Dysregulation of Immune Cell Glycolysis and Oxidative Phosphorylation Correlates with Development of Pre-liver Transplant Immune Dysfunction and Post-transplant Mortality
1Transplant Surgery, Rutgers NJMS, Newark, NJ, 2Transplant Surgery, Houston Methodist Hospital, Houston, TX
Meeting: 2021 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 657
Keywords: Gene expression, Immune deviation, Infection, Liver cirrhosis
Topic: Clinical Science » Biomarkers, Immune Assessment and Clinical Outcomes
Session Information
Session Name: Biomarkers, Immune Assessment and Clinical Outcomes
Session Type: Poster Abstract
Session Date & Time: None. Available on demand.
Location: Virtual
*Purpose: Cirrhosis-related immune dysfunction contributes to early morbidity and mortality following liver transplant (LT). We have previously identified a pre-LT biomarker panel, the immune frailty index (IFI), which accurately stratifies patients at high risk for post-transplant morbidity and mortality due to immune dysfunction. Prior work shows that impaired immune cell differentiation is central to this process. Here, we evaluate the genetic mechanisms responsible for these immunophenotypic alterations.
*Methods: IFI was calculated from pre-transplant HCV viremia, Eotaxin, MMP3, and Fractalkine. Pts with low IFI (Score 0-2) have a 95.5% 1yr survival compared with 46.2% for high IFI (Score 3-4). IFI-high were matched 1:2 with IFI-low based on age, sex, and cause of liver disease and were compared to healthy controls (NHC). RNA-seq was performed on PBMCs (d-1) and gene expression was used for principal component analysis (PCA) and clustering.
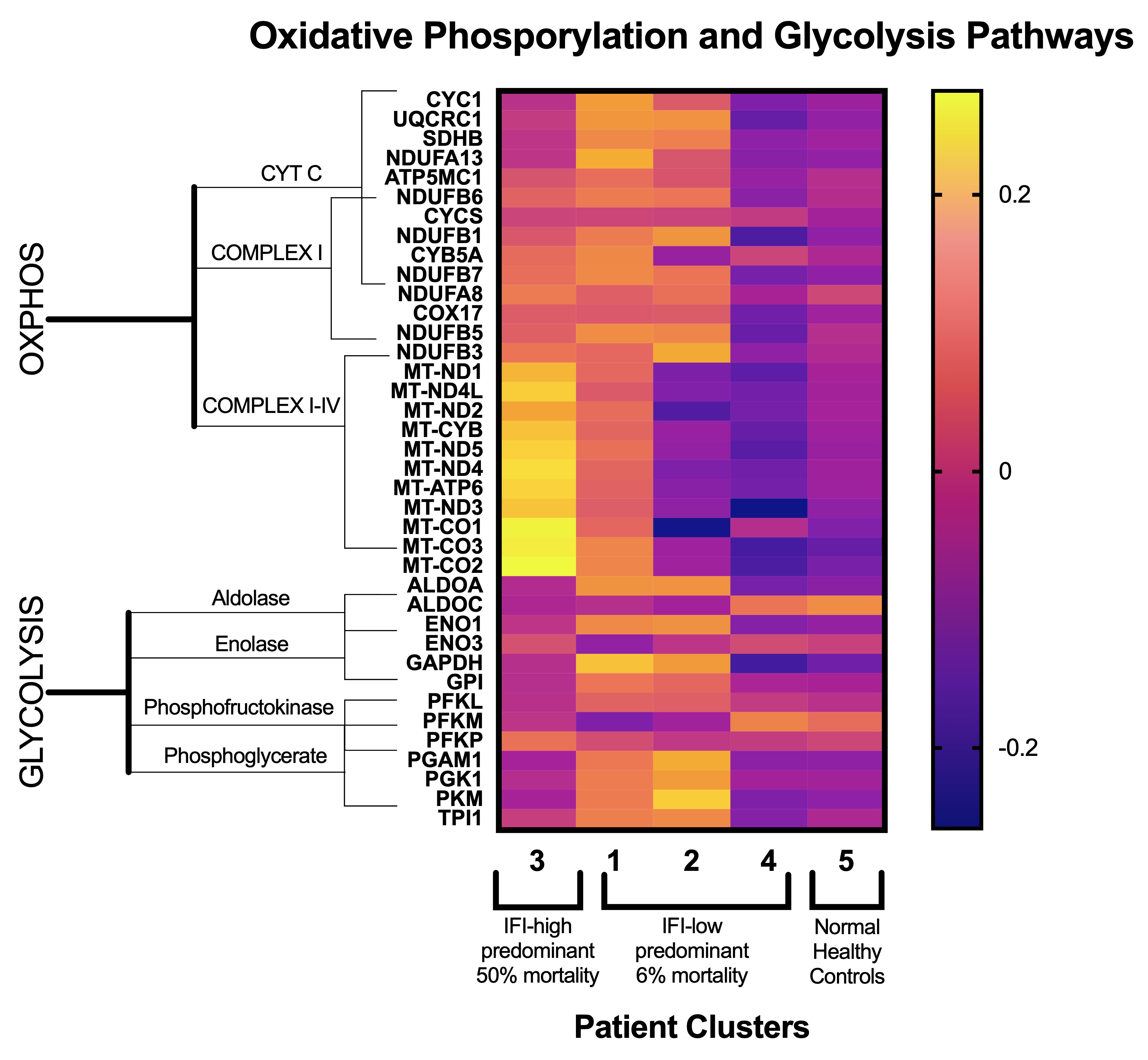
*Results: Gene expression analysis was performed on 22 LT recipients (n=7 IFI-high, n=15 IFI-low) and 8 NHCs. Donor and recipient characteristics were similar between groups. IFI-high had more positive cultures within 1yr post-op (4 vs 1, p<0.01) and lower 2yr survival (56% vs 100%, p<0.01). PCA analysis demonstrated 4 patterns of gene expression (clusters 1, 2, 3, and 4) with IFI-high predominantly in cluster 3; NHCs grouped together (cluster 5), Figure 1. Four patients died during median follow up of two years, all within the IFI-high cohort. Among these, 3/4 (75%) died secondary to infection-related complications (i.e. immune dysfunction), all in cluster 3. Gene analysis revealed mitochondrial function and oxidative phosphorylation genes were comparatively upregulated and glycolysis was comparatively downregulated in this patient group.
*Conclusions: Pre-transplant immune dysfunction in LT recipients is associated with significant alterations in immune cell metabolic pathways, including oxidative phosphorylation and glycolysis. Such metabolic dysregulation is known to abrogate immune cell differentiation into functional effectors. These alteration may direct immune frailty and increase LT recipients’ susceptibility to complications and death. Further evaluation of these pathways may offer a potential novel target to interrupt pre-transplant immune dysfunction and improve LT outcomes.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Panayotova G, Jin L, Lemenze A, Simonishvili S, Qin Y, Minze L, Dikdan G, Paterno F, Li XC, Ghobrial M, Guarrera JV, Lunsford KE. Dysregulation of Immune Cell Glycolysis and Oxidative Phosphorylation Correlates with Development of Pre-liver Transplant Immune Dysfunction and Post-transplant Mortality [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2021; 21 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/dysregulation-of-immune-cell-glycolysis-and-oxidative-phosphorylation-correlates-with-development-of-pre-liver-transplant-immune-dysfunction-and-post-transplant-mortality/. Accessed March 13, 2026.« Back to 2021 American Transplant Congress