Does the Model for End Stage Liver Disease (MELD) Score Predict Outcome in Total Artificial Heart Patients?
Cedars-Sinai Heart Institute, Los Angeles
Meeting: 2017 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: C96
Keywords: Artificial heart, Heart/lung transplantation
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session C: Hearts and VADS: All Topics
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Monday, May 1, 2017
Session Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Location: Hall D1
The total artificial heart (TAH) is being used for biventricular failure in patients with severe heart disease. Patients(pts) who have received a left ventricular assist device (LVAD) have used the MELD score to predict outcome. The MELD score is used in liver transplantation to determine the severity of illness. The MELD score consists of the following factors: recipient age, total-bilirubin (mg/dl), serum sodium (mEq/L), INR, serum creatinine (mg/dl), prevalence of dialysis (dialysis twice, or 24 hrs of CVVHD, within a week prior to the serum creatinine test). A prognostic indicator for TAH pts is lacking. We sought to determine whether the MELD score can predict outcome in TAH patients at our single center.
Methods: Between 2012 and 2016 we assessed 76 pts implanted with a TAH device at our center. Pts were divided into the following OPTN MELD level ranges: MELD ≤10 (Group A, n=12), MELD 11-18 (Group B, n=22), MELD 19-24 (Group C, n=20), MELD > 24 (Group D, n=22). The MELD score was calculated for each patient immediately prior to TAH implant via OPTN MELD calculator.
Results: In general, there is a correlation of increasing MELD score to decreasing survival (figure). Particularly, the worse MELD score group (>24) had significantly lowest survival. The lowest MELD score has only 12 pts. 8/12 (67%) deaths in the highest MELD group was due to multi-organ system failure.
Conclusion: The MELD score appears to predict pts undergoing TAH with increased risk for mortality. Further studies with larger population sizes and follow-up are warranted to confirm these results.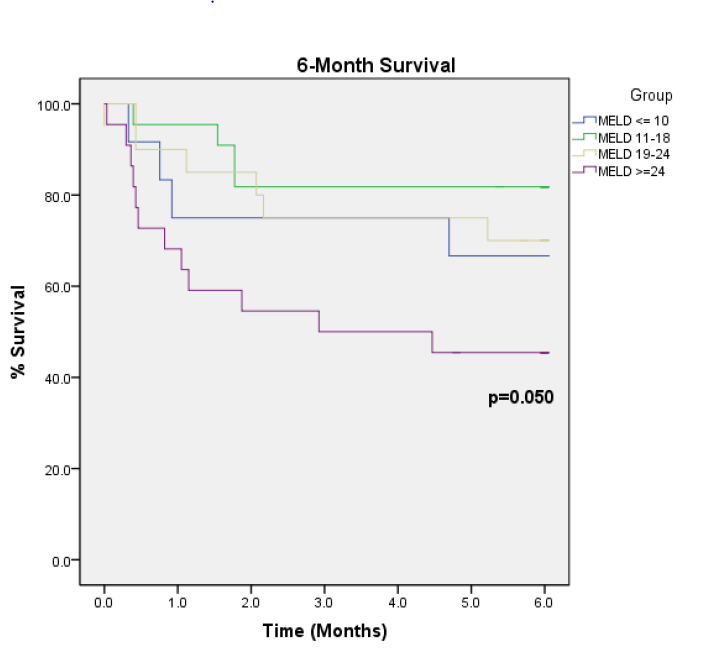
CITATION INFORMATION: Rafiei M, Moriguchi J, Kittleson M, Patel J, Aintablian T, Passano E, Sharoff R, Kwan J, Kransdorf E, Chang D, Czer L, Kobashigawa J, Arabia F. Does the Model for End Stage Liver Disease (MELD) Score Predict Outcome in Total Artificial Heart Patients? Am J Transplant. 2017;17 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Rafiei M, Moriguchi J, Kittleson M, Patel J, Aintablian T, Passano E, Sharoff R, Kwan J, Kransdorf E, Chang D, Czer L, Kobashigawa J, Arabia F. Does the Model for End Stage Liver Disease (MELD) Score Predict Outcome in Total Artificial Heart Patients? [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2017; 17 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/does-the-model-for-end-stage-liver-disease-meld-score-predict-outcome-in-total-artificial-heart-patients/. Accessed July 12, 2025.« Back to 2017 American Transplant Congress
