COVID-19 Infection in Kidney versus Non-kidney Solid Organ Transplant Recipients: A Single Center Study
J. Schaenman1, H. Byford2, T. R. Grogan3, S. Fraschilla2, K. Meneses4, J. C. Alejos5, M. Rivera6, S. Saab7
1Infectious Diseases, UCLA, Los Angeles, CA, 2Transplant Administration, UCLA, Los Angeles, CA, 3Division of General Internal Medicine and Health Services Research, UCLA, Los Angeles, CA, 4Liver Transplantation, UCLA, Los Angeles, CA, 5Pediatric Heart Transplantation, UCLA, Los Angeles, CA, 6Pediatric Kidney Transplantation, UCLA, Los Angeles, CA, 7Liver Transplantation, David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA, Los Angeles, CA
Meeting: 2021 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 766
Keywords: Kidney transplantation, Liver transplantation, Lung transplantation, Pneumonia
Topic: Clinical Science » Infectious Disease » All Infections (Excluding Kidney & Viral Hepatitis)
Session Information
Session Name: All Infections (Excluding Kidney & Viral Hepatitis)
Session Type: Poster Abstract
Session Date & Time: None. Available on demand.
Location: Virtual
*Purpose: The COVID-19 pandemic has caused significant morbidity and mortality in patients around the world. A significant impact has been observed in immunocompromised patients such as solid organ transplant (SOT) recipients, with increased rates of intubation and mortality compared to non-transplant patients. Our aim was to analyze risk factors, clinical presentation, and outcomes at a single high volume transplant center.
*Methods: We reviewed the records of adult SOT recipients during the COVID-19 pandemic from March to October 2020 to identify 143 SOT recipients diagnosed with COVID-19 by SARS-CoV-2 PCR testing, the majority of whom required hospitalization. 12 cases were from pediatric patients and were excluded from further analysis, leaving 131 adult patients for analysis. Recipient demographics, clinical presentation, and outcomes were compared by transplant type.
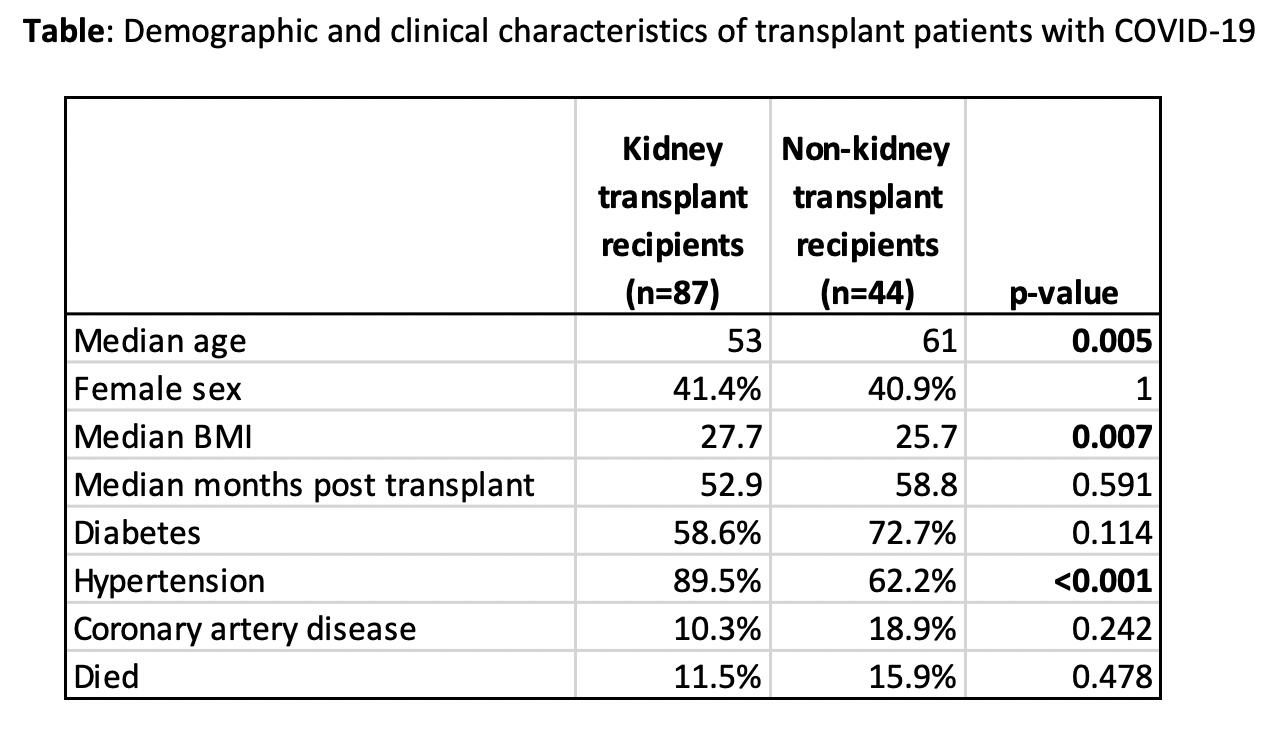
*Results: Kidney transplant recipients comprised the majority of COVID-19 cases (n=87), followed by liver (n=18), lung (n=18), heart (n=7), and intestinal (n=1) transplants. Non-kidney transplant recipients were significantly older than kidney transplant recipients (n=0.005), while kidney transplant recipients were more likely to be overweight or obese (p=0.007) and have a diagnosis of hypertension (p<0.001) (Table). Time between transplant and positive COVID-19 PCR test, sex, ethnicity, incidence of diabetes, and coronary artery disease were similar across transplant types. Presenting symptoms were also comparable, with similar incidence of shortness of breath, cough, fever, nausea and vomiting, diarrhea, and loss of smell or taste. Mortality rates were not significantly different in the kidney compared with the non-kidney transplant recipients (p=0.478).
*Conclusions: Although presenting symptoms were similar, kidney transplant recipients with COVID-19 had significant differences in comorbidities compared with non-kidney transplant recipients. Future studies will compare mortality rate in transplant patients compared with non-transplant patients with COVID-19 at our center after adjusting for comorbidities, including diabetes, hypertension and obesity.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Schaenman J, Byford H, Grogan TR, Fraschilla S, Meneses K, Alejos JC, Rivera M, Saab S. COVID-19 Infection in Kidney versus Non-kidney Solid Organ Transplant Recipients: A Single Center Study [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2021; 21 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/covid-19-infection-in-kidney-versus-non-kidney-solid-organ-transplant-recipients-a-single-center-study/. Accessed February 27, 2026.« Back to 2021 American Transplant Congress