Enhancing Kidney Function Following DCD Donation With Thrombolytic Therapy: A Preliminary Report of a Multicenter Prospective Quasi-Blinded Randomized Trial
1Transplant Institute, University Hospitals Case Medical Center, Cleveland, OH
2Transplant Center, Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, OH
3LIfebanc, Cleveland, OH.
Meeting: 2015 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: B93
Keywords: Donors, Kidney transplantation, Machine preservation, non-heart-beating, Pulsatile preservation
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session B: Kidney and Donor Evaluation/Utilization
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Sunday, May 3, 2015
Session Time: 5:30pm-6:30pm
 Presentation Time: 5:30pm-6:30pm
Presentation Time: 5:30pm-6:30pm
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Kidneys from donors following cardiac death (DCD) are at risk for inferior outcomes, possibly due to microthrombi and additional warm ischemia. We describe an organ procurement organization (OPO)-wide trial utilizing thrombolytics during machine pulsatile perfusion (MPP).
Methods: Following DCD recovery, a kidney from each pair was prospectively randomized to receive tPA (50 mg Alteplase) or no tPA in the MPP perfusate (850 mL IGL Pulsatile Perfusion Solution). If only one recipient enrolled, that patient received the tPA kidney; if both recipients enrolled in the trial, tPA status was kept blinded.
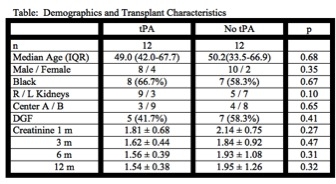
Results: From 2011 to 2013, 24 kidneys were placed with enrolled recipients from 18 DCD kidney donors. There were no significant differences for absolute values of flow or resistance while undergoing MPP between the groups. Also, discrete flow and resistance targets were reached at similar rates. Recipient demographics and transplant characteristics are shown in the Table. While there was a trend towards lower creatinine (mean±SD), in the tPA group, at 3, 6, and 12 months, these differences were not significant. Delayed graft function (DGF) rates were 41.7% vs 58.4% in the tPA and control group, respectively (p=0.41).
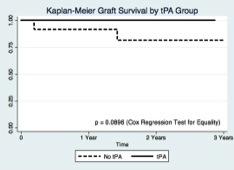
There was one death 70 days post-engraftment in a non-tPA patient, with a second graft failure at 520 days in a non-tPA patient who had chronic poor function and chronic pyelonephritis (Figure).
Conclusion: In this pilot study, encouraging trends are seen in kidney allograft survival and function in DCD kidneys receiving thrombolytic tPA and MPP, compared with standard MPP.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Woodside K, Goldfarb D, Rabets J, Sanchez E, Lebovitz D, Schulak J, Fung J, Eghtesad B. Enhancing Kidney Function Following DCD Donation With Thrombolytic Therapy: A Preliminary Report of a Multicenter Prospective Quasi-Blinded Randomized Trial [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2015; 15 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/enhancing-kidney-function-following-dcd-donation-with-thrombolytic-therapy-a-preliminary-report-of-a-multicenter-prospective-quasi-blinded-randomized-trial/. Accessed July 12, 2025.« Back to 2015 American Transplant Congress
