Crosstalk Between micro-RNAs, mRNAs, and Long Non-Coding RNAs in Human Hepatic Ischemia Reperfusion Injury
1Transplant Research Institute, James D. Eason Transplant Institute, Department of Surgery, The University of Tennessee Health Science Center, Memphis, TN, 2James D. Eason Transplant Institute, Department of Surgery, The University of Tennessee Health Science Center, Memphis, TN, 3Surgery, University of Maryland, Baltimore, MD, 4University of Tennessee/Methodist Transplant Institute, Memphis, TN
Meeting: 2022 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 476
Keywords: Gene expression, Ischemia
Topic: Basic Science » Basic Science » 16 - Biomarkers: -omics and Systems Biology
Session Information
Session Name: Biomarkers: -omics and Systems Biology
Session Type: Rapid Fire Oral Abstract
Date: Tuesday, June 7, 2022
Session Time: 3:30pm-5:00pm
 Presentation Time: 4:10pm-4:20pm
Presentation Time: 4:10pm-4:20pm
Location: Hynes Room 304 / 306
*Purpose: Present study utilizes multiple omics tools and clinical samples with a system biology approach characterizing mRNAs, long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) and small non-coding RNAs in human hepatic ischemia reperfusion injury (IRI) since hepatic IRI is still one of the major obstacles in liver transplantation.
*Methods: Total RNA including small RNA species such as miRNAs and tRNA derived RNA fragments (tRFs) was isolated from paired pre-implantation and post reperfusion liver tissues (48 patients=96 samples). RNA-seq and small RNA-seq libraries were prepared separately from same patient. Small RNA library data was analyzed using Unitas tool which considers all types of small RNAs including miRNAs and tRFs. Differentially expressed mRNAs and miRNAs in post reperfusion versus pre-implantation biopsies were accessed using DeSeq2 tool. Integration of data was performed using TargetScan and miRTarVis tools.
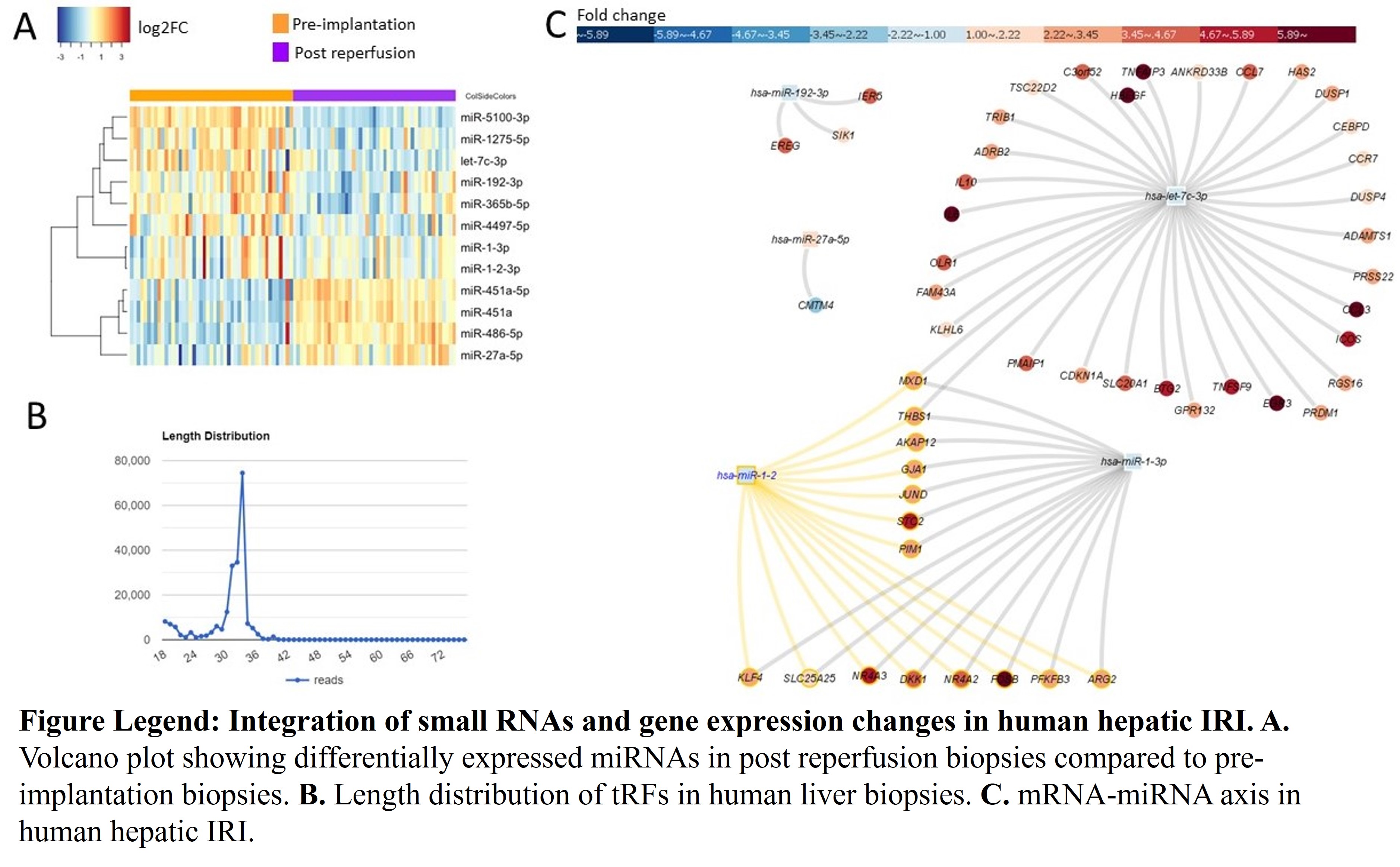
*Results: We identified 12 differentially expressed miRNAs in post reperfusion biopsies compared to pre-implantation biopsies (Fig. A). In addition to miRNAs, we achieved to detect tRFs in liver tissues (Fig. B). tRFs are upregulated under stress conditions including hypoxia. We also observed overexpression of tRFs in post reperfusion biopsies. In addition, there are >500 differentially expressed genes in post reperfusion. Interestingly, 109 of them were classified as lncRNAs and were not studied in human hepatic IRI previously. Integrative analysis using miRNAs and mRNAs revealed that let-7c, miR-1, miR-27a and miR-192 are potential regulators of gene expression changes in human hepatic IRI.
*Conclusions: Profiling small RNAs by RNA-seq identifies potential new targets such as tRFs and lncRNAs in human hepatic IRI. Integration of small RNA and gene expression changes indicated that a novel cross talk among different omics data such as miRNA, mRNAs and lncRNAs. Their important regulatory roles need further investigation in human hepatic IRI.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Kuscu C, Naik S, Eymard C, Bajwa A, Maluf D, Mas V, Eason J, Kuscu C. Crosstalk Between micro-RNAs, mRNAs, and Long Non-Coding RNAs in Human Hepatic Ischemia Reperfusion Injury [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2022; 22 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/crosstalk-between-micro-rnas-mrnas-and-long-non-coding-rnas-in-human-hepatic-ischemia-reperfusion-injury/. Accessed March 3, 2026.« Back to 2022 American Transplant Congress