CPRA Values Are Substantially Increased for Some Candidates Subsequent to Inclusion of Unacceptable C-locus (UA-C) Antigens While Listing Practices Remain Unchanged
1UNOS, Richmond
2Emory University Hospital, Atlanta
3Stanford University, Palo Alto.
Meeting: 2015 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: D64
Keywords: HLA antibodies, Kidney transplantation, Public policy, Sensitization
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session D: Immunology, Biomarkers and Immunosuppression
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Tuesday, May 5, 2015
Session Time: 5:30pm-6:30pm
 Presentation Time: 5:30pm-6:30pm
Presentation Time: 5:30pm-6:30pm
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Background: CPRA is the % of deceased donors expected to have one or more UAs with a given candidate. Prior to 12/5/13, candidates with UA-C were excluded from offers but their CPRA did not reflect those UAs. On 12/5/13, the CPRA formula was modified to include HLA-C.
Data and Methods: This study was performed for the OPTN Histocompatibility Committee using OPTN data. Patterns of reporting UA-C for kidney registrations (KRegs) were examined before and after the change to determine if the addition of C to CPRA calculation resulted in increased reporting of UA-C. In addition, the impact of the change was evaluated by comparing CPRA value without UA-C to the new CPRA value (including UA-C). HLA and ethnic frequencies were updated prior to the assessment. The study population included all KRegs with UA-C on the Waitlist at the time of the change (N=11315).
Results: % of KRegs with UA-Cs reported on the Waitlist had increased between 2006 and 2011. However, subsequent to the change, reporting remained stable (0.9% on 9/30/06, 10.8% on 9/30/13, 10.3% on 9/30/14). In contrast, the addition of C resulted in increased CPRA for 6435 (56.9%) KRegs with UA-C. The % increase in CPRA ranged from 1% (22%), 2-4% (24%), 5-9% (17%), to ≥10% points (37%) (Fig 1). CPRA increased from <80% to ≥80% for 573 KRegs, making them eligible for 4 additional allocation points. 6702 of the KRegs with UA-C would move into a higher CPRA group based on a sliding CPRA scale used for the New KI allocation (KAS) starting 12/4/14. CPRA values remained the same for 4880 (43.1%) KRegs with UA-C but of these, 81.3% had 100% CPRA value without UA-C.
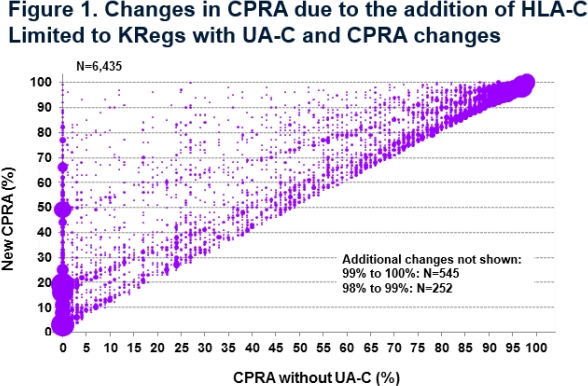
Conclusions: Following the addition of C into the CPRA calculation, reporting of UA-C on the waiting list remained stable suggesting that centers did not change their practices. However, the CPRA values for some candidates were substantially affected in that 21.2% of KRegs with UA-Cs increased their CPRA by ≥10% points and 5.1% moved into the ≥80% category ensuring appropriate and equitable allocation priority.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Kucheryavaya A, Bray R, Miller A, Tyan D. CPRA Values Are Substantially Increased for Some Candidates Subsequent to Inclusion of Unacceptable C-locus (UA-C) Antigens While Listing Practices Remain Unchanged [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2015; 15 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/cpra-values-are-substantially-increased-for-some-candidates-subsequent-to-inclusion-of-unacceptable-c-locus-ua-c-antigens-while-listing-practices-remain-unchanged/. Accessed March 2, 2026.« Back to 2015 American Transplant Congress
