COVID-19 Vaccination Induces a Poor Interleukin-21 Memory T-cell Response in Kidney Transplant Recipients
S. R. Malahe1, Y. den Hartog1, R. de Kuiper1, D. Reijerkerk1, D. Geers2, C. H. GeurtsvanKessel2, M. M. Kho1, R. D. de Vries2, M. E. Reinders1, C. C. Baan1
1Internal Medicine, Nephrology and Transplantation, Erasmus MC, Rotterdam, Netherlands, 2Viroscience, Erasmus MC, Rotterdam, Netherlands
Meeting: 2022 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 680
Keywords: COVID-19, Kidney transplantation, T cell reactivity, Vaccination
Topic: Clinical Science » Infection Disease » 24 - All Infections (Excluding Kidney & Viral Hepatitis)
Session Information
Session Name: All Infections (Excluding Kidney & Viral Hepatitis) I
Session Type: Poster Abstract
Date: Saturday, June 4, 2022
Session Time: 5:30pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 5:30pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 5:30pm-7:00pm
Location: Hynes Halls C & D
*Purpose: COVID-19-related morbidity and mortality is high among kidney patients. Several studies recently suggested low humoral and cellular immune responses after two doses of mRNA-1273 (Moderna) in these patients. Interleukin (IL)-21 is key in orchestrating an effective immune response against viral infections, is mainly produced by activated CD4+ T-cells and stimulates both humoral and cellular immunity. However, T-cell function may be impaired in kidney patients and this may explain the poor response to vaccination. Currently, there is limited data available on the vaccine-induced IL-21 memory T-cell response in these patients. We studied the induction of SARS-CoV-2-specific IL-21 memory T-cell response after mRNA-1273 vaccination in 3 groups of kidney patients.
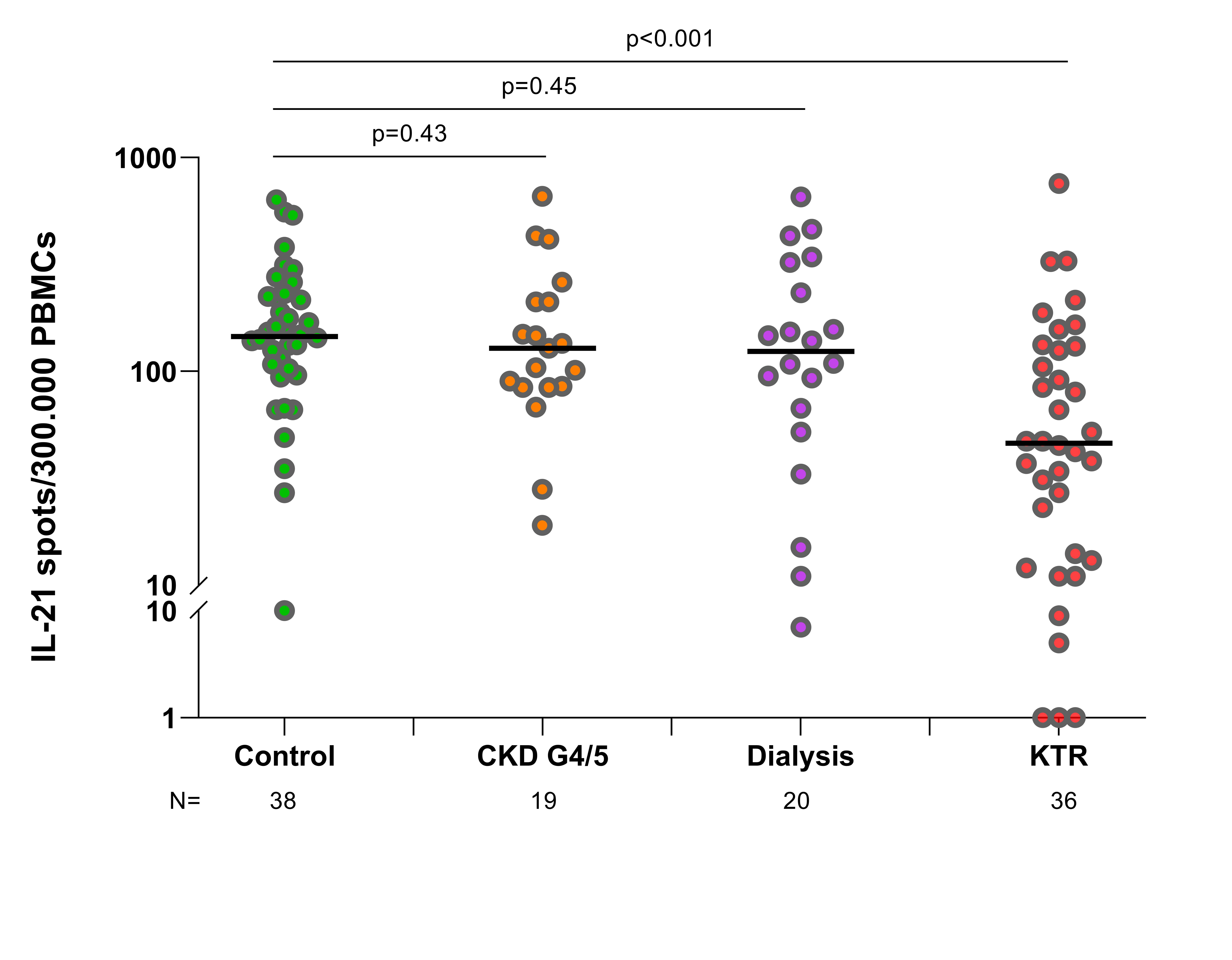
*Methods: 113 participants were randomly selected from a prospective controlled multicenter cohort study, including 38 controls, 19 chronic kidney disease (CKD) stages G4/5 (eGFR <30 mL/min/1.73m2), 20 dialysis and 36 kidney transplant patients. All participants received 2 doses of mRNA-1273. To assess the vaccine-induced IL-21 memory T-cell response, we performed an IL-21 ELISpot (per 3.105 PBMCs) in these participants at baseline and 28 days after the second vaccination. SARS-CoV-2 S1-specific IgG antibody levels were already measured in the context of the multicenter cohort study.
*Results: Kidney transplant recipients had a significantly lower number of SARS-CoV-2-specific IL-21 producing memory T-cells when compared to controls (median of 46 versus 146, P<0.001). Participants with CKD G4/5 or on dialysis also had reduced SARS-CoV-2-specific IL-21 producing memory T-cells compared to controls (median of 128 [19-658] and 124 [7-654] versus 146 [10-635], p=0.43 and p=0.45, respectively), but the difference was less pronounced. In addition, a positive correlation was found between the number of SARS-CoV-2-specific IL-21 producing memory T-cells and SARS-CoV-2 S1-specific IgG antibody levels for all groups (Pearson correlation coefficient of 0.2, p=0.028).
*Conclusions: Kidney transplant recipients have an impaired antibody response after two doses of mRNA-1273 (Moderna), which correlates with poor SARS-CoV-2-specific T-cell reactivity. These findings suggest that poor IL-21 memory T-cell response might hamper protection against COVID-19.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Malahe SR, Hartog Yden, Kuiper Rde, Reijerkerk D, Geers D, GeurtsvanKessel CH, Kho MM, Vries RDde, Reinders ME, Baan CC. COVID-19 Vaccination Induces a Poor Interleukin-21 Memory T-cell Response in Kidney Transplant Recipients [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2022; 22 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/covid-19-vaccination-induces-a-poor-interleukin-21-memory-t-cell-response-in-kidney-transplant-recipients/. Accessed March 10, 2026.« Back to 2022 American Transplant Congress