Decreased Expression of Mitochondrial Aldehyde Dehydrogenase 2 Induces Liver Injury Via Activation of the MAPK Pathway in Grafts from Brain-Dead Donors
1Zhongnan Hospital of Wuhan University, Institute of Hepatobiliary Diseases of Wuhan University, Transplant Center of Wuhan University, Hubei Key Laboratory of Medical Technology on Transplantation, Wuhan, Hubei, China
2The 3rd Xiangya Hospital of Central South University, Research Center of National Health Ministry on Transplantation Medicine Engineering and Technology, Changsha, Hunan, China
3Massachusetts General Hospital, Department of Urology, Boston, MA.
Meeting: 2015 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: C283
Keywords: Apoptosis, Brain death
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session C: Translational Biomarkers and Immune Monitoring
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Monday, May 4, 2015
Session Time: 5:30pm-6:30pm
 Presentation Time: 5:30pm-6:30pm
Presentation Time: 5:30pm-6:30pm
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Objective: To determine the role of ALDH2 in the injury of liver from brain-dead donors.
Methods: Using brain-dead rabbit model, the expression of ALDH2 and apoptosis rates in tissues and cell lines were detected by western blot, transferase (TdT)-mediated biotin-16-dUTP nick-end labelling (TUNEL) assays and flow cytometry. After inhibiting or overexpression of ALDH2 (Ad-ALDH2) during hypoxia-ischemia, the accumulations of 4-Hydroxynonenal (4-HNE) and molecules involved in mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling pathway were analyzed by western blot.
Results: The low expression of phosphorylated ALDH2 in liver were time-dependent in the brain-dead groups, immunohistochemistry showed expression of ALDH2 was primarily located in endothelial cells. TUNEL demonstrated apoptosis rates in the brain-dead groups significantly increased with time. In vitro, after 8 hours' hypoxia-ischemia (HI group), the apoptosis rates of HUVECs (7.450±0.755%) were sharply increased (0.250±0.129%) (P<0.001), furthermore, the expression of 4-HNE, P-P38, P-ERK, P-JNK, cleaved caspase-3 and Bax were significantly higher when compared with normal control (P<0.05). Following the treatment of inhibitor of ALDH2, daidzin, the apoptosis rates in HUVECs (25.60±2.877%), the levels of 4-HNE, P-JNK, and cleaved caspase-3 in cells were significantly increased in contrast to HI group, but which all decreased after overexpression of ALDH2 when compared with HI group (P<0.001) .
Conclusion: We found low expression of ALDH2 and high rates of apoptosis in the livers of donor brain-dead rabbits. Furthermore, decreased ALDH2 led to apoptosis in HUVECs through MAPK pathway.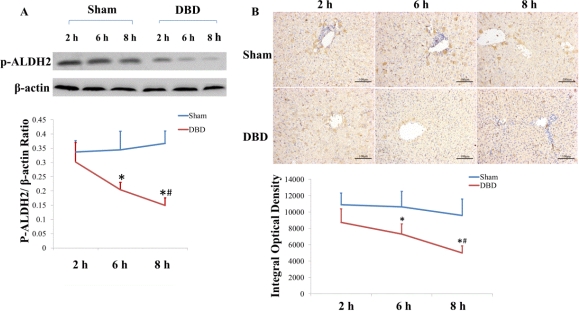
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Zhong Z, Ye S, Xiong Y, Fan X, Huang W, Ko D, Wang Y, Ye Q. Decreased Expression of Mitochondrial Aldehyde Dehydrogenase 2 Induces Liver Injury Via Activation of the MAPK Pathway in Grafts from Brain-Dead Donors [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2015; 15 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/decreased-expression-of-mitochondrial-aldehyde-dehydrogenase-2-induces-liver-injury-via-activation-of-the-mapk-pathway-in-grafts-from-brain-dead-donors/. Accessed March 4, 2026.« Back to 2015 American Transplant Congress
