Effects of Anti-HLA Antibodies on Endothelial Expression and Serum Levels of Thrombomodulin in Kidney Recipients.
Medicine, Universite Laval, Quebec, QC, Canada
Meeting: 2017 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: C9
Keywords: Alloantibodies, Endothelial cells, Kidney transplantation, Rejection
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session C: Antibody and B Cell
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Monday, May 1, 2017
Session Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Location: Hall D1
Background: Thrombomodulin (TBM) is an anticoagulant and anti-inflammatory protein expressed on endothelial cells (ECs). Mutations of TBM are seen in thrombotic microangiopathies due to aHUS. DSA, particularly those against HLA-II, are involved in endothelial allograft damage during ABMR, but mechanistic knowledge is still lacking. Thus far, the effects of anti-HLA I vs II antibodies on TBM have not been characterized.
Methods:We used human glomerular microvascular ECs to examine TBM expression by fluorescence microscopy and western blot on anti-HLA-treated cells. We then tested sera from 55 kidney recipients for soluble TBM by ELISA.
Results: Treatment of ECs with anti-HLA-I led to a dose-dependent increase in membrane TBM expression, whereas treatment with anti-HLA-II and TNF-α led to minimal levels of the protein. Western Blot on extracted membrane proteins confirmed these results and showed a different molecular weight for TBM in the anti-HLA-II well. 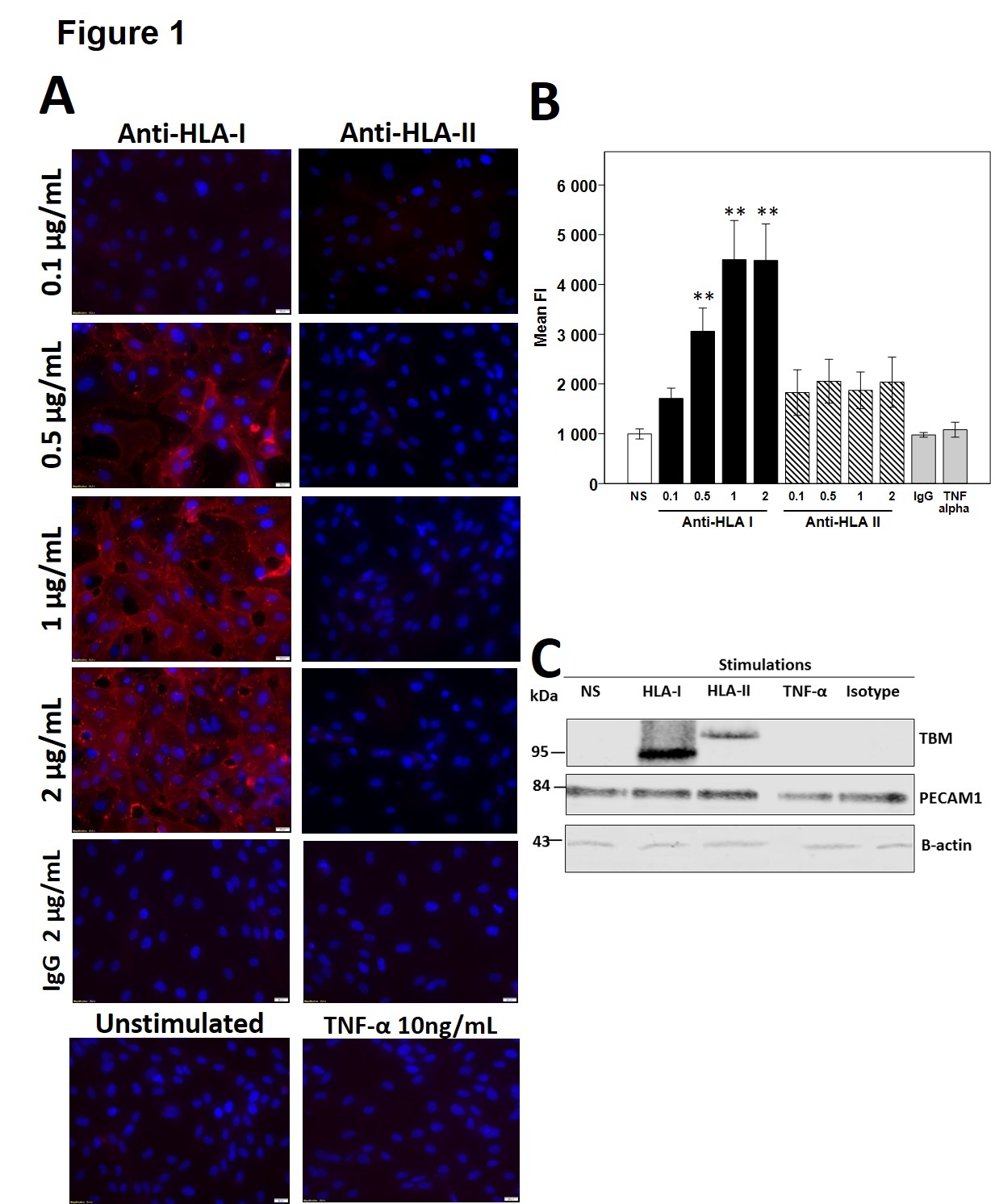 Neither stimulation with anti-HLA-I nor II increased TBM levels in cell culture supernatants, but TNF-α stimulation induced high levels, suggesting different pathways between TNF-α and anti-HLA-II. We next measured cytosolic TBM and observed an accumulation with anti-HLA-II, but not with TNF-α.
Neither stimulation with anti-HLA-I nor II increased TBM levels in cell culture supernatants, but TNF-α stimulation induced high levels, suggesting different pathways between TNF-α and anti-HLA-II. We next measured cytosolic TBM and observed an accumulation with anti-HLA-II, but not with TNF-α.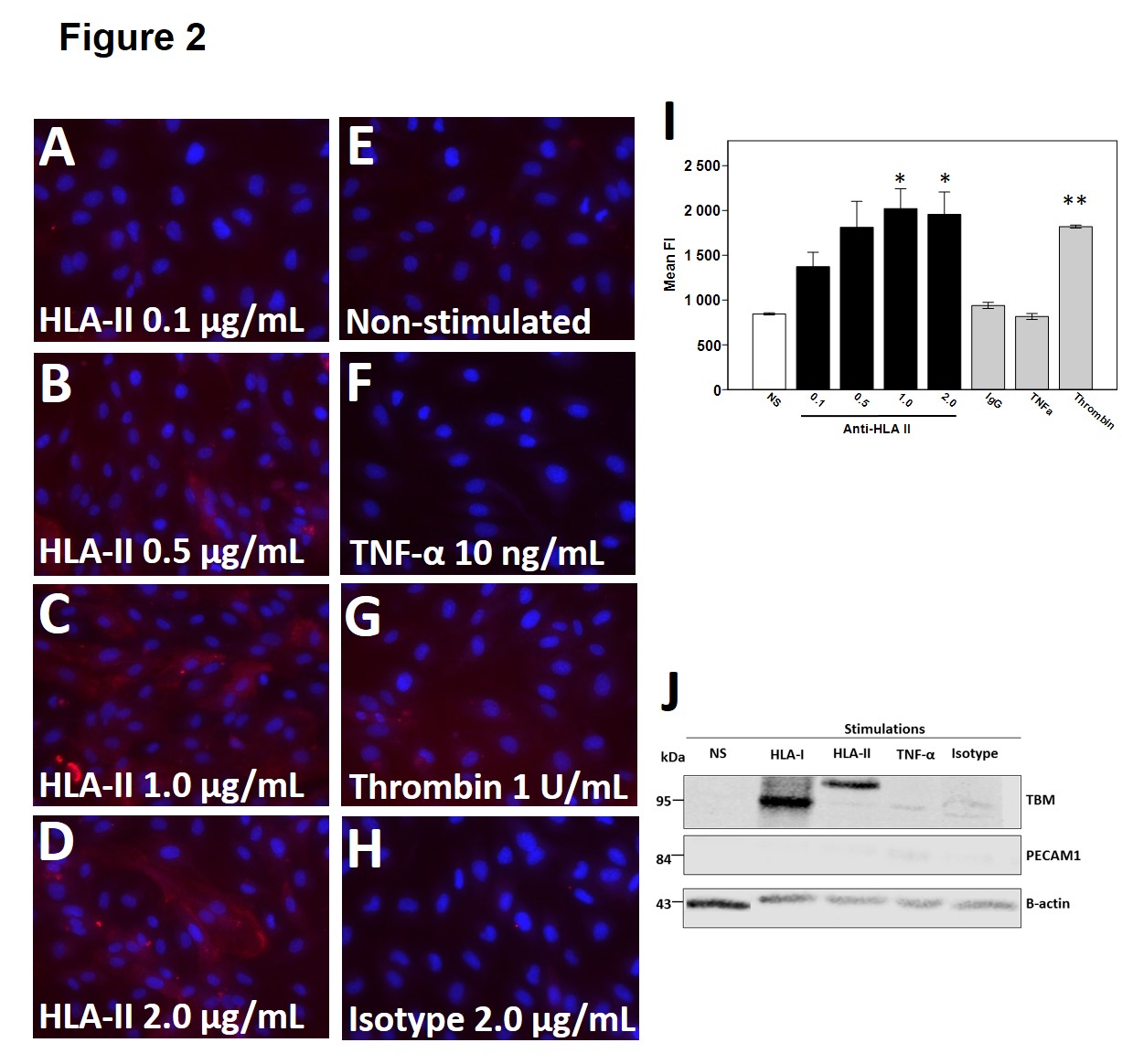 In patients, we found a significant association between the presence of circulating anti-HLA-II DSA and low serum levels of TBM.
In patients, we found a significant association between the presence of circulating anti-HLA-II DSA and low serum levels of TBM.
Conclusions:Ligation of anti-HLA-I and II produces different effects on the endothelial surface expression of TBM and on serum levels in kidney recipients. Anti-HLA-II stimulation leads to a cytosolic accumulation of TBM with little membrane expression, suggesting a modification of the protein. This phenotype may be associated with a prothrombotic state, which could explain the higher occurrence of TG and the poor outcomes observed in patients with these antibodies.
CITATION INFORMATION: Beland S, Desy O, Valin P, De Serres S. Effects of Anti-HLA Antibodies on Endothelial Expression and Serum Levels of Thrombomodulin in Kidney Recipients. Am J Transplant. 2017;17 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Beland S, Desy O, Valin P, Serres SDe. Effects of Anti-HLA Antibodies on Endothelial Expression and Serum Levels of Thrombomodulin in Kidney Recipients. [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2017; 17 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/effects-of-anti-hla-antibodies-on-endothelial-expression-and-serum-levels-of-thrombomodulin-in-kidney-recipients/. Accessed February 26, 2026.« Back to 2017 American Transplant Congress
