Estrogen Mediated Protection in Renal Ischemia Reperfusion Injury (IRI) is Extrinsic to the Kidney
1Surgery, Perelman School of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA, 2Pathology, Children's Hospital of Philadelphia, Philadelphia, PA
Meeting: 2019 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: B22
Keywords: Ischemia, Kidney, Kidney transplantation, Mice
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session B: Ischemia Reperfusion & Organ Rehabilition
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Sunday, June 2, 2019
Session Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Location: Hall C & D
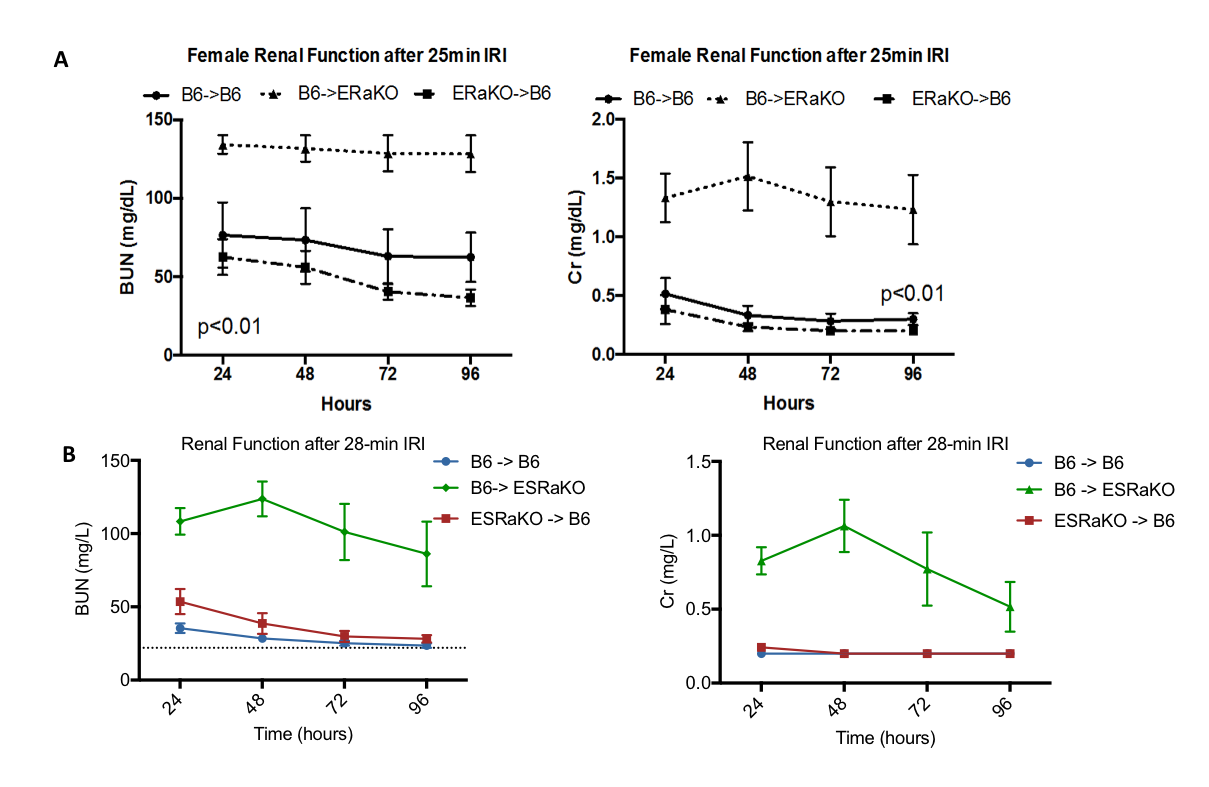
*Purpose: IRI causes morbidity in renal transplantation and other surgical scenarios. A better understanding of the molecular mechanisms of IRI is required so that strategies for prevention and treatment can be developed. We have shown females have greater IRI tolerance than males, that supplemental estrogen ameliorates injury after IRI, and this effect is modulated by the estrogen receptor alpha (ER-a). Whether these effects are intrinsic to the kidney tissue or are mediated by immune factors is of interest in developing targeted therapies.
*Methods: Murine renal transplantation with native nephrectomy, followed by 2 weeks of recovery and 25 minutes of warm unilateral renal IRI under strict temperature control were performed in wild-type (B6) and ER-a knockout female mice (ERaKO), using B6->B6, B6->ERaKO, and ERaKO->B6. In a separate experiment, B6 and ERaKO female mice underwent irradiation, followed by bone marrow transplantation (BMT) with either ERaKO marrow or B6 marrow, supplemental estrogen administration, and subsequent warm renal IRI with contralateral nephrectomy at 4-6 weeks post-BMT. Creatinine and BUN were examined at 24-, 48-, 72-, and 96-hours post-IRI.
*Results: B6->ERaKO renal transplant had the greatest degree of injury, whereas B6->B6 and ERaKO->B6 had equivalent lesser injury (Figure 1a). BMT of B6 into ESRaKO animals had the greatest degree of injury, followed by B6->B6 and ESRaKO->B6 that again were equivalent (Figure 1b, p<0.001).
*Conclusions: ER-a mediated renal protection appears extrinsic to the kidney in a standardized model of renal IRI. Moreover, BMT of B6 into ERaKO animals does not provide protection, demonstrating the estrogen responsive element must not be in the bone marrow. We are currently pursuing various mechanisms of extrarenal estrogen-mediated protection in renal IRI.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Aufhauser DD, Concors SJ, Hernandez PT, Wang Z, Krumeich L, Murken DR, Ge G, Hancock WW, Levine MH. Estrogen Mediated Protection in Renal Ischemia Reperfusion Injury (IRI) is Extrinsic to the Kidney [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2019; 19 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/estrogen-mediated-protection-in-renal-ischemia-reperfusion-injury-iri-is-extrinsic-to-the-kidney/. Accessed March 10, 2026.« Back to 2019 American Transplant Congress