Establishing an Induction Protocol for Long-Term Multilineage Mixed Chimerism in Rhesus Macaques
1Columbia Center for Translational Immunology, Columbia University, New York City, NY, 2Institute for Comparative Medicine, Columbia University, New York City, NY, 3Department of Pathology and Cell Biology, Columbia University, New York City, NY
Meeting: 2020 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: A-382
Keywords: Immunosuppression, Kidney transplantation, Primates, Tolerance
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session A: Tolerance / Immune Deviation
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Saturday, May 30, 2020
Session Time: 3:15pm-4:00pm
 Presentation Time: 3:30pm-4:00pm
Presentation Time: 3:30pm-4:00pm
Location: Virtual
*Purpose: Mixed chimerism (MC) induction via non-myeloablative conditioning and bone marrow transplantation (BMT) induces tolerance to solid organs. Our standard MC induction protocol in cynomologous macaques achieves transient MC lasting 20 – 60 days, with T-cell chimerism of 5%. We established an induction protocol that yields higher and longer lasting MC in rhesus macaques as an operational tolerance model to kidney transplantation.
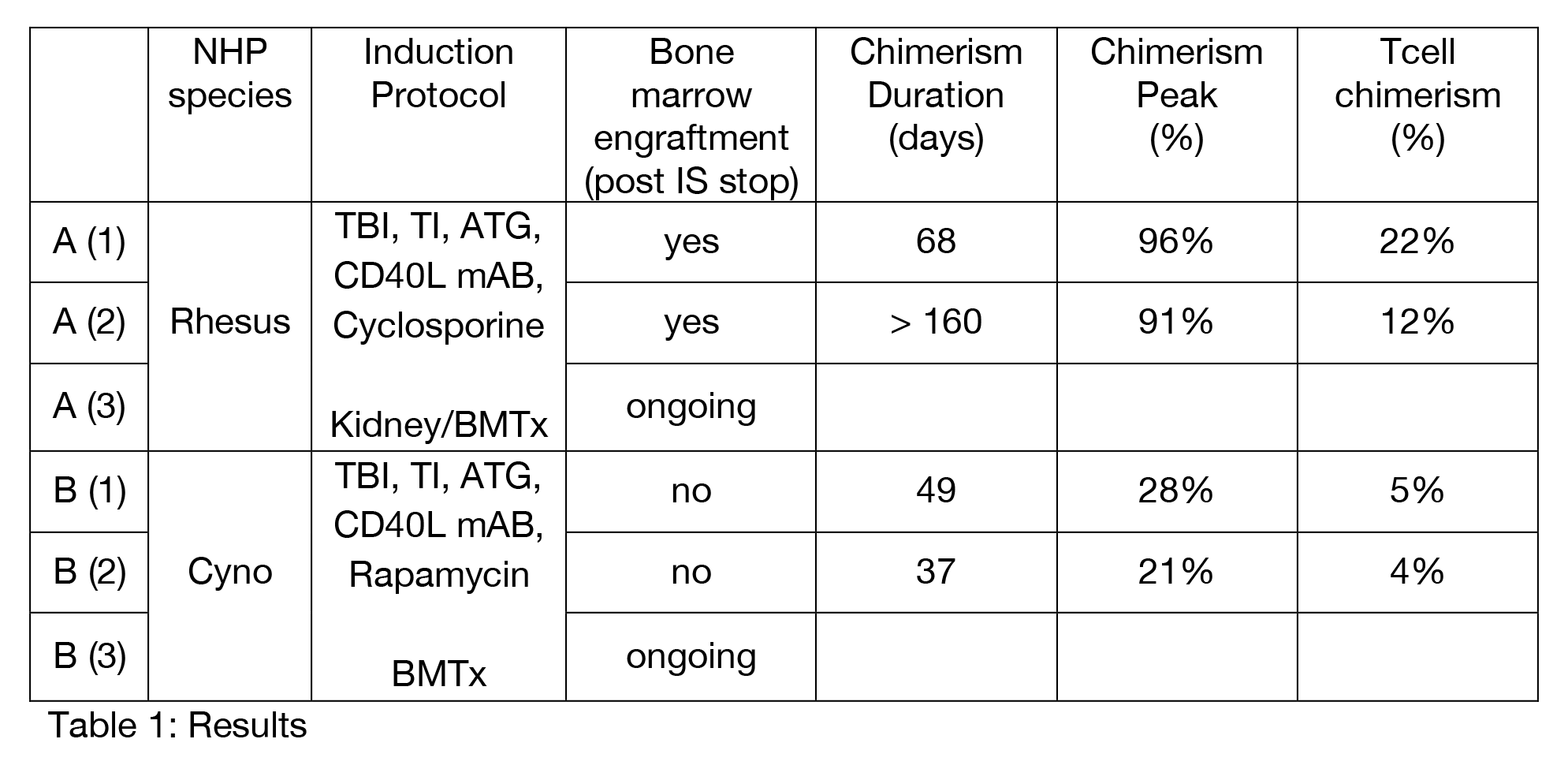
*Methods: Conditioning with total body irradiation (125cGy), thymic irradiation (7Gy), anti-CD154 mAbs and horse ATG followed by combined allogeneic MHC-mismatched BMT/kidney transplant and 1 month of cyclosporine, after which all immunosuppression (IS) was withdrawn. 3 rhesus macaques underwent this regimen and their mixed chimerism development as well as bone marrow engraftment was compared with 3 cynomolgous macaques receiving our standard induction protocol (Table 1).
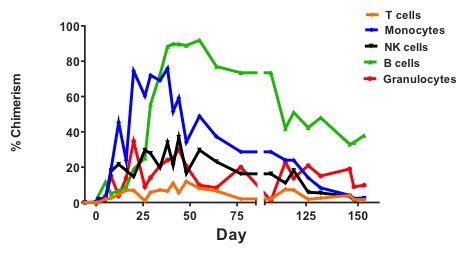
*Results: Rhesus macaques developed multilineage MC that was high in peak percentage (>90%) and showed T-cell chimerism >10% (Figure1). Bone marrow engraftment was evident after IS withdrawal and persisted significantly longer compared to cynomolgus controls. One animal developed long-term multilineage chimerism >30% for 5 months (ongoing). During the chimeric period, recipients showed donor-specific hyporesponsiveness in MLR and Elispot. No animal developed graft-versus-host disease. Animals accepted their donor kidney graft for 150 days and longer.
*Conclusions: While a similar induction regimen in other species has historically failed to achieve permanent chimerism, this protocol shows the development of higher chimerism overall, T-cell chimerism >10%, bone marrow engraftment after IS withdrawal and persistent macrochimerism for >5 months. The rhesus macaque as a more robust species harbors significant advantages as a NHP model for tolerance induction in solid organ transplantation.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Bruestle K, Sakai H, Fredriksson F, Piegari B, Ekanayake-Alper D, McLuckie A, Ober R, Weiner J, Iuga A, Coley SM, Sykes M, Griesemer A. Establishing an Induction Protocol for Long-Term Multilineage Mixed Chimerism in Rhesus Macaques [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2020; 20 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/establishing-an-induction-protocol-for-long-term-multilineage-mixed-chimerism-in-rhesus-macaques/. Accessed March 6, 2026.« Back to 2020 American Transplant Congress