Efficacy and Safety Outcomes with De Novo Use of Everolimus-Based Regimen in Renal Transplant Recipients with Delayed Graft Function from the TRANSFORM Study
1TRANSFORM Study Group, Basel, Switzerland, 2Novartis Pharma AG, Basel, Switzerland
Meeting: 2019 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 103
Keywords: Graft function, Graft survival, Kidney transplantation, Renal function
Session Information
Session Name: Concurrent Session: Kidney Immunosuppression: Novel Regimens and Drug Minimization I
Session Type: Concurrent Session
Date: Sunday, June 2, 2019
Session Time: 4:30pm-6:00pm
 Presentation Time: 4:42pm-4:54pm
Presentation Time: 4:42pm-4:54pm
Location: Veterans Auditorium
*Purpose: To evaluate the effect of everolimus with reduced CNI (EVR+rCNI) vs mycophenolic acid with standard CNI (MPA+sCNI) on efficacy and safety outcomes in RTxR with DGF in the TRANSFORM study (NCT01950819).
*Methods: In this 24-month (M), multicenter, open-label study, de novo RTxR were randomized to EVR+rCNI (N=1022) or MPA+sCNI (N=1015) with induction + steroids. DGF was defined as need for dialysis within 21 days of Tx. Drug exposure, overall efficacy (eGFR <50 mL/min/1.73 m2, tBPAR, graft loss [GL] or death), renal function, and safety were assessed at M24.
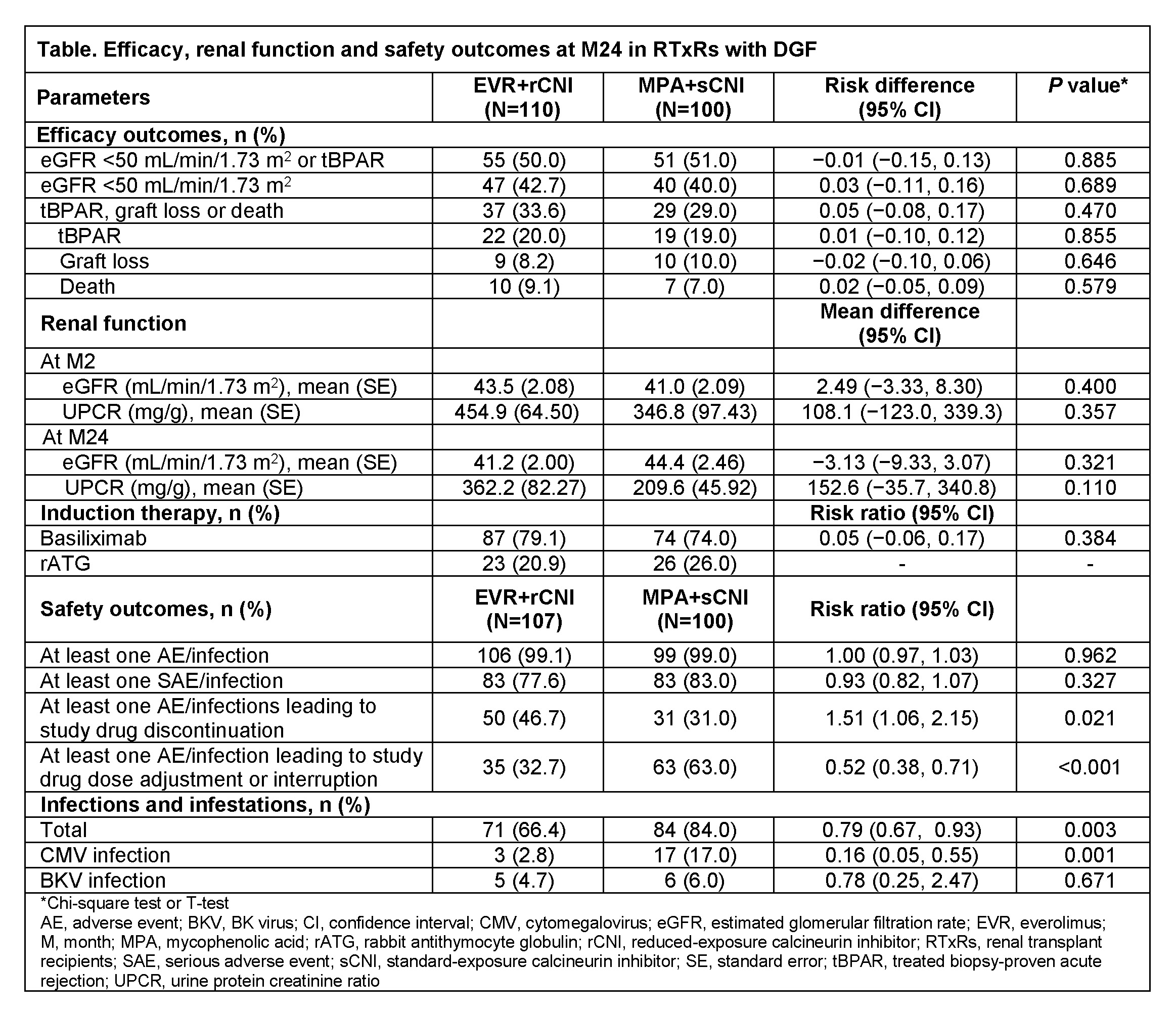
*Results: Of 2037 RTxR, 210 (10.3%) developed DGF compared to 1827 (89.7%) without DGF. RTxR with DGF had significantly higher rates of tBPAR (19.5% vs 9.6%, P<0.001), GL (9.1% vs 2.7%, P<0.001), death (8.1% vs 2.8%, P<0.001), and eGFR<50 mL/min/1.73 m2 (41.4% vs 33.3%, P=0.018) vs without DGF. Incidence of DGF was similar for EVR+rCNI (10.8%) and MPA+sCNI (9.9%). Baseline characteristics of those with DGF were comparable in both arms. DGF occurred in RTxR with expanded criteria deceased donors in 25 (26.3%) EVR+rCNI and 26 (33.3%) MPA+sCNI patients. Cold ischemia time >20 h was more common in EVR+rCNI vs MPA+sCNI (34.5% vs 22.2%) arm. Mean TAC trough levels at Day 7 were within target range in EVR+rCNI (6.8 ng/mL; target 4-7 ng/mL) and MPA+sCNI (8.5 ng/mL; target 8-12 ng/mL) arms. At M24, rates of tBPAR, GL, death and eGFR<50 mL/min/1.73 m2 did not differ between arms (Table). Proteinuria as an AE was more frequent in EVR+rCNI arm (24.3% vs 12.0%); however, most patients in both arms had low-grade proteinuria (spot urine protein/creatinine ratio 30-<500 mg/g: EVR+rCNI, 30/39 [76.9%] vs MPA+sCNI, 46/50 [92.0%]). The incidence of adverse events (AEs) and serious AEs was comparable between treatment groups. Overall incidence of infections and infestations, including CMV infection was significantly lower in EVR+rCNI vs MPA+sCNI arm.
*Conclusions: RTxR with DGF incur higher risks of tBPAR, renal dysfunction, GL and death within 2-years of Tx. These outcomes did not differ between RTxR receiving conventional IS and EVR-based regimen. Reduced incidence of CMV infection was observed for those on EVR.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Chadban S, Oppenheimer F, Citterio F, Witzke O, Garcia VD, Gutierrez-Dalmau A, Narvekar P, Gutierrez MPHernandez, Bernhardt P, Wiseman A. Efficacy and Safety Outcomes with De Novo Use of Everolimus-Based Regimen in Renal Transplant Recipients with Delayed Graft Function from the TRANSFORM Study [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2019; 19 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/efficacy-and-safety-outcomes-with-de-novo-use-of-everolimus-based-regimen-in-renal-transplant-recipients-with-delayed-graft-function-from-the-transform-study/. Accessed February 22, 2026.« Back to 2019 American Transplant Congress