Determination of Programmed Cell Death Protein 1 (PD1) by Flow Cytometry, a Possible Follow-Up Tool in Renal Transplantation of High Immune Risk
1Nephrology, Hospital Central Sur Alta Especialidad "Picacho", CDMX, Mexico, 2Genetics, Hospital General de México Dr. Eduardo Liceaga-Facultad, Ciudad de México, México, CDMX, Mexico, 3Transplant, Hospital General de México Dr. Eduardo Liceaga-Facultad, Ciudad de México, México, CDMX, Mexico, 4Unidad de investigación en inmunoqímica,, Hospital de Especialidades Centro Médico Siglo XXI IMSS, CDMX, Mexico, 5Unidad de investigación en inmunoqímica,, Hospital de Especialidades Centro Médico Siglo XXI IMSS, Ciudad de México, México, CDMX, Mexico, 6Transplant, Instituto Nacional de Ciencias Médicas y Nutrición Salvador Zubirán, CDMX, Mexico
Meeting: 2020 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: C-339
Keywords: Allorecognition, Co-stimulation, Rejection, T cells
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session C: Biomarkers, Immune Assessment and Clinical Outcomes
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Saturday, May 30, 2020
Session Time: 3:15pm-4:00pm
 Presentation Time: 3:30pm-4:00pm
Presentation Time: 3:30pm-4:00pm
Location: Virtual
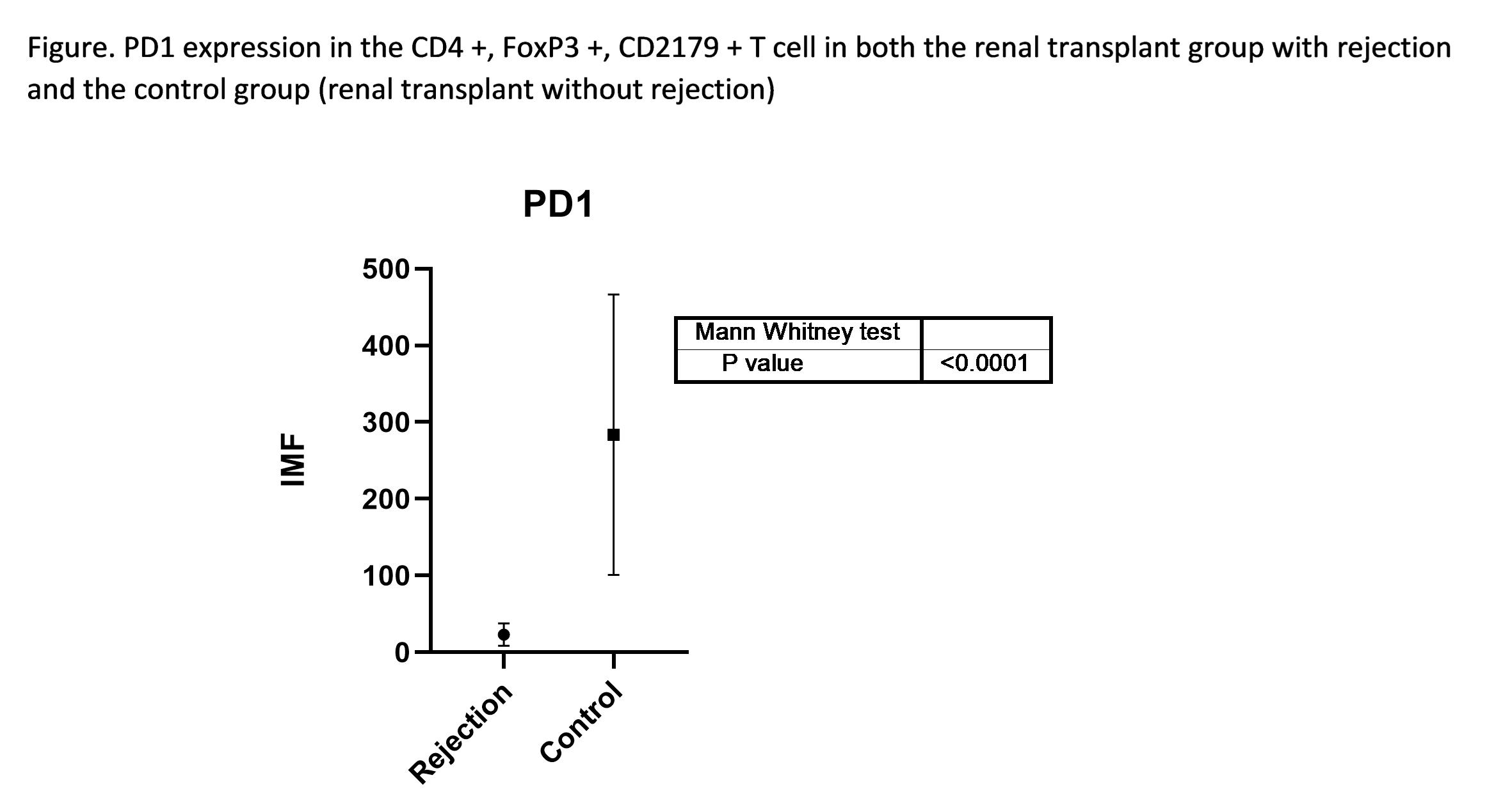
*Purpose: Introduction: Currently, the follow-up of patients remains to be the serum creatinine level, being highly specific, however, with little sensitivity to determine the occurrence of immunological events in the renal allograft. Objective: To evaluate the proportion of regulatory T cells (CD3 +, CD4 +, CD25 +, FOXP3 +, CD279 +) in peripheral blood of patients with renal transplants with rejection (TRRX).
*Methods: Material or Patients and Method: Venopuncture was performed on patients with renal transplantation, both normoevolutive, as well as patients with acute rejection. The study group was composed of 26 patients, without rejection, and three patients with acute rejection diagnosed by biopsy. This protocol was accepted by research and ethics committees. All participants voluntarily agreed to participate prior to signing the informed consent. The experimental part was performed in the 3-lane FACSAria Flow-Cell Sorter Cytometer, BD, the results were analyzed in the Infinicyt Cytognos version 2.0.
*Results: Mononuclear cells were obtained by density separation. The proportion of regulatory T cells in the TRRX group was 6.7%. The mean values of the mean immunofluorescence intensity for PD1 in the rejection group was 21.37 SD 20.35 unlike the control group of patients with normal normoplant transplantation of 283.7 DS 182.7. The contrast of both groups using a non-parametric Mann-Whitney statistic, shows a p = 0.0005 in a two-way analysis (two tails).
*Conclusions: We can use flow cytometry to follow-up on patients with renal transplantation, especially in those with high immunological risk since it is able to find differences between patients with TRRX and NRT. The study of PD1 CD4 + T cell, FoxP3 +, could give a guideline in the follow-up of patients with renal transplantation, especially those with high immunological risk.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Carmona-Escamilla M, Fonseca M, Chávez JPrieto, Arriaga L, Oviendo F, SA Hernández-Mendoza, Alberu J, Queipo G. Determination of Programmed Cell Death Protein 1 (PD1) by Flow Cytometry, a Possible Follow-Up Tool in Renal Transplantation of High Immune Risk [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2020; 20 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/determination-of-programmed-cell-death-protein-1-pd1-by-flow-cytometry-a-possible-follow-up-tool-in-renal-transplantation-of-high-immune-risk/. Accessed March 2, 2026.« Back to 2020 American Transplant Congress