Development and Validation of a Novel Peripheral Blood Based Gene Signature for Acute Rejection Following Renal Transplantation
Department of Urology, Beijing Chao-Yang Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing, China
Meeting: 2021 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 111
Keywords: Genomic markers, Kidney transplantation, Rejection
Topic: Clinical Science » Biomarkers, Immune Assessment and Clinical Outcomes
Session Information
Session Name: Biomarkers, Immune Assessment and Clinical Outcomes - II
Session Type: Rapid Fire Oral Abstract
Date: Sunday, June 6, 2021
Session Time: 4:30pm-5:30pm
 Presentation Time: 4:30pm-4:35pm
Presentation Time: 4:30pm-4:35pm
Location: Virtual
*Purpose: The aim of this study is to utilize advanced machine learning methods to construct a peripheral blood-based gene signature for acute rejection following kidney transplantation.
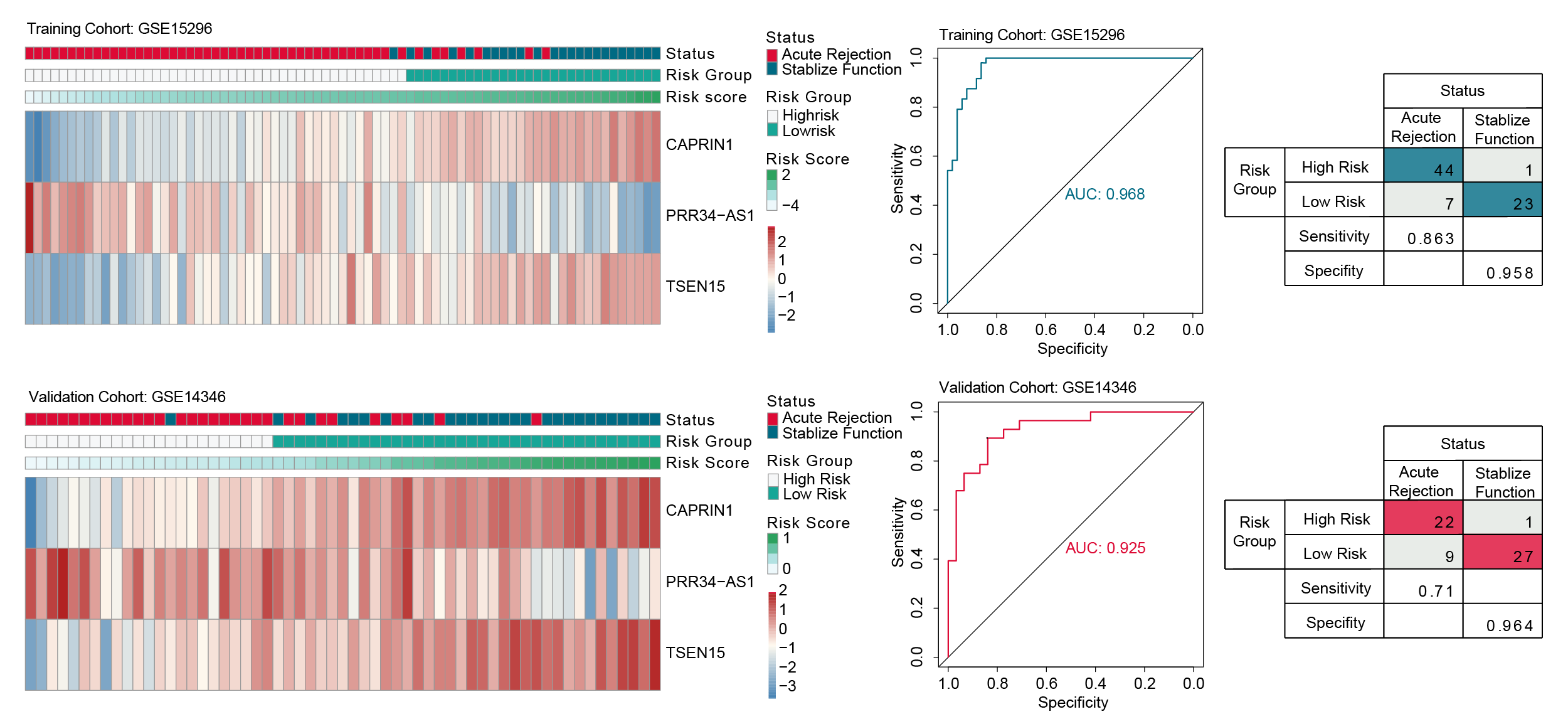
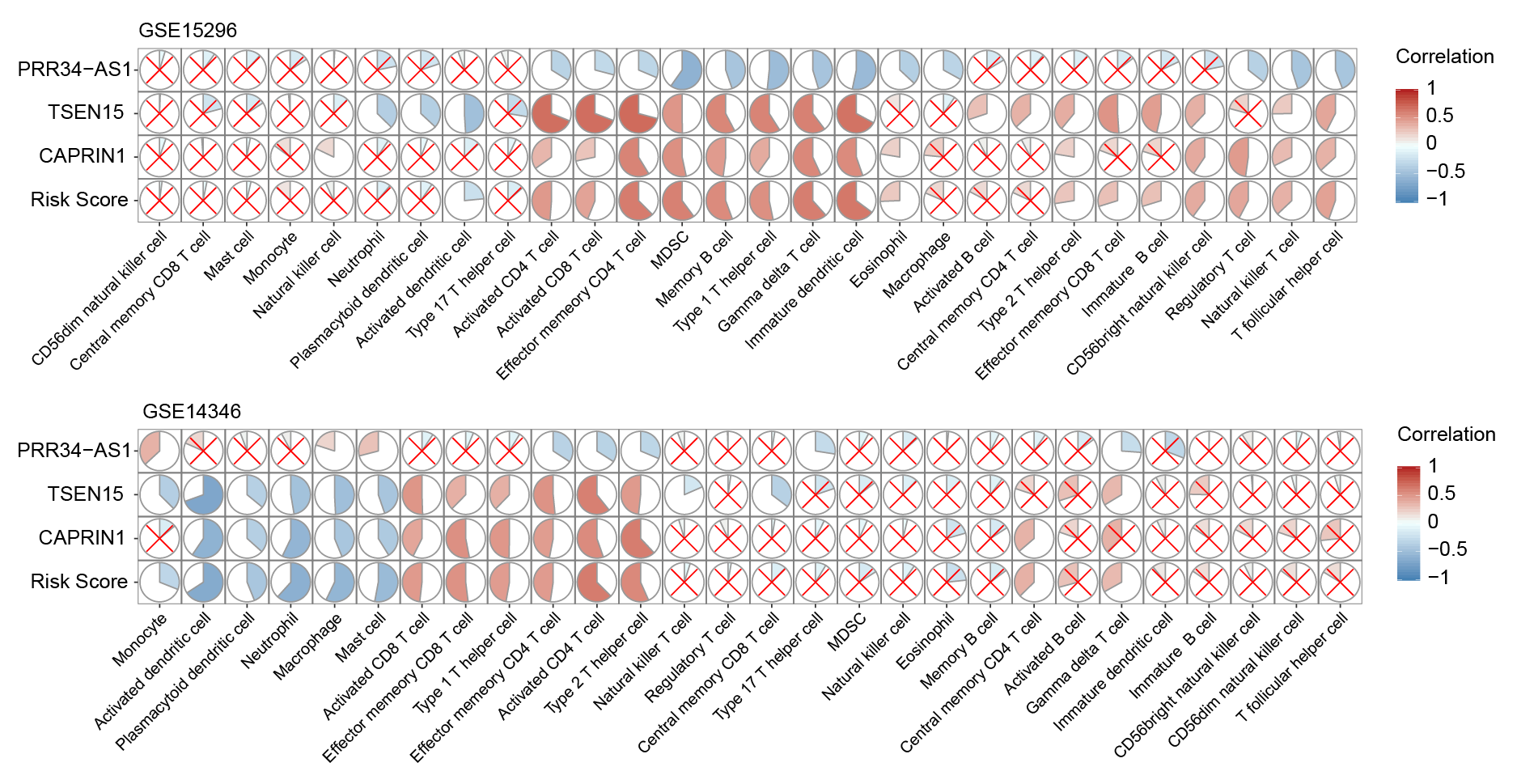
*Methods: After systematically screened the databases, two independent cohorts of high quality with blood expression profiles and biopsy-proven graft status from the Gene Expression Omnibus database were employed as training and validation cohorts. Then, two machine learning algorithms (support vector machine recursive feature elimination and random forest) were used to identify key biomarkers for acute rejection. Subsequently, the least absolute shrinkage and selector operation logistic regression method was applied to construct a gene signature for acute rejection in the training cohort. Patients were divided into high-risk and low-risk groups based on the cutoff point identified by the ROC curve. The signature was validated in an independent validation cohort with fixed formula and same cutoff point. ssGSEA was used to estimate immune cells in the blood.
*Results: Combining two advanced machine learning algorithms, seven key biomarkers were filtered out. Then, using the least absolute shrinkage and selector operation logistic regression method, a novel three-gene signature was constructed. The signature had high accuracy in both training (AUC=0.968) and validation cohort (AUC=0.925). Notably, the signature had high specificity in diagnosing acute rejection (0.958 in training cohort and 0.964 in validation cohort). Additionally, these three genes were found to have significant and consistent relationships with blood immune cells in both cohorts.
*Conclusions: We developed a novel blood-based three-gene signature to non-invasively diagnose renal acute rejection, which offered an accurate and convenient tool for clinical practice. Besides, the current study addressed the promising prospect of blood gene biomarkers in the field of kidney transplantation.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Zhang D, Wang Y, Hu X. Development and Validation of a Novel Peripheral Blood Based Gene Signature for Acute Rejection Following Renal Transplantation [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2021; 21 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/development-and-validation-of-a-novel-peripheral-blood-based-gene-signature-for-acute-rejection-following-renal-transplantation/. Accessed July 18, 2025.« Back to 2021 American Transplant Congress