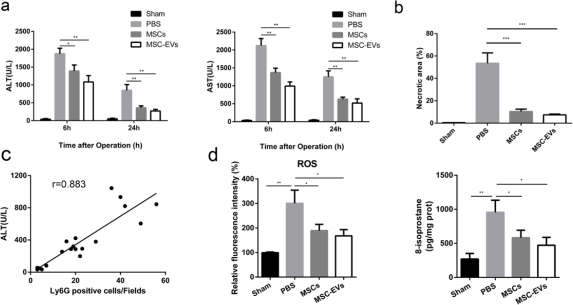 Meanwhile, huc-MSC-EVs reduced respiratory burst of neutrophils as well as prevented hepatocytes from oxidative stress-induced cell death in vitro. Furthermore, we identified that MnSOD, an antioxidant enzyme, was rich in huc-MSC-EVs and reduced oxidative stress. Knockdown of MnSOD in huc-MSCs decreased the expression of MnSOD in huc-MSC-EVs and attenuated the antioxidant and anti-apoptosis of capacities of huc-MSC-EVs.
Meanwhile, huc-MSC-EVs reduced respiratory burst of neutrophils as well as prevented hepatocytes from oxidative stress-induced cell death in vitro. Furthermore, we identified that MnSOD, an antioxidant enzyme, was rich in huc-MSC-EVs and reduced oxidative stress. Knockdown of MnSOD in huc-MSCs decreased the expression of MnSOD in huc-MSC-EVs and attenuated the antioxidant and anti-apoptosis of capacities of huc-MSC-EVs.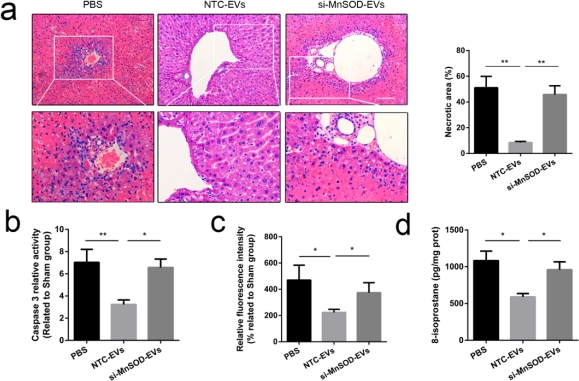 In conclusion, these findings provide new clues to reveal the therapeutic effects on hepatic IRI and evaluate the pre-clinical application of of huc-MSC-EVs.
In conclusion, these findings provide new clues to reveal the therapeutic effects on hepatic IRI and evaluate the pre-clinical application of of huc-MSC-EVs.
CITATION INFORMATION: Yao J., Cai J., Zheng J., Chen L., Zhang Y., Yang Y. Extracellular Vesicles Derived from Huc-MSCs Alleviate Rat Hepatic Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury by Suppressing Oxidative Stress and Neutrophil Inflammatory Response Am J Transplant. 2017;17 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Yao J, Cai J, Zheng J, Chen L, Zhang Y, Yang Y. Extracellular Vesicles Derived from Huc-MSCs Alleviate Rat Hepatic Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury by Suppressing Oxidative Stress and Neutrophil Inflammatory Response [abstract]. https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/extracellular-vesicles-derived-from-huc-mscs-alleviate-rat-hepatic-ischemia-reperfusion-injury-by-suppressing-oxidative-stress-and-neutrophil-inflammatory-response/. Accessed March 10, 2026.« Back to 2018 American Transplant Congress
