Developing a Rationale for an Appropriate Immunosuppressive Regimen in Lung vs Kidney Transplant Recipients: Effects of Induction Therapy
1Transplantation Research Center, Renal Division, Brigham and Women's Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA
2Nephrology Department, Clinica Universidad de Navarra, Pamplona, Spain
3Renal Division, Department of Internal Medicine, Gospel Hospital, Kosin University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea
4Pulmonary Division, Brigham and Women's Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA.
Meeting: 2018 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: B144
Keywords: Induction therapy, Kidney transplantation, Lung transplantation
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session B: Kidney Immunosuppression: Induction Therapy
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Sunday, June 3, 2018
Session Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Location: Hall 4EF
Introduction
The appropriate use of Thymoglobulin (ATG) or Basiliximab as induction therapy is not fully understood. We studied circulating cytokine profiles following kidney and lung transplantation to understand the effects of induction therapy and design a more rational approach to its use.
Material and Methods
We included in the study 17 lung and 10 kidney transplant patients. Serum samples were obtained pre-transplant and days 1, 2, 3, 4, 14 and 30 post-transplant. A profile including 26 cytokines was analyzed by Luminex. Differences in cytokines between the kidney and lung transplant patients, and according to the type of induction therapy, ATG or Basiliximab were analyzed.
Results
Basiliximab was used as induction therapy in all the lung transplants and 40% of the kidney patients with ATG used in the rest. Rates of infections and hospitalization were higher in the lung transplant group. The peak of IL5, IL6 and IL15 the day 2 post-transplant was statistical significant higher in the group of lung transplants. In the kidney transplant group, MIG maintained higher levels (p <0.05) than in the lung transplant group until day 4 post-transplant. Figure 1 shows the change in the levels of these cytokines. 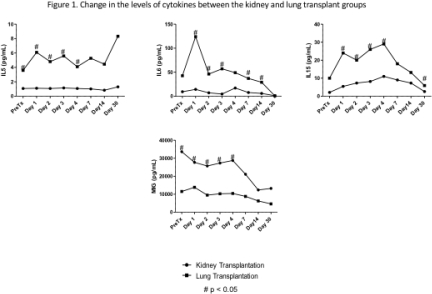 With regards to the circulating level of cytokines by induction therapy, only MIG at day 4, Eotaxin at day 2 and IL8 at day 3 showed a statistically significant difference (p <0.05) between the use of ATG or Basiliximab as induction therapy.
With regards to the circulating level of cytokines by induction therapy, only MIG at day 4, Eotaxin at day 2 and IL8 at day 3 showed a statistically significant difference (p <0.05) between the use of ATG or Basiliximab as induction therapy.
Conclusions
Circulating cytokine profile are different between kidney and lung transplant recipients. Higher levels of post-transplant IL6 in the group of lung transplant recipients may suggest a potential benefit for the use of anti-IL6 as induction therapy but it is necessary to do study with a higher number of patients.
CITATION INFORMATION: Martin-Moreno P., Shin H., Goldberg H., Chandraker A. Developing a Rationale for an Appropriate Immunosuppressive Regimen in Lung vs Kidney Transplant Recipients: Effects of Induction Therapy Am J Transplant. 2017;17 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Martin-Moreno P, Shin H, Goldberg H, Chandraker A. Developing a Rationale for an Appropriate Immunosuppressive Regimen in Lung vs Kidney Transplant Recipients: Effects of Induction Therapy [abstract]. https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/developing-a-rationale-for-an-appropriate-immunosuppressive-regimen-in-lung-vs-kidney-transplant-recipients-effects-of-induction-therapy/. Accessed February 18, 2026.« Back to 2018 American Transplant Congress
